Today, when choosing a new home wireless router, you should pay attention to Wi-Fi 6 class solutions, which are widely represented on the market, from the budget to the premium segment. This standard has existed for several years; most modern wireless devices support it, so saving on it no longer makes sense.
In this article we will look at the TP-Link Archer AX80 AX6000 class router, equipped with 2.5 Gbps and USB 3.0 ports. Attentive readers of our resource probably remember the review of a similar model published in August last year. Therefore, we were somewhat surprised when we were given a “new product” for testing.

It turned out that the manufacturer decided to confuse users a little: now on the site you can find two AX80 devices with the suffixes “RU” and “EU”. In terms of technical characteristics they are very similar, but in design they are completely different. The previous version was in a «spider» format with eight antennas, and the «European» version has built-in antennas and a vertical housing. Let's try to figure out if there are any other differences.
Delivery set and appearance
Thanks to the new case design, the packaging is quite compact. The design is traditional for this manufacturer: proprietary color combinations, glossy varnish and “golden” elements. Particular attention is paid to support for Wi-Fi 6, OneMesh and HomeShield technologies, as well as the presence of a 2.5 Gbps port.

The packaging contains photographs of the router, technical specifications, descriptions of ports and controls. The main language is English; Russian contains only a brief description in one sentence.

The package includes a router, a universal mount, a 12 V 2 A power supply with a 1.5 m cable and a standard round plug, a gray Category 5E patch cord 1.2 m long, a leaflet in English with instructions for getting started, multilingual a book (including Russian) with the same content, a warranty card and several additional leaflets.

The router body is made of black plastic with predominantly matte surfaces, complemented by several glossy elements. The form factor of this model is rare and reminiscent of modern high-rise buildings: a vertical tower with rounded corners, expanding at the top. Overall dimensions excluding fastening are approximately 190×60×200 mm.
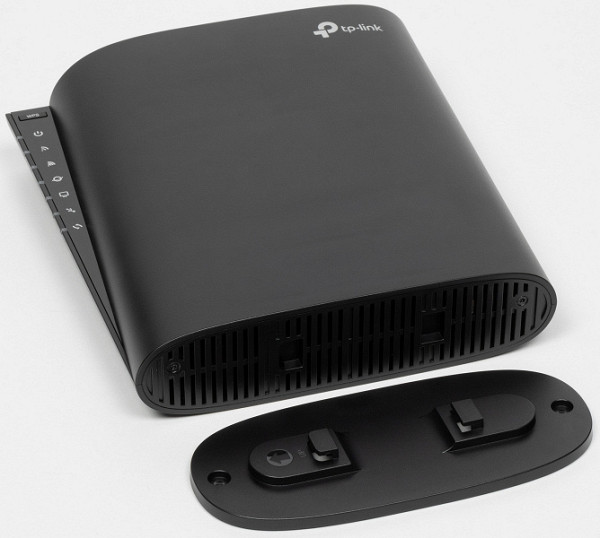

The router can be installed in two ways: vertically on a flat surface or along a wall. For both options, a complete plate with four rubber feet and two holes is used.

In general, one can imagine the option of placing it horizontally on the same plate, but it will look somewhat strange.

There are ventilation grilles on the lower and upper surfaces. On the left is a vertical block of LED indicators, at the top of which there is a WPS button. LEDs are predominantly neutral white in color and do not cause annoying flashing. If there is no Internet access, the corresponding indicator lights up red.
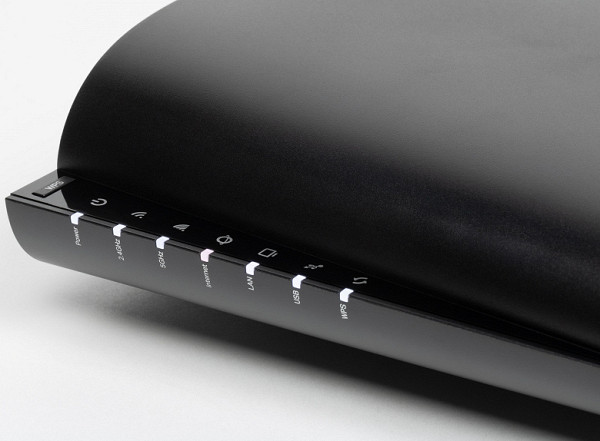

On the right in the niche there is a button to turn off Wi-Fi and LEDs, a hidden reset button, three gigabit LAN ports, one gigabit LAN/WAN port and one 2.5 Gbps port with selectable LAN or WAN operating mode. Unfortunately, the ports are not equipped with indicators, and you can only find out their status through the web interface. There is also a USB 3.0 Type A port, a power supply input, and a hardware power switch.
On the front side there is a manufacturer's logo at the top; on the rear panel there are holes for wall mounting and an information sticker.

The use of built-in antennas and the ability to mount on a wall can be considered advantages of the model. The device will fit well into the design of modern apartments, including the role of an additional unit with EasyMesh technology.
Hardware specifications
It is difficult to disassemble the device, and it was not possible to find public official information about the chips used, so the data in this section may be incorrect.
Judging by the firmware, the device is built on the MediaTek MT7986A processor, which includes four ARM Cortex A53 architecture cores operating at 2 GHz. The amount of RAM is 512 MB. Flash memory for firmware has a capacity of 128 MB. The chip also includes native support for one USB 3.0 port and a 2.5 Gbps port. A separate switch is probably installed to service gigabit ports.
The router body houses four dual-band antennas, which provides maximum connection speeds of up to 1148 Mbit/s for 2.4 GHz and 4804 Mbit/s for 5 GHz. The final class of the model is AX6000. This speed headroom can be useful for serving a large number of clients simultaneously, given that most modern client devices only support two antennas and the corresponding connection speeds are half as slow. The use of special FEM modules for antennas (probably chips from the MT7976* line) ensures their efficiency, not inferior to external antennas.
The router was tested on firmware version 1.1.1 Build 20240129 rel.36389(4555).
Settings and features
The model in question, as the name implies, is aimed at the European market, but the web interface supports the Russian language, which makes use comfortable for Russian-speaking users. In the settings you can also select the operating mode — “router” or “access point”, which is useful for expanding the network coverage area together with the main router from another manufacturer.
The functionality of the firmware complies with the manufacturer's standards, the details of which are already widely described in available publications. The company also provides access to web interface emulators on its website, which allows users to clarify the details of the device themselves.
When you connect for the first time, you are prompted to go through a setup wizard, where you can set a new administrator password, select a time zone, configure an Internet port, enter settings for connecting to your provider and configure wireless networks, as well as activate auto-update of the firmware.
Optionally, here you can register the device in the TP-Link cloud for access through the mobile application. In general, for many users this wizard will be enough for basic router setup.
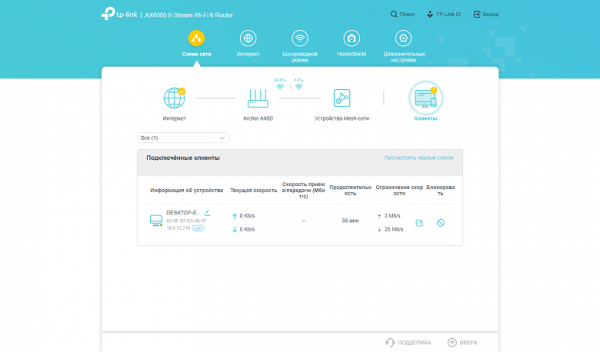
There are five items at the top level of the menu. The first one is Network Map, which provides information about the current state of the device and network. Among the useful functions are the display of the status of wired ports, the load on the processor and RAM, Wi-Fi parameters, the ability to temporarily block clients and limit their speed, as well as information about Mesh network nodes.
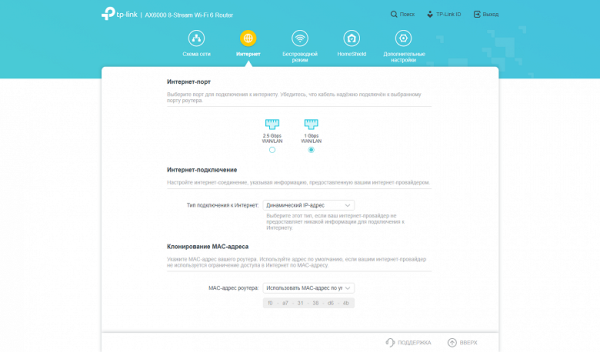
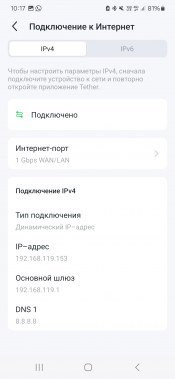
On the Internet page, you can select a port to connect to your provider via cable, configure the connection mode (static IP, dynamic IP, PPPoE client, PPTP or L2TP). It is also possible to change the MAC address on the WAN port.
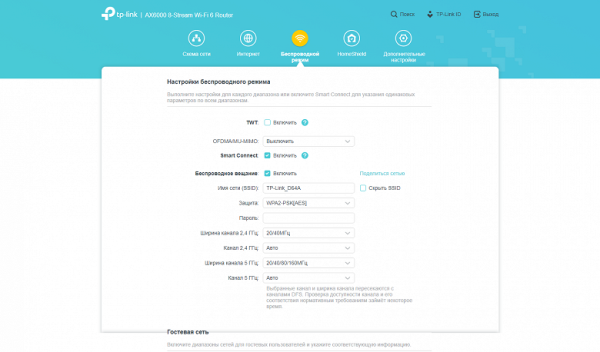
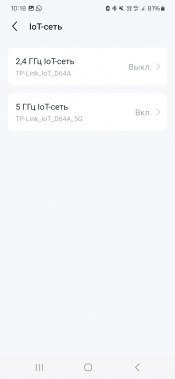
Basic settings for wireless networks are standard: setting the network name, security, selecting a channel and operating mode. It is also possible to use the same network name for different ranges (Smart Connect function), disable ranges individually and hide the SSID. Particular attention should be paid to the 5 GHz range, where only channels 36-48, 52-64 and 100-128 are available in accordance with the requirements of European regulators. Interesting features include creating guest networks with a separate range of IP addresses and restricting access to the main network, as well as networks for IoT devices that connect with separate Wi-Fi settings to the main network. This solution improves interoperability without compromising core network performance or security.
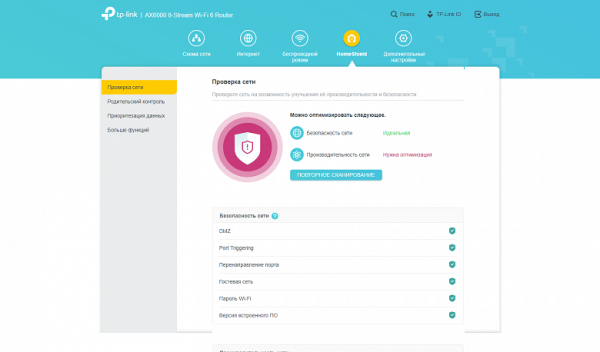
We have already talked about the features of HomeShield in previous materials. Even without a paid subscription, functions available for testing network security and efficiency, setting up profile-based parental controls with the ability to block resources by category or list, as well as completely blocking Internet access for a certain time (for example, “night time”) and individual transfer speed limits data for each client.
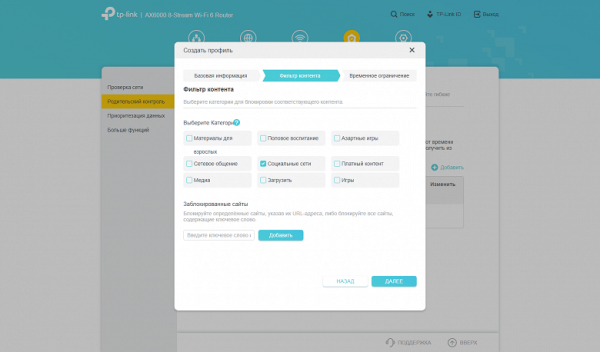
If you subscribe to a paid version (currently not available in Russia), the functionality expands significantly. It provides more flexible content filtering, additional traffic protection functions and the ability to collect Internet usage statistics.
The Advanced group has a two-level menu, including a dozen sections with a total volume of up to fifty pages.
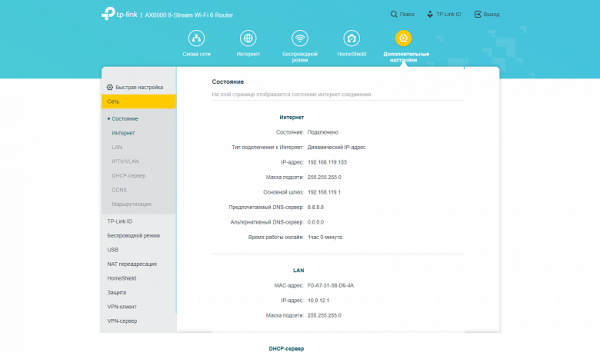
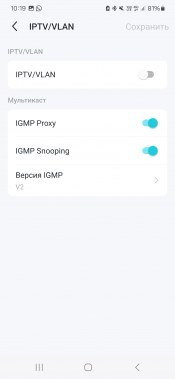
The “Network” section provides the opportunity to configure a connection to the provider, local network addressing, settings for working with IPTV (including a dedicated port for the set-top box, VLAN and multicast). A DDNS client and aggregation mode for LAN2 and LAN3 ports are also available here. If your provider supports IPv6, then the corresponding settings are available in a special section with the same name.
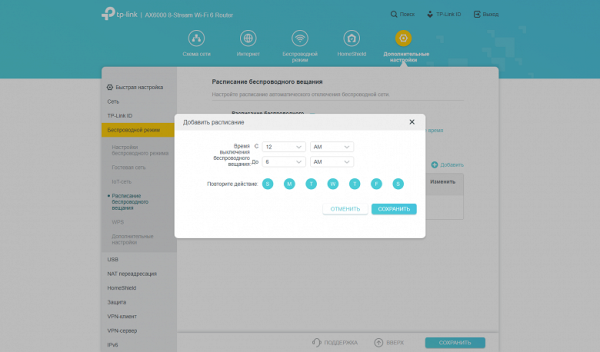
In the advanced settings of wireless access points, you can adjust the transmitter power, limit the operating time of the guest network, create a Wi-Fi schedule and activate the WPS function.
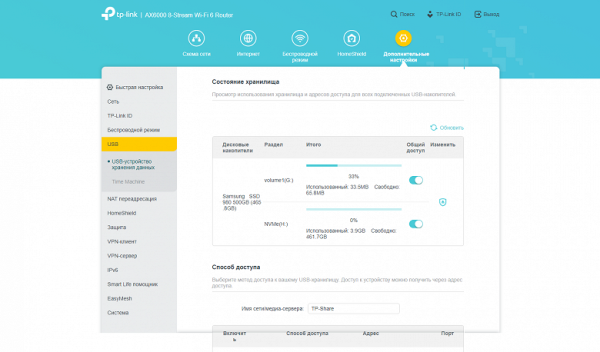
The router is equipped with a USB 3.0 port for connecting storage devices. FAT32, exFAT, NTFS and HFS+ file systems are supported. Files can be accessed via SMB and FTP protocols, which can also be activated for access via WAN. Setting file access rights is simple — you can specify two types of access: full and read-only. These settings apply to all volumes at once. Media server services based on MiniDLNA and Time Machine backup server are also available. It is important to note that there is no support for cellular modems for connecting to the Internet.
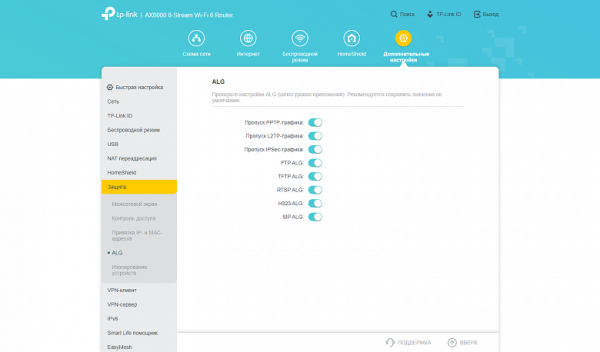
To provide remote access to services on the local network in the presence of a “white” address from the provider, standard NAT settings are used. This includes translation and port forwarding rules, UPnP and DMZ support. In addition, there is ALG support for popular network protocols.
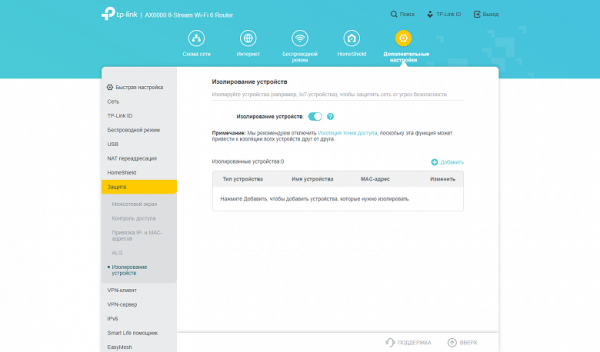
For the firewall, in addition to the usual options, client isolation functions are available. This feature is designed for IoT devices and aims to improve the security of your core home network.
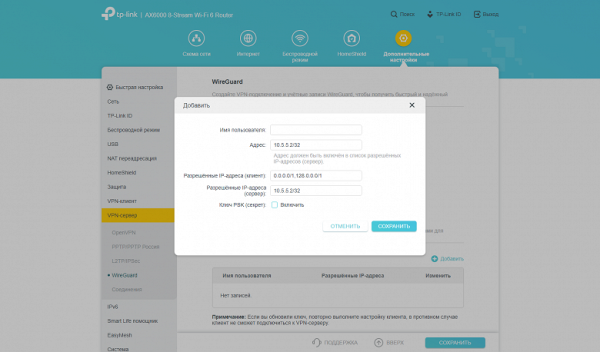
Yönlendiricinin OpenVPN, WireGuard, PPTP ve L2TP/IPSec protokollerini destekleyen yerleşik bir VPN istemcisi vardır. Bu işlevsellik, uzak ağlara bağlanmak için yönlendiriciyi kullanmanızı sağlar. Uzak bir VPN sunucusu üzerinden çalışacak belirli yerel ağ istemcilerini seçmek de mümkündür. Tersine, yönlendirici aynı protokollere sahip bir VPN sunucusu olarak çalışarak ev ağınıza güvenli erişim sağlayabilir.
Yönlendiriciyi TP-Link bulutuna bağlamak, onu Amazon Alexa ve Google Assistant gibi sesli asistanlarla daha da entegre etmenize olanak tanır. Ancak bu hizmetlerin Rusya'daki performansı sınırlı olabilir.
TP-Link's wireless mesh network system is called EasyMesh. Most current router and repeater models support this technology. When purchasing a new router, you can configure it as the main one, and use the old one as a mesh network node. The manufacturer focuses on ease of setup, scalability and seamless client switching.
The last section is “System”. Here, as usual, we see items for updating the firmware, working with the configuration, changing the administrator password, access control to the management interface, system event log, network diagnostic utilities, time settings, restart (including on a schedule), turning off the LEDs.
The manufacturer also offers its own cloud service for managing the router via the Internet from a mobile application. This option is easy to set up and works even if you only have a “gray” address from your provider.
The mobile application has fewer settings available than the web interface, but all the basic functions are present. In addition, through the program it is convenient to check the status of the router, load and connected clients.
Testing
One of the key features of the model in question is the presence of a wired port supporting a speed of 2.5 Gbit/s. We'll also run some additional tests in this article.
In particular, in the first graph we will look at routing in IPoE and PPPoE modes, and also analyze the use of a 2.5 Gbps port with one and two clients as a WAN. In this case, internal clients will always be connected via gigabit ports.
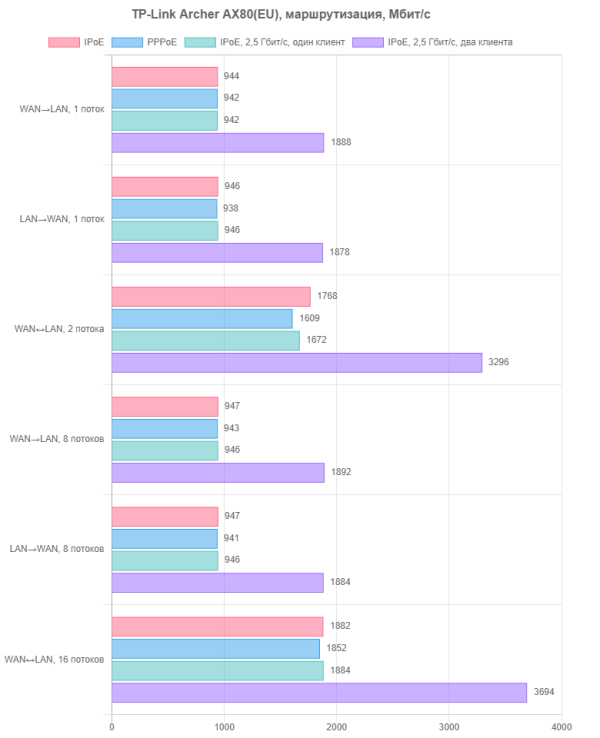
Our results show that all speeds are fully consistent with modern gigabit connections. Using a 2.5 Gbps port to connect to the provider does not have a negative impact on speed when working with a single client and in all scenarios allows you to double the overall speed.
However, getting more than a gigabit from your provider at home is still quite difficult. Most likely, the 2.5 Gbps port will be used as a LAN. The most likely scenario for its use will be connecting a home server. Therefore, the first test we decided to choose was to check the switching speed between 2.5 and 1 Gbit/s ports within the internal local network. The first scenario is a server and client on 1 Gbps ports; the second is a 2.5 Gbit/s server and a 1 Gbit/s client; the third is a 2.5 Gbit/s server and two 1 Gbit/s clients.
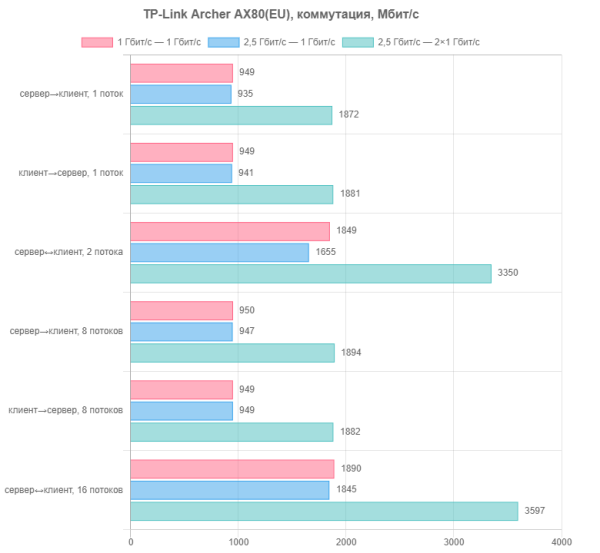
From the point of view of network communications, the configurations in question operate without any problems, fully complying with the technical specifications. It is important to note that the router supports Gigabit port aggregation mode. However, for the home user, this is a less common and useful option, requiring a specialized switch or network card on the client with appropriate support. A real increase in speed in such scenarios is not always justified, especially given the difficulties in supporting this feature in non-server operating systems after Intel and Microsoft stopped supporting it.
We also tested with port trunking mode, where the server was connected to two network ports of the router on which this mode was activated, and the clients were connected to free gigabit ports. However, using the 2.5 Gbps port as the only client is a non-standard configuration, more experimental than useful in practice.
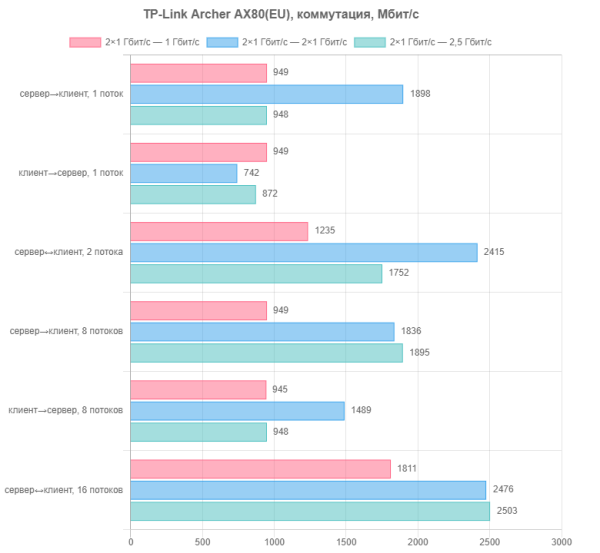
Yes, the overall picture is less impressive than in the previous graph. However, in some cases there is a speedup, including the latest configuration.
Now let's move on to Wi-Fi tests. In the first group, the clients were Intel 7265 and Intel AX210 network cards. The first supports devices of previous generations with 802.11n at 2.4 GHz and 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) at 5 GHz. The second is a modern Wi-Fi 6 class model with a maximum connection speed of 2402 Mbit/s. Testing of these clients was carried out at a distance of 10 meters from the router with direct visibility.
The test results at 2.4 GHz have no practical value in this case and are presented rather according to tradition.
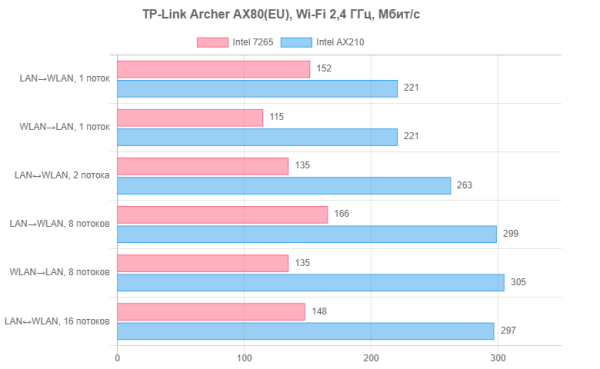
The connection speeds in this case correspond to the stated specifications: the first adapter reaches 300 Mbit/s, while the second adapter reaches 574 Mbit/s. The average speeds were 140 Mbit/s and 270 Mbit/s, respectively.
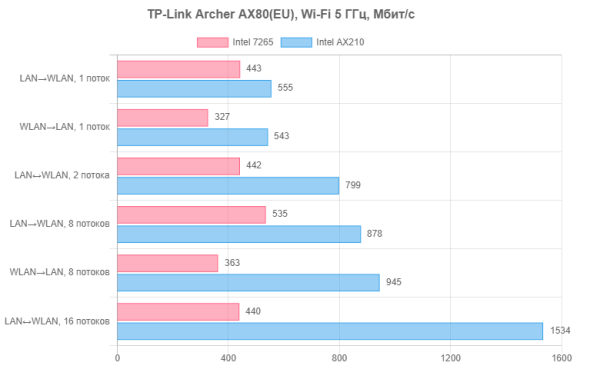
At 5 GHz, connection speeds matched the capabilities of the devices: 867 Mbps for the older client and 2402 Mbps for the Wi-Fi 6 model. The actual speed for the newer client in multi-threaded mode can be described as “gigabit over the air”, while for the previous generation model, the speed ranged from 330 to 530 Mbit/s, which is also a good result for this type of device.
The quality of the coverage area was assessed using smartphones Xiaomi Mi9 (Wi-Fi 5, up to 867 Mbit/s at 5 GHz) and Huawei P40 Pro (Wi-Fi 6, up to 2402 Mbit/s). Testing was carried out at two points: at a distance of 10 meters with direct visibility (similar to tests with PC adapters) and at a distance of 15 meters through two walls. The 2.4 GHz test is primarily for academic purposes, but it does provide an indication of the quality of area coverage for customers using IoT, home automation, CCTV, and other similar devices.
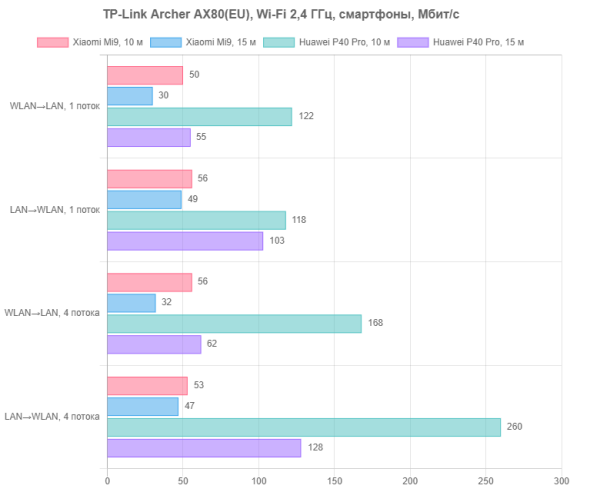
At 2.4 GHz, devices do not work very well. On the other hand, even over long distances with obstacles, the connection is stable. So the robot vacuum cleaner should not get lost in a large apartment.
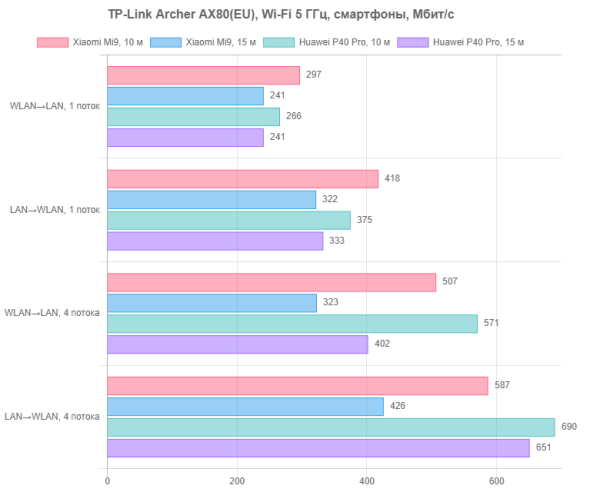
Operation at 5 GHz has significant differences. Maximum speeds reach several hundred megabits per second, allowing you to efficiently download high-resolution content to mobile devices, install large applications and quickly transfer files created by modern photo and video cameras to the cloud.
Let's move on to checking the work with files. This test used an NVMe SSD connected via a fast USB 3.0 adapter. File system — NTFS. The programs used for testing were robocopy and FileZilla, and the file size was about 4 GB. The client connection was tested via cable at speeds of 1 Gbit/s and 2.5 Gbit/s, as well as via Wi-Fi using an Intel AX210 adapter in the 5 GHz range.
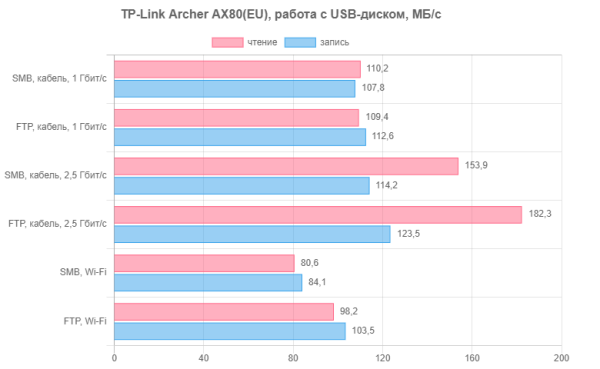
On gigabit, the speed remains stable — about 110 MB/s. Connecting to 2.5 Gbps allows for slightly faster read speeds. Over a wireless connection, you can achieve speeds from 80 to 100 MB/s, depending on the protocol and direction of data transfer.
The last test in this post is to check the speed of the VPN server. This functionality can be useful for providing secure remote access to the router’s local network. The test tested the PPTP (with MPPE), OpenVPN, L2TP/IPSec and WireGuard protocols. Service settings remained at default. Clients used the latest versions of official clients built into Windows. For the test, after establishing a connection from the WAN segment, the client connected to the server configured in the LAN segment.
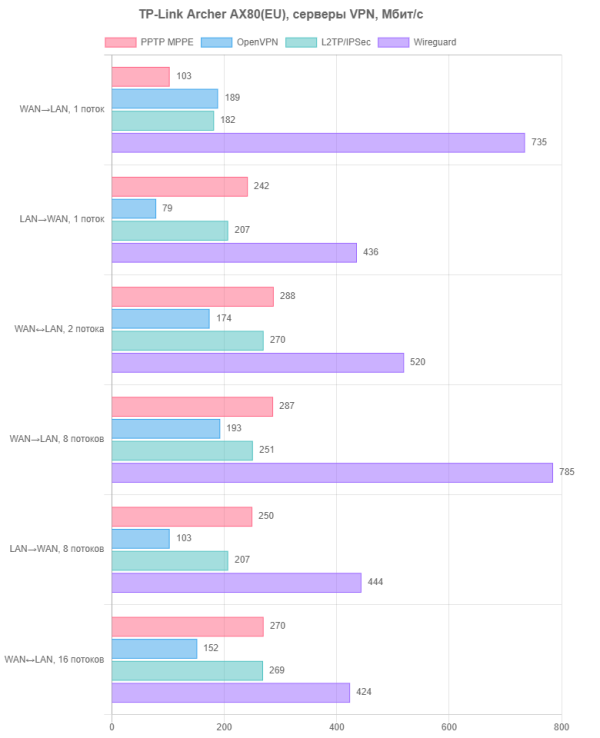
In our protocol comparisons, WireGuard has long demonstrated consistent superiority. With the router in question, it reaches an average speed of 560 Mbps. And most often there is no particular reason to choose something else. The exception is when it is necessary to support devices with limited capabilities that only work with legacy standard protocols.
Conclusion
The TP-Link Archer AX80(EU) router is built on the modern high-performance MediaTek platform, which is widely used in modern wireless devices from various manufacturers, which indicates its reliability and stability. This product belongs to the AX6000 class, equipped with a wired network port supporting speeds up to 2.5 Gbps and USB 3.0, which makes it a representative of the high end of the market.
One of the undeniable advantages of the device is its original design, which differs from many models with external antennas. At the same time, the tests showed that this design did not reduce the speed and coverage area of the wireless network.
The built-in software provides most of the popular features that are typical for the mass market. Key features include support for cloud management, a mobile application, EasyMesh technology and VPN services.
According to the results of performance testing, the router demonstrated compliance with the declared characteristics without causing any comments.
The device will be of interest to users who need a wireless router with support for modern standards, high data transfer speeds, extended coverage area and convenient setup, as well as an original design.