Specifications, delivery set
| Manufacturer | ID-Cooling |
|---|---|
| Model name, link | Frozn A620 Black |
| Model code | ID-CPU-FROZN-A620-BLACK; EAN: 6931393305646 |
| Cooling system type | for the processor, air tower type with active airflow of the radiator located on the heat pipes |
| Compatibility | mat. boards with processor sockets: Intel: LGA 1700 , 115x and 1200; AMD: AM5, AM4 |
| Cooling capacity | TDP 270 W |
| Fan type | axial (axial), 2 pcs. |
| Fan model | AF-125-K (ID12025M12F) |
| Fan power | 12 V, 0.25 A |
| Fan dimensions | 120×120×25 mm |
| Fan speed | 500—2000 rpm |
| Fan performance | 132.9 m³/h (78.25 ft³/min) |
| Fan static pressure | 26.3 Pa (2.68 mm water column) |
| Noise level | 29.85 dBA maximum |
| Fan bearing | Fluid Dynamic Bearing |
| Fan life | no data |
| Cooler Dimensions (H×W×D) | 154×120×140 mm |
| Cooler weight | 1190 g |
| Radiator material | aluminum plates (0.4 mm thick) and copper heat pipes (6 pcs. ∅6 mm), copper heat sink |
| Thermal interface of the heat sink | Frost X25 thermal paste in a syringe |
| Connection | fans: 4-pin connectors (power, rotation sensor, PWM control) into the splitter connectors, and the splitter into the CPU cooler connector on the motherboard |
| Peculiarities |
|
| Delivery set (better to check before purchasing) |
|
Description
The processor cooler is delivered in a strictly designed box made of medium-thick corrugated cardboard.

The kit includes assembly instructions, presented in the form of illustrations with explanations in three languages: English, Chinese and Russian. Most fasteners are made of hardened steel, with the exception of support posts and bushings, and are finished with a durable galvanized or black paint finish.

The cooler is equipped with a double remote radiator that effectively removes heat from the processor through six copper heat pipes. The lower part of the thermal block and tubes are made of copper coated with a black semi-matte varnish, which improves heat transfer due to radiation. The upper part of the thermal block is made of aluminum alloy. The tubes are securely soldered to the thermal block. The thermal block sole has a fine concentric texture and is lightly polished, with a slight convex profile towards the center with a height difference of about 0.1mm.
No factory-applied thermal interface was found, but the manufacturer supplies the cooler with a small syringe with thermal paste. During testing, we used high-quality thermal paste from another manufacturer. The following will show the distribution of thermal paste after testing is completed.
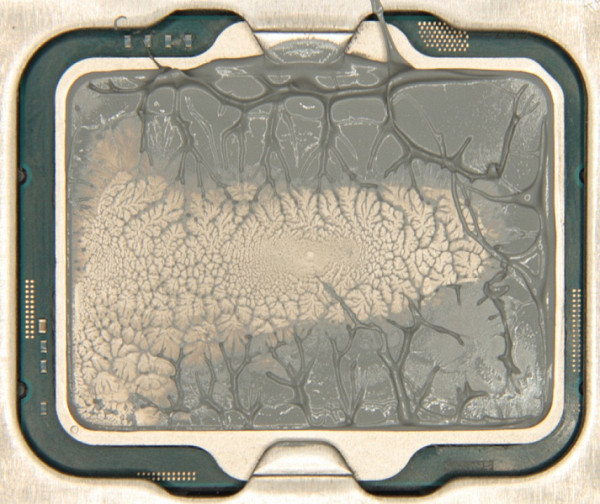

And on the base of the heat sink:
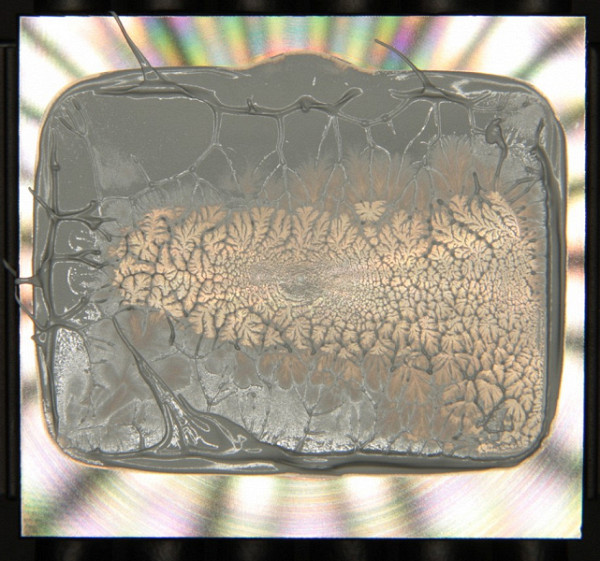
The thermal paste is evenly distributed along the plane of the processor cover, with excess being squeezed out along the edges, forming a large patch of tight contact.
The radiator consists of two stacks of aluminum plates tightly fitted onto heat pipes. The heat pipes are spaced apart, which improves the efficiency of the cooler. The stacks of plates are covered with plastic decorative covers on top.
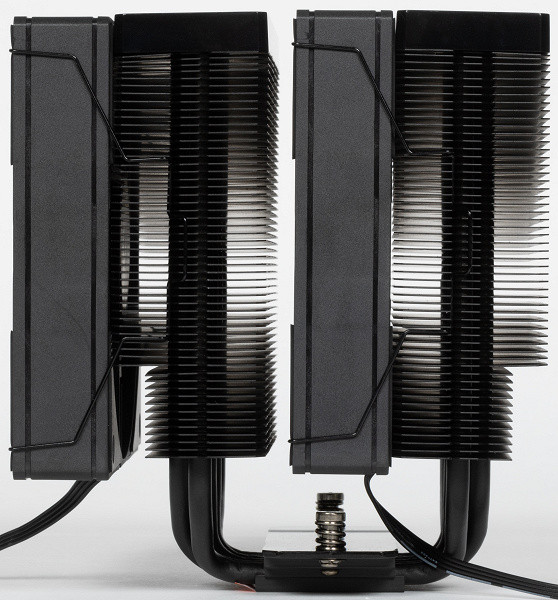

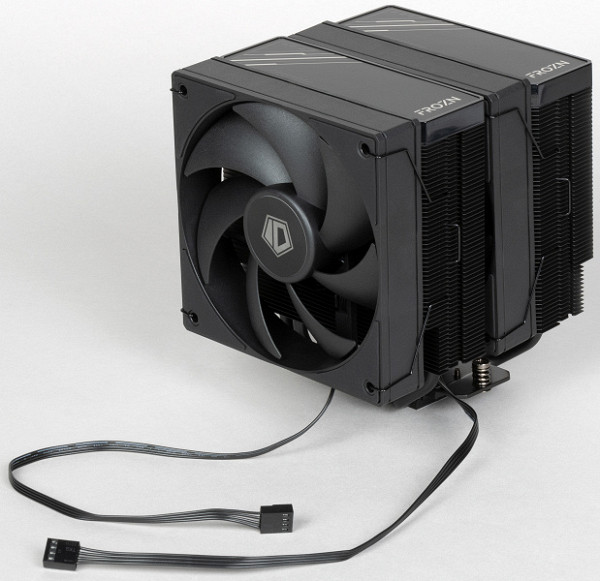
Standard size of complete fans is 120 mm.
The fans are secured with typical steel brackets. A third set of brackets will allow you to install another fan. The fans support regulation using PWM.

The dimensions of the cooler are quite large, and, for example, in the case of LGA1700, all RAM slots are covered on top by a radiator and fan. For example, in the case of the ASRock Z790 PG Sonic motherboard:
However, the radiator has plates with a reduced depth, and the fan can be moved upward, which, according to our measurements, will allow the use of memory modules up to 64 mm in height (one is up to 66 mm, but with a slight skew — see the photo above). Without raising the fan higher than the radiator, the maximum height is 36 mm.
Note that the design of the fastener eliminates too weak or too strong a clamp (it is enough to simply tighten the nuts all the way without using excessive force) and reduces the likelihood of misalignment due to two-point clamping.
Testing
Below in the summary table we present the results of measurements of a number of parameters.
| Cooler weight (with mounting kit for LGA1700), g | 1266 |
|---|---|
| Radiator weight only, g | 830 |
| Heat sink platform dimensions, mm | 43×40 |
| Fan power cable length, cm | 30.5 |
| Fan power splitter length, cm | 20+10+10 |
Determining the dependence of the cooler fan speed on the PWM duty cycle and/or supply voltage
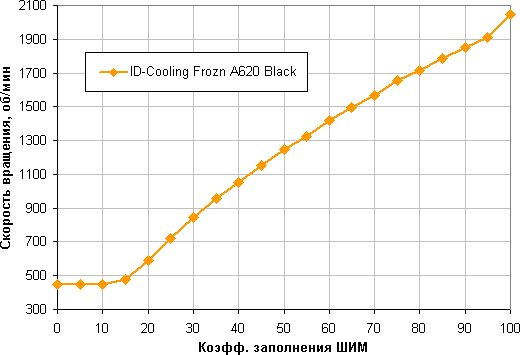
An excellent result is achieved thanks to a smooth increase in fan rotation speed when changing the fill factor (FC) from 10% to 100% and a wide adjustment range. It is worth noting that with a short circuit of 0% the fan does not stop. Therefore, in a hybrid cooling system with passive mode, at minimum load, such fans will have to be stopped by reducing the supply voltage.
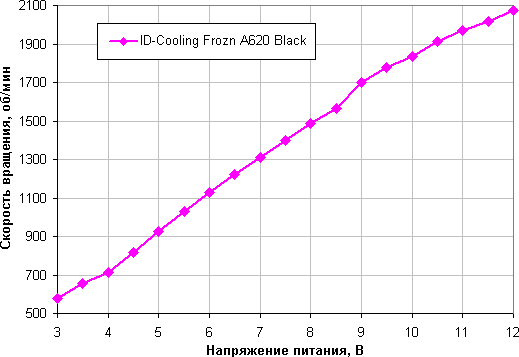
The range of adjustment using voltage in this case is approximately the same. The fan stops when the voltage drops to 2.5 V and starts from 2.6 V. This means that the fan can be quite safely connected to a 5 V source.
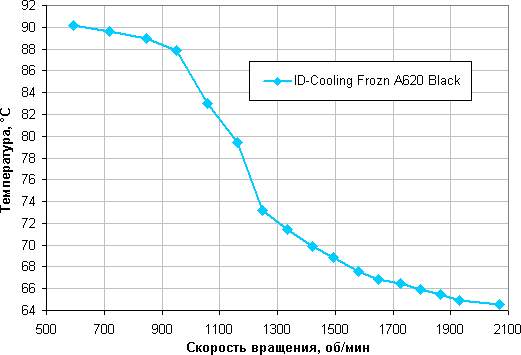
Determining the dependence of the temperature of the Intel Core i9-13900K processor when it is fully loaded on the rotation speed of the cooler fan(s)
In this test, all cores of the Intel Core i9-13900K processor ran at 4.0 GHz.
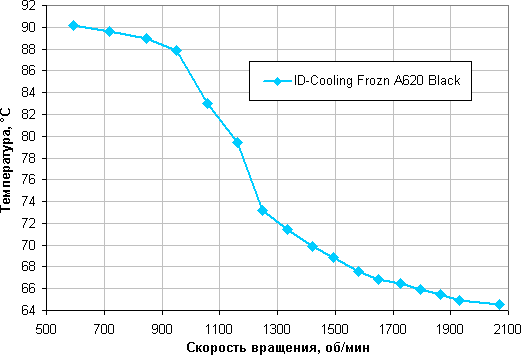
In fact, under test conditions, this processor at 24 degrees of ambient air overheats at a short circuit of 35% (which is approximately 950 rpm) and lower, since some cores heat up to a critical temperature for this processor of 100 °C. Under the conditions of this test, the maximum consumption for additional 12 V connectors per mat. The board reaches 262 W.
Determining the noise level depending on the rotation speed of the cooler fan(s)
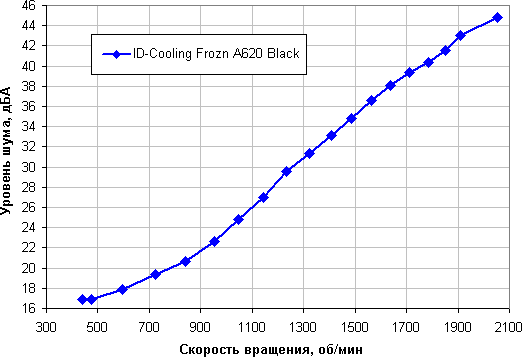
Of course, it all depends on individual characteristics and other factors. However, in the case of coolers, noise levels around 40 dBA and above are considered very high for a desktop system. From 35 to 40 dBA can be classified as tolerable. With a noise level below 35 dBA, the noise from the cooling system will not stand out much compared to typical quiet PC components such as case fans, power supply, graphics card and hard drives. Somewhere below 25 dBA the cooler can be considered relatively silent. The background level was 16.0 dBA (the conventional value shown by the sound level meter). At maximum fan speed this cooler is quite loud.
Plotting the dependence of real maximum power on noise level
Taking 25 dBA as a criterion for conditional noiselessness, we obtain the approximate maximum power consumption of processors such as the Intel Core i9-13900K, corresponding to this level, about 156 W. In conditions where noise levels are not taken into account, the power limits can be increased to approximately 205 W. However, it should be clarified that these estimates are valid under harsh conditions, such as blowing air at the heatsink at 44 °C, and reaching a maximum processor temperature of 80 °C (although it is possible that the maximum processor temperature could be 100 °C). As the ambient temperature decreases or the maximum permissible processor temperature increases, the specified power limits for silent operation and maximum power will also increase.
conclusions
To understand the findings, it is important to remember the following:
The purpose of testing is to determine the cooling capacity of the cooler (or LCC). The processors being tested are used only as a heating element to determine the thermal resistance of the cooler in various modes. Thus, the power (heat dissipation) of the processor is regulated depending on the capabilities of the cooling system, and can be either less or more than the standard values. The main thing is to avoid overheating the processor throughout the entire range of the cooler's cooling capacity (at least at 25 dBA), and also to ensure a significant change in processor temperature.
Based on the characteristics of the ID-Cooling Frozn A620 Black air cooler, you can create a computer with conditionally silent operation (noise level 25 dBA or lower), equipped with an Intel Core i9-13900K processor. To do this, it is necessary that the heat dissipation of the processor under maximum load does not exceed 156 W, and the air temperature inside the case does not rise above 44 °C, with the maximum processor temperature limited to 80 °C. Provided the cooling air temperature is reduced, the processor temperature threshold is increased (up to 100 °C), or noise requirements are less stringent, the power limits can be increased. The cooler's advantages include its neat design, while its disadvantages include limited compatibility with high-end memory modules.





