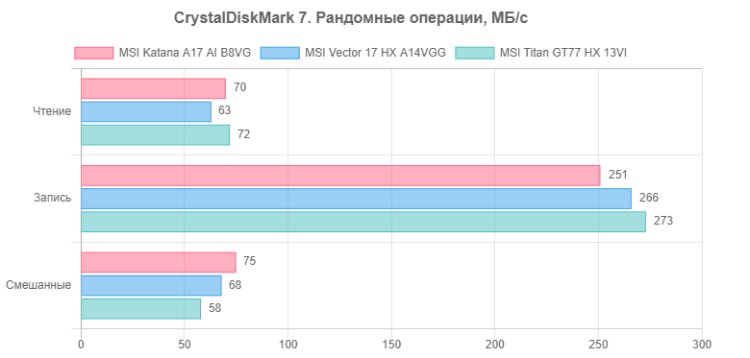A year ago, we tested the previous version of the MSI Katana 17 B13VGK (471RU) with a 17-inch screen, an Intel Core i7-13620H processor, and a similar graphics card (details can be found in the report from August 4, 2023). Externally, the 2024 modification retained the main features of its predecessor, but the internal components have undergone changes. For the first time in the MSI Katana line, the “red” AMD Ryzen 9 8945HS is used as a central processor.

In the manufacturer's online catalog, the new product is presented in three modifications, which differ from each other in the models of video cards (Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070, 4060 or 4050 Laptop).
First, we present a table of specifications according to the manufacturer's data , supplemented by data obtained during testing.
| MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG (858RU) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 9 8945HS (Zen 4, AMD XDNA): 8 cores/16 threads, 4.0/5.2 GHz, TDP 45 W (35-54 W), Tj max 100 °C, AMD Ryzen AI block | |
| RAM | 2×8GB DDR5-5600 SO-DIMM Samsung M425R1GB4BB0 max 64GB | |
| Video subsystem | integrated graphics: AMD Radeon 780M (2.8 GHz) video card: Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop, 8 GB GDDR6 (1.98 GHz, 105 W) | |
| Screen | 17.3 inches, IPS, 2560×1440, semi-matte, 240 Hz, DCI-P3 color gamut 100%, maximum brightness 312 cd/m² | |
| Sound subsystem | 2 speakers 2W each | |
| Accumulators | SSD NVMe 1 ТБ WD SN560 (SDDPNQE-1T00-1032), M.2, PCIe 4.0 ×4 | |
| Cartographer | No | |
| Kensington Castle | No | |
| Network interfaces | Wired network | Ethernet 1 Gbps |
| Wireless Wi-Fi network | AMD RZ616 (Mediatek MT7922A22M ) Wi-Fi 6E (2,4/5/6 GHz) | |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.2 | |
| Interfaces and ports | USB | 1×USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-C (with DisplayPort support) 2×USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-A 1×USB 2.0 Type-A |
| RJ-45 | There is | |
| Video outputs | 1 × HDMI 2.1 1 × DisplayPort 1.4 (USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-C) | |
| Audio connectors | 3.5 mm combo for headset connection | |
| Input devices | Keyboard | membrane with four-zone backlighting |
| Touchpad | clickpad | |
| IP telephony | Webcam | 720p at 30 fps, no mechanical shutter |
| Microphone | stereo | |
| Battery | 3-cell lithium-polymer, 53.5 Wh | |
| Dimensions | 398×273×28 mm (excluding supports) | |
| Weight without power supply | 2.76 kg | |
| Power adapter | Chicony A21-200P2B: 200W (20V/10A), 600g with 1.8m non-detachable laptop power cable and 1.2m detachable mains power cable | |
| operating system | Windows 11 Home | |
| Manufacturer's warranty | 1 year |
The laptop's components are certainly not top-notch, but they are quite interesting: an AMD Ryzen 9 8945HS processor, an Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop graphics card with 8 GB of GDDR6 (albeit with a power consumption limitation), 16 GB of RAM, and a 1 TB NVMe drive. Against this background, the port set looks budget (lack of USB 3.2 Gen2 and USB 4, although the chipset supports them) and Wi-Fi 6E and Ethernet adapters with support only up to 1 Gbps. The manufacturer focuses on the implementation of artificial intelligence technologies, which are implemented in the laptop. Among the MSI Center utility profiles, a special place is occupied by the MSI AI Engine (more on this below). The laptop is also provided with one-year service support and a limited warranty. In this review, we will periodically compare the MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG with other laptops that have passed similar tests:
- MSI Vector 17 HX A14VGG:
- Intel Core i9-14900HX
- 16 GB DDR5-5600 (2 × 8 GB SK Hynix)
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop with 16 GB GDDR6 (2.18 GHz, 140 W)
- 1 TB NVMe SSD WD SN560, PCIe 4.0 ×4
- MSI Titan GT77 HX 13VI-096RU:
- Intel Core i9-13980HX
- 32 GB DDR5-4800 (2 × 16 GB Samsung)
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 Laptop with 16 GB GDDR6 (2 GHz, 175 W) — 2 TB SSD Micron Pyrite, PCIe 4.0 ×4
Appearance and ergonomics

The packaging made from recycled paper is well designed but overloaded with details. There is no handle for carrying the box, although this accessory cannot be called superfluous.

The delivery set is minimal. In addition to the machine itself and the power adapter (details below), it only includes the traditional leaflets.

The case is made of impact-resistant plastic, which is another compromise in favor of savings. All surfaces quickly collect fingerprints. The cover has the MSI gaming series logo, which is not backlit and looks quite discreet.
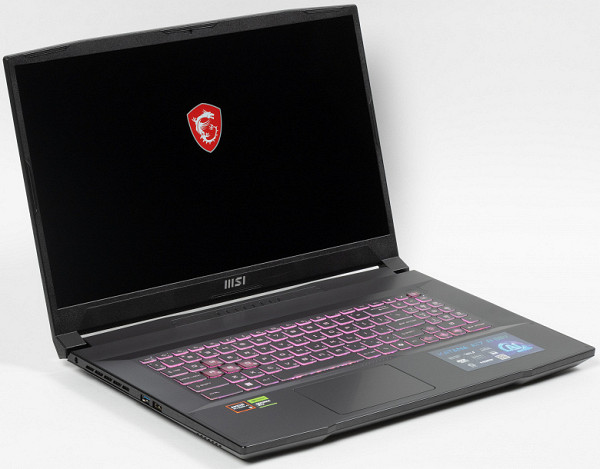

The model is equipped with a 17-inch screen with an «IPS-level» matrix (as the manufacturer claims). Along the entire length of the front edge of the lid there is a special protrusion that allows you to easily hook it with your fingers and open the laptop.

The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG opens to 180°. The lid is fixed without locks or magnets, held only by hinges and a closer. Although the hinges are quite tight, when opened with one hand, the laptop slides along the table, since the case does not act as a counterweight.
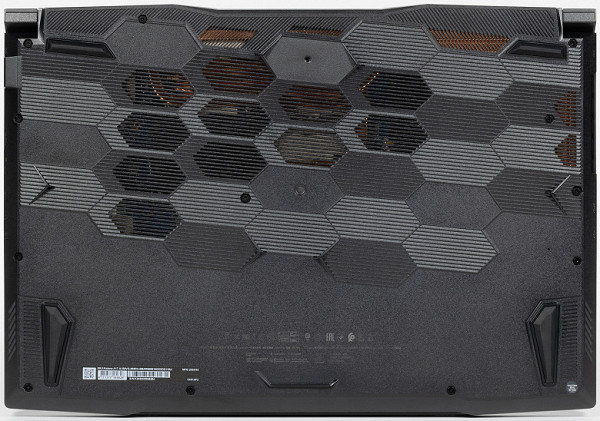

The lower air intakes are located under the cooling fans. There are small grilles at the front edge for sound output.

On the back panel, on the left and right, there are massive grilles through which heated air is evacuated from the internal volume of the laptop. There are no connectors.

On the left side are a coaxial connector for the power adapter (without an LED indicator), a side grill for the cooling system, as well as USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-A and USB 2.0 ports.

There are no significant details on the front bottom of the case.

On the right side are a combined audio jack for connecting a headset, USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-A and USB 3.2 Gen1 Type-C ports (with DisplayPort support), HDMI video output, and an RJ-45 socket.

The screen bezel is 14mm wide at the top, 7mm on the right and left, and rises 1.5mm above the display surface.

The top frame has a built-in miniature webcam for video conferencing (720p, 30 fps). It does not have a mechanical shutter.
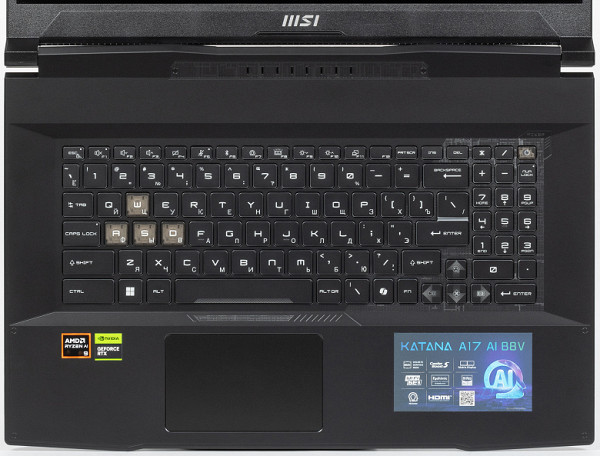

The keyboard is a membrane type with a traditional layout. Despite the presence of a numeric block and arrows, it is less functional compared to a classic desktop keyboard. The game keys (W, A, S, D) are noticeably different from the rest. The Latin markings are perfectly readable, but the small Cyrillic looks sloppy.
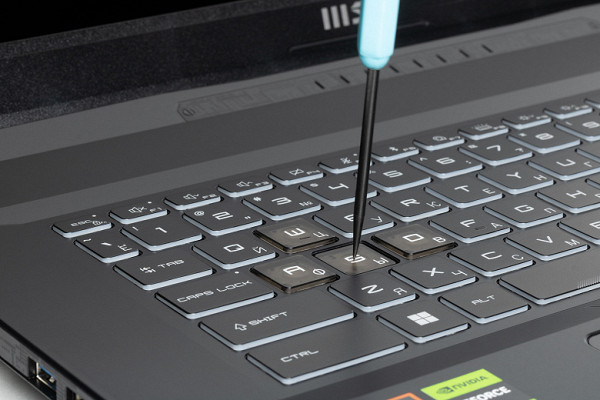

The alphanumeric keys are quite large (16×16 mm) with a distance between the centers of 18 mm and between the edges of 3 mm. The numeric block is fully functional, but its keys, like the arrow keys, are reduced in size (13×12 mm). The space bar is wide (92 mm). The right Shift is 25 mm wide, the left is 34 mm, Backspace is 30 mm, Caps Lock is 25 mm, Enter is 35 mm. The function keys F1-F12 are also reduced in size (13×9 mm). The system supports independent processing of keystrokes (n-key rollover), which allows registering any number of simultaneous keystrokes. The key travel is about 1.7 mm and is well felt tactilely.
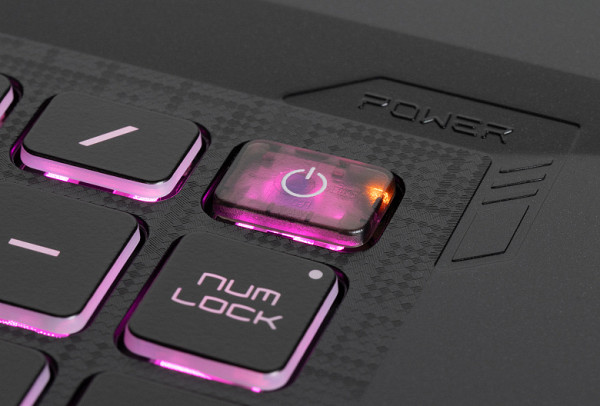

The power button is located in the upper right corner of the keyboard field and differs from the surrounding ones in its appearance and the presence of its own LED.
The keyboard is equipped with a four-zone backlight with the ability to adjust the brightness in four levels (plus the option of complete shutdown). Switching levels is carried out using the key combination «Fn + F8». Both symbols and key contours are illuminated, and the latter glow brighter. Due to the peculiarities of light distribution and marking, Latin symbols are best seen.
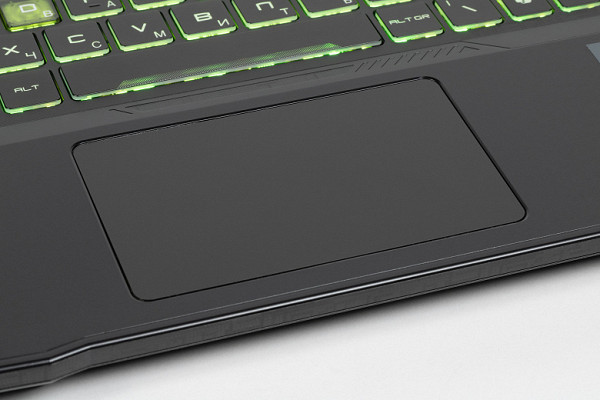

The touchpad has no dedicated buttons, but pressing is accompanied by clear clicks and tactile feedback. It is slightly offset to the left from the center of the keyboard panel. All standard gestures are supported, and the panel itself responds well to touches and presses.
Internal structure
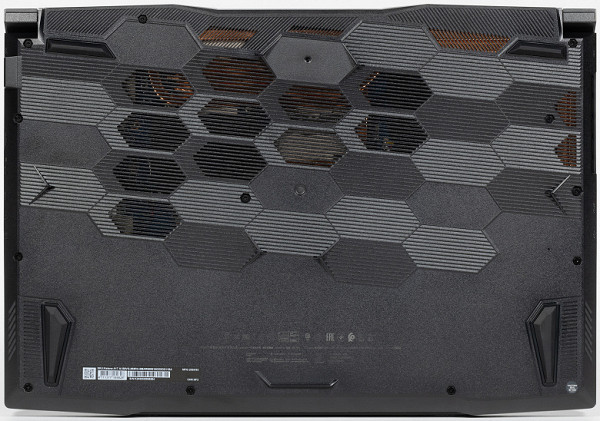

The bottom is secured to the body with 12 Phillips-head screws. The one on the left in the near corner (on the right in the photo) is covered with a factory sticker.
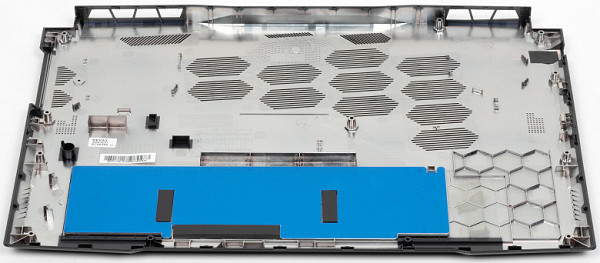
The bottom panel is made of plastic and therefore does not look very reliable.
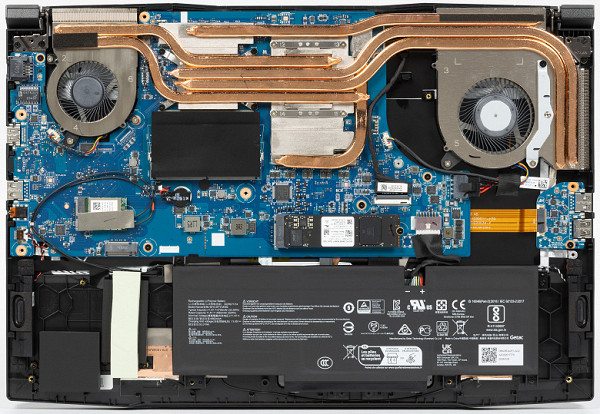
The most noticeable elements of the design are the cooling system, the block with SO-DIMM slots (hidden under the cover in the photo) and the battery. The motherboard also includes an additional module with an audio jack and a USB Type-A port. Upgrade options include changing the RAM configuration, replacing the wireless adapter and battery. A second slot for an NVMe drive is present, but its installation outside the service center is difficult due to the lack of a hole for a fixing screw.
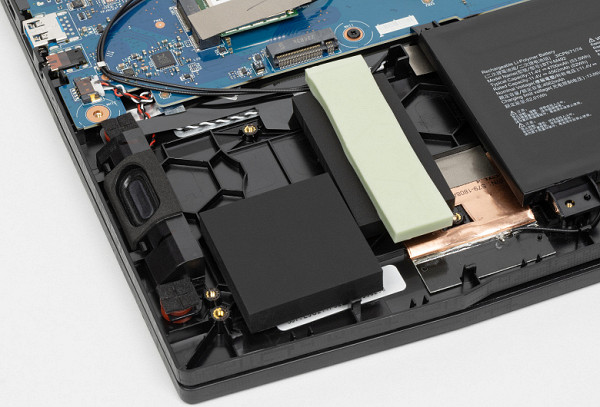

At the bottom right (on the left in the photo) is an area that looks like a bay for installing a 2.5-inch drive, but there are no connectors here and the space is occupied by plugs.
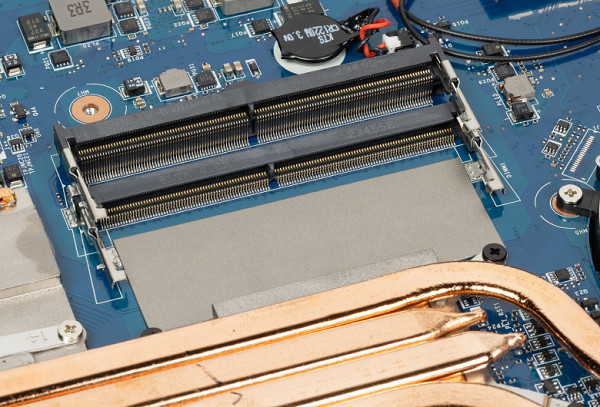
The slots for RAM modules are located on two levels, which undoubtedly increases the thickness of the case.

The laptop is equipped with 16 GB of RAM, which operates in dual-channel mode and consists of two 8 GB SO-DIMM DDR5-5600 modules (Samsung M425R1GB4BB0).

The system storage for programs and data is a Western Digital WD PC SN560 NVMe drive with a capacity of 1 TB and a PCIe 4.0 ×4 connection interface.
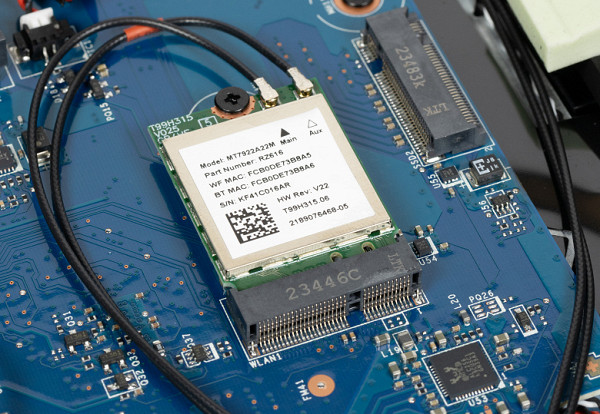

The wireless adapter is a Mediatek MT7922, branded by AMD as RZ616. It complies with the Wi-Fi 6E standard.
Software
The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG laptop comes with Windows 11 Home, a trial version of Microsoft Office 365, an installation package of Yandex, as well as a set of utility utilities such as Nahimic and SteelSeries. The most important utility is MSI Center, which, although partially translated into Russian, provides significant opportunities for configuring parameters and selecting operating modes.
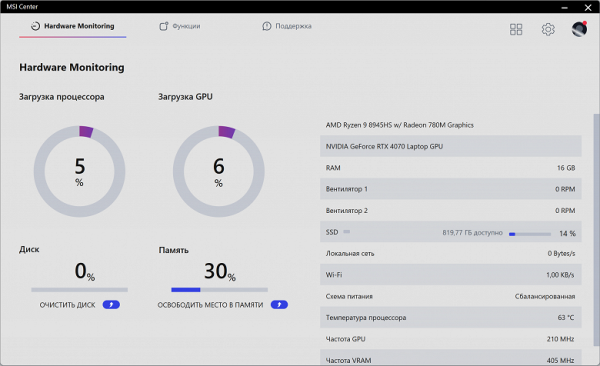
The main options are grouped into three tabs: Hardware Monitoring, Features, and Support. The Hardware Monitoring tab provides information about CPU and GPU load, system storage and RAM status, and fan speed.
In the Function Sets section, options are grouped into blocks according to their purpose.
The «Features» section features four components, including the MSI AI Engine, a module that optimizes settings using artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. According to the manufacturer, the MSI AI Engine analyzes operating conditions and automatically adjusts settings based on the current usage scenario.
General Settings, general settings.
User Scenario, user profiles.
There are four subsections in the Support section.
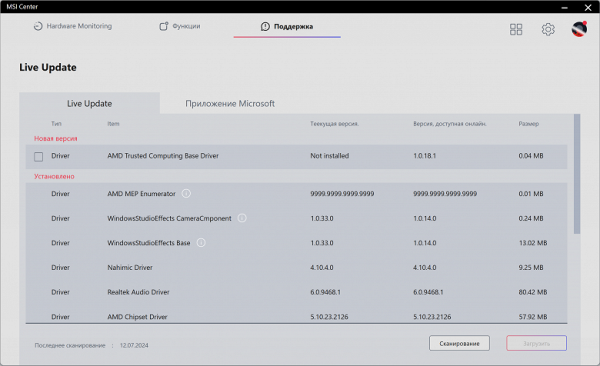
«Support» allows you to identify and install updates to the system's software components.
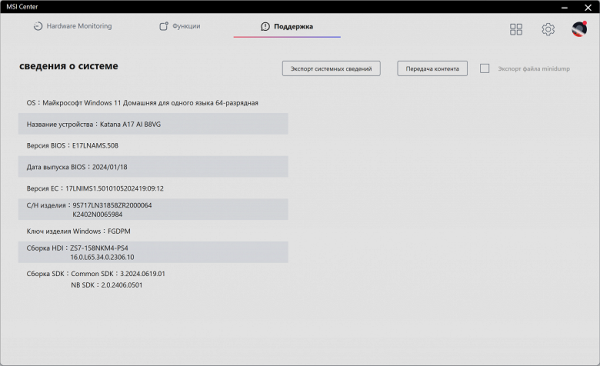
The second subsection contains information about the device.
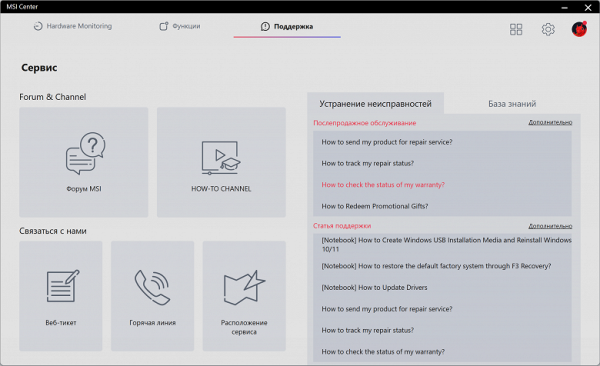
The «Service» subsection provides the user with information useful for maintenance and repair, including FAQ on malfunctions and how to fix them.
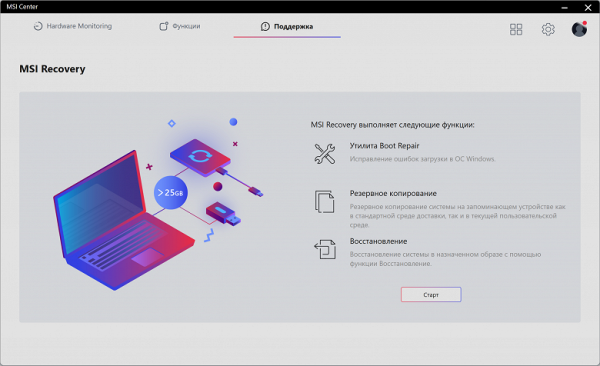
The MSI Recovery subsection contains options for creating a system backup and restoring it.
The Settings section allows you to change MSI Center launch options, its appearance and operating style.
Screen
The notebook is equipped with a 17.3-inch IPS matrix with a resolution of 2560×1440. The screen has a black, hard, semi-matte surface with a pronounced mirror effect, without an anti-glare coating or air gap. When running on mains or battery power, as well as with manual brightness control (there is no automatic control), the maximum brightness is 312 cd/m² (measured in the center of the screen on a white background). This high brightness allows you to comfortably work or play outdoors on a clear day, if you are in the shade.
To assess the readability of the screen outdoors, we use the following criteria based on testing screens in real-life conditions:
| Maximum brightness, cd/m² | Conditions | Readability assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Matte, semi-matte and glossy screens without anti-glare coating | ||
| 150 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | unreadable |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | barely readable | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work | |
| 300 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | barely readable |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | work comfortably | |
| 450 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | work comfortably | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | work comfortably |
These criteria are preliminary and may be changed as more data is accumulated. Improved screen readability may be observed if the matrix has transreflective properties, which allow the image to be seen with the backlight off due to the reflection of light from the substrate. Glossy screens can sometimes be turned so that they reflect a dark and uniform object (for example, the sky on a clear day), which will improve readability. While matte screens require protection from light to improve readability. In bright artificial lighting (about 500 lux), you can comfortably work even with a maximum screen brightness below 50 cd / m², that is, in such conditions, the maximum brightness is not so critical.
As for the screen of the tested laptop, when setting the brightness to 0%, it decreases to 15 cd / m², which allows you to comfortably use it in complete darkness.
There is no significant backlight modulation (PWM) at any brightness level, as evidenced by the brightness vs. time graphs at different brightness settings.
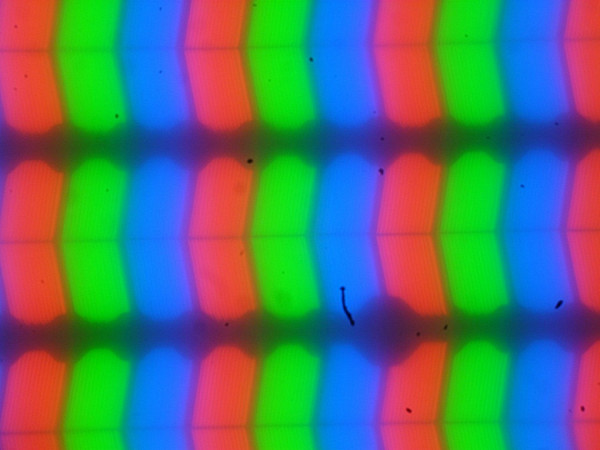
This laptop uses an IPS matrix. Microphotographs demonstrate the typical IPS subpixel structure (the black dots are dust on the camera matrix):
Focusing on the screen surface revealed randomly located microdefects on the surface that are responsible for the matte properties:
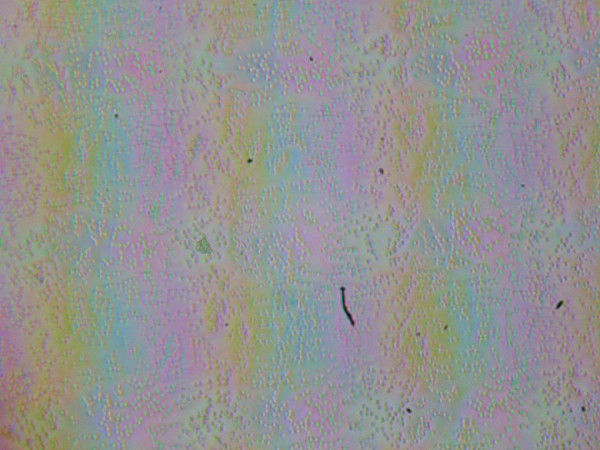

The graininess of these defects is significantly smaller than the subpixel sizes (the photos have approximately the same scale), which makes focusing on microdefects and focus «jumping» across subpixels less noticeable. As a result, there is no pronounced «crystal» effect, although barely noticeable changes in brightness and hue at the subpixel level are still present.
We measured the brightness at 25 screen points located at a step of 1/6 of the width and height of the screen (the screen borders were not taken into account). Contrast was calculated as the ratio of the brightness at the measured points.
| Parameter | Average | Deviation from the mean | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min., % | max., % | ||
| Black field brightness | 0.28 cd/m² | −12 | 30 |
| Brightness of white field | 300 cd/m² | −5,3 | 7,3 |
| Contrast | 1100:1 | −28 | 12 |
If you step back from the edges of the screen, the uniformity of the white field is good, but the uniformity of the black field and, as a result, the contrast, is noticeably worse. The contrast for this type of matrix is slightly above average. The black field in some areas, especially closer to the bottom edge and corners, may be slightly lightened. However, the unevenness of the black illumination is noticeable only in very dark scenes and almost complete darkness, so it cannot be called a significant drawback. It is worth noting that the screen cover does not have high rigidity and is easily deformed with a little effort, which can affect the nature of the black field illumination. However, without external influence, everything returns to its original state.
The screen demonstrates good viewing angles without significant color changes when deviating from the perpendicular, and without inverting shades. With a diagonal deviation, the black field is greatly lightened, but remains conditionally neutral gray.
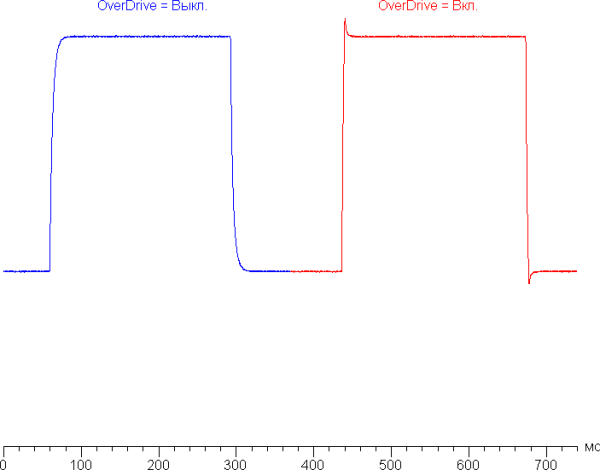
The screen response time depends on the inclusion of the matrix overclocking function in the proprietary utility (the OverDrive parameter). Below is a chart showing the change in black-white-black transition on and off times (the «on» and «off» bars), as well as the average total time for midtone transitions (the «GTG» bars) at a refresh rate of 240Hz.
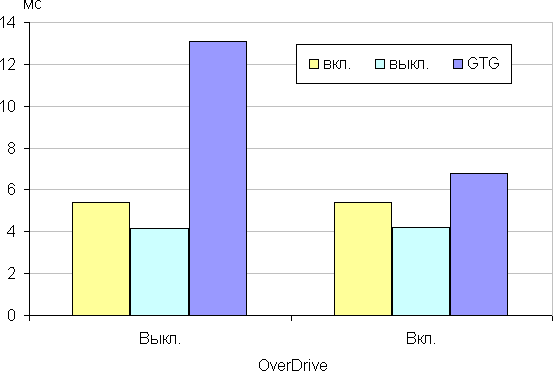
In any case, the matrix demonstrates a high response rate. After activating the overclocking function, brightness spikes with a small amplitude are observed at the fronts of some transitions. The graphs for the transition between shades of gray of 40% and 60% (where the Y axis shows brightness, and the X axis shows time) illustrate these changes.
Let's see if this matrix speed is enough to output an image with a frequency of 240 Hz. Here is the dependence of brightness on time when alternating a white and black frame with a frame rate of 240 Hz:
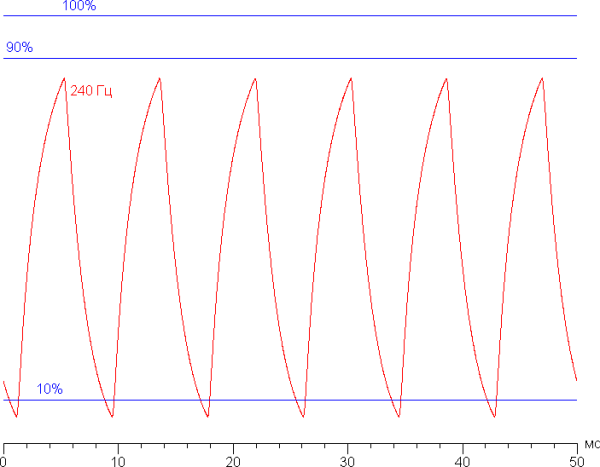
At a refresh rate of 240 Hz, the maximum brightness of a white frame reaches less than 90% of the white level, and the minimum brightness of a black frame drops below 10%. The resulting amplitude swing is about 79%, which indicates a slight deficit in the matrix speed for full image display at 240 Hz.
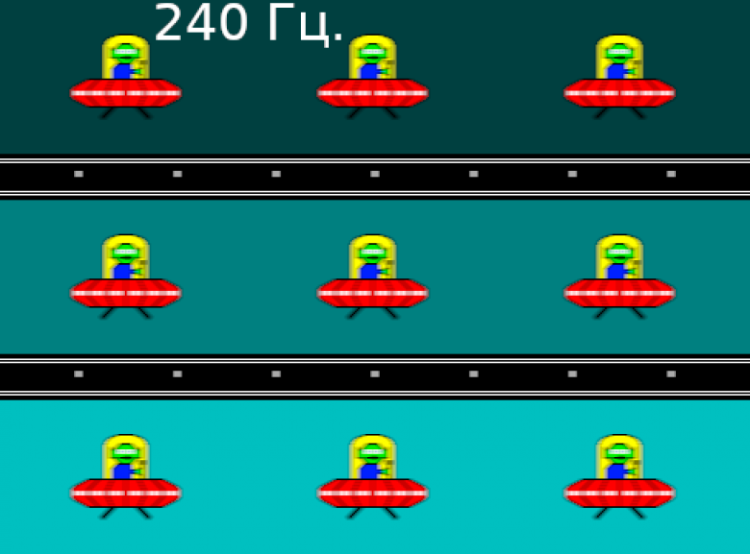
To visualize how such a matrix speed affects the display of moving objects and possible acceleration artifacts, we will provide a series of shots taken with a moving camera. These shots demonstrate what the user sees when observing a moving object on the screen using the recommended settings (movement speed of 960 pixels/s, shutter speed of 1/15 s).
As the refresh rate and overclocking level increase, the image clarity improves, and even with overclocking, artifacts become almost unnoticeable.
To imagine what this might look like with a matrix with instant pixel switching, consider the following examples: at a refresh rate of 60 Hz, an object moving at a speed of 960 pixels per second is blurred by 16 pixels, while at 240 Hz — by 4 pixels. The blurring occurs because the focus of vision moves at a specified speed, and the object is displayed on the screen for only 1/60 or 1/240 of a second. To visualize this effect, we simulate a blur of 16 and 4 pixels.
After overclocking, the image clarity on this laptop is slightly inferior to the ideal matrix.
We measured the total delay from switching video buffer pages to the start of displaying the image on the screen. At a refresh rate of 240 Hz, this delay is 5 ms. This is a very small delay that is not noticeable when working on a PC and does not affect performance in dynamic games.
In the display settings for the discrete video card, two refresh rates are available — 60 and 240 Hz. The output is carried out with a color depth of 8 bits per color. The frequency of 240 Hz is useful for both games and for watching movies, where frames will be displayed with equal duration. According to the control panel of the integrated video adapter, the screen supports AMD FreeSync in the range of 60-240 Hz. Enabling FreeSync provided smooth movement without tearing in the frame.
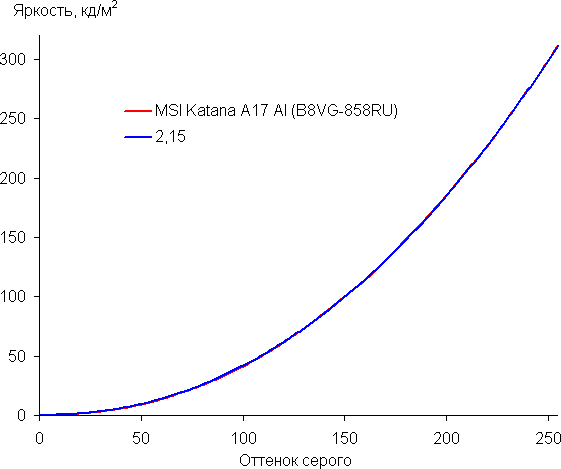
To evaluate the brightness, we measured 256 shades of gray (from 0, 0, 0 to 255, 255, 255). The graph below shows the increase in brightness between adjacent halftones (not the absolute value).
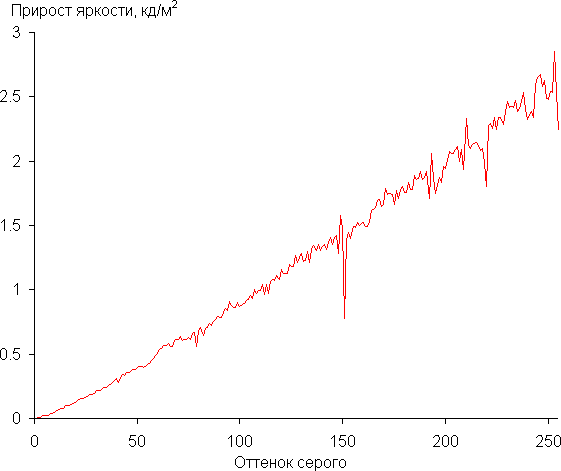
The increase in brightness on the gray scale is more or less uniform, and each subsequent shade is brighter than the previous one. In the darkest area, all shades are distinguished by hardware and visually:
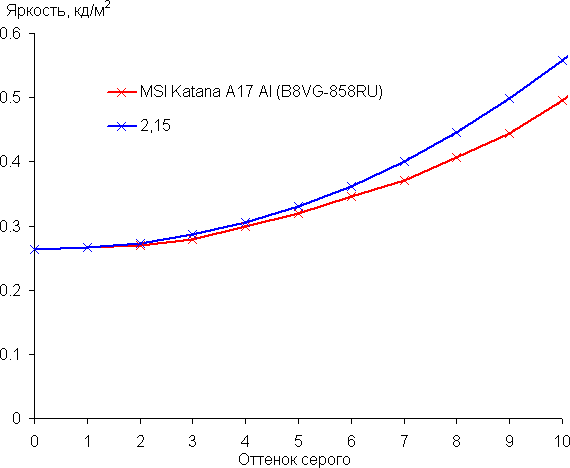
The approximation of the obtained gamma curve gave an indicator of 2.15, which is slightly lower than the standard value of 2.2, while the real gamma curve deviates little from the approximating power function:
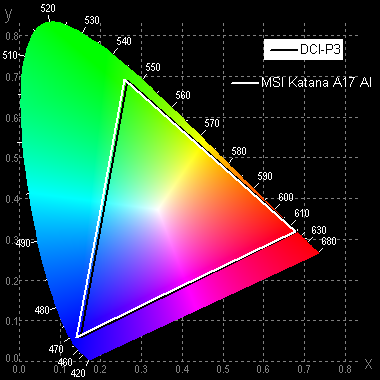
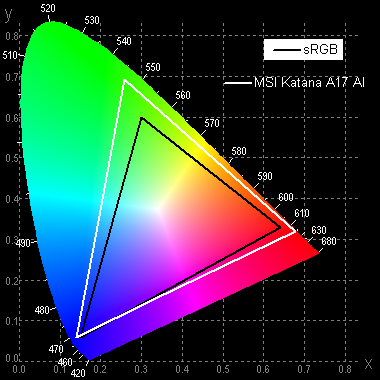
The color gamut is wider than sRGB (99.5% coverage and 148% volume) and close to P3 (96.5% coverage and 105% volume):
Below is the spectrum for the white field (white line), superimposed on the spectra of the red, green and blue fields (lines of the corresponding colors):
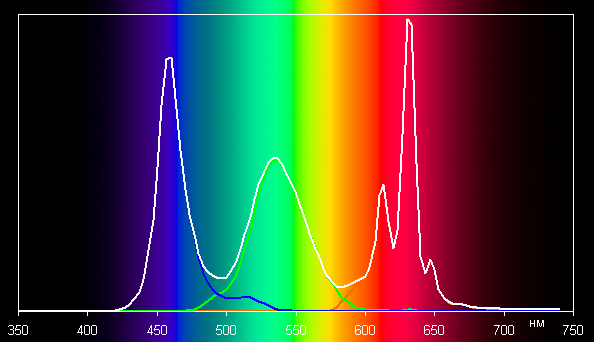
It seems that this display uses LEDs with a blue emitter and phosphors for green and red colors. This combination provides good separation of color components and a wide color gamut.
There is no built-in profile for the sRGB color gamut. On wide-gamut displays that are not adjusted for sRGB devices, regular images may look oversaturated. However, modern operating systems such as Windows and advanced image software can achieve the necessary color correction using color management systems. For example, you can use a color profile created by DisplayCAL software. So, the wide color gamut is not a disadvantage. Some issues with color accuracy may occur in games and when watching movies, but they can be resolved.
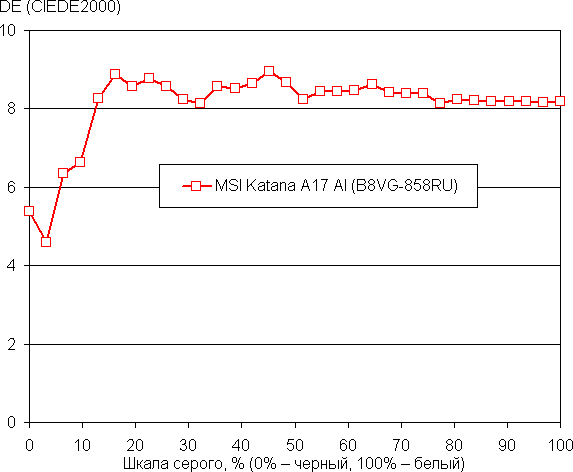
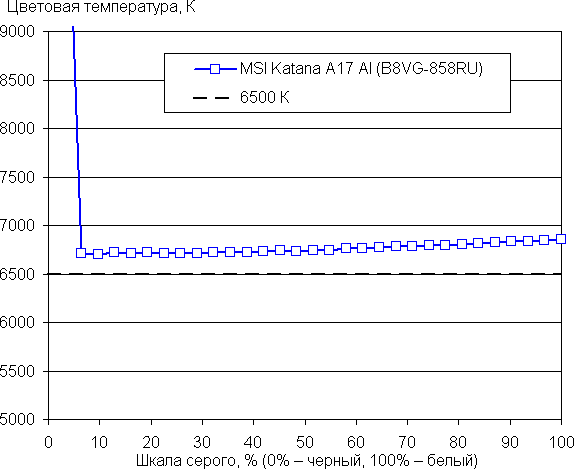
The balance of shades on the gray scale is good, since the color temperature is close to the standard 6500 K, and the deviation from the black body spectrum (ΔE) is below 10, which is good for consumer devices. The color temperature and ΔE remain stable when changing shades, which has a positive effect on the accuracy of the color balance. (Very dark areas of the gray scale can be ignored, since the color balance is less critical there, and the measurement error at low brightness can be significant.)
So, let's sum it up. The screen of this laptop demonstrates high maximum brightness (312 cd/m²), which allows you to use it outdoors during daylight hours, if you avoid direct sunlight. In complete darkness, the brightness can be reduced to a comfortable level (up to 15 cd/m²). The advantages of the screen include low response time and output lag (5 ms), high refresh rate (240 Hz), good color balance and wide color gamut. The main disadvantage is the decrease in black stability when deviating your gaze from the perpendicular to the screen. Overall, the screen is of high quality, which makes the laptop suitable for gaming tasks.
Battery operation

The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG is equipped with a three-cell lithium-polymer battery with a total capacity of 53.5 Wh. To evaluate its real-life battery life, we use the testing methodology using the Battery Benchmark v1.0 script. During testing, the screen brightness is set to 100 cd/m² (which corresponds to about 41% in Windows 11 settings) to eliminate the influence of low-brightness screens. All battery life tests were conducted with the keyboard backlight disabled.
| Load scenario | MSI AI Engine | Super battery |
|---|---|---|
| Working with text | 4 hours 38 minutes | 4 hours 49 minutes |
| Watch video | 5 hours 58 minutes | 6 hours 11 minutes |
When working on battery power with text or when browsing the Internet without heavy scripts and using the integrated video accelerator in economy mode, the MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG provides up to 4 hours 49 minutes of battery life. For watching videos, the battery life is 6 hours 11 minutes. When activating the MS AI Engine, these figures are reduced by 11 and 12 minutes, respectively. For maximum battery life, it is recommended to manually activate the «Super Battery» profile.
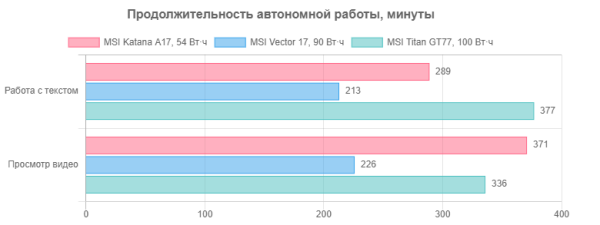
Compared to its competitors, the hero of the review looks good, especially considering the fact that its battery capacity is much smaller.

The power adapter is more compact and lightweight compared to similar ones used in high-end gaming laptops. This is especially important considering that you will need to carry it with your laptop at all times.

The power cable connector is coaxial, so if the adapter breaks down, it is easy to find a replacement.
Below is a graph of the battery charging from 1% to 100%. Measurements were taken at one-minute intervals.
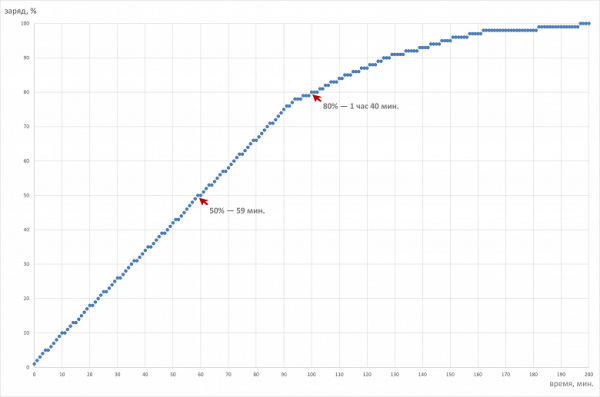
The battery reaches half its capacity in 59 minutes, which is quite fast. It takes 1 hour 40 minutes to charge to 80%, and 3 hours 17 minutes to fully charge, which is quite long. The last 10% takes another hour to charge. In real-world use, it is wise to keep the charge level between 10% and 80% to extend the battery life and increase the duration of charge and discharge cycles.
Operation under load and heating
The cooling system of MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG has a number of differences from the traditional one for gaming portable machines.

Standard cooling systems usually use two identical coolers, but in this laptop the graphics card fan is much larger and more powerful than the CPU cooler. The GPU fan directs air in two directions (back and left), while the CPU cooler only directs it back. As a result, the cooling system has three output paths and radiators, not the usual four. Heat is dissipated through six heat pipes, four of which connect both processors. This connection allows the coolers to rotate at approximately the same speed under load on the CPU and GPU.
The MSI Center utility gives the user the ability to choose from various operating scenarios (profiles, modes or presets), which gives a wide range of settings depending on preferences.
MSI AI Engine is a special operating mode that automatically controls overclocking, consumption, heating and fan noise using artificial intelligence technologies.
The following operating modes are available in the laptop:
- Extreme Performance: provides maximum CPU and GPU consumption with maximum speed of all four fans.
- Balanced: seeks to find the optimal balance between performance and the intensity of the cooling system.
- Silent: operates at minimum fan speed to achieve the lowest noise level, which can reduce system performance.
- Super Battery: maximizes battery life at the expense of performance.
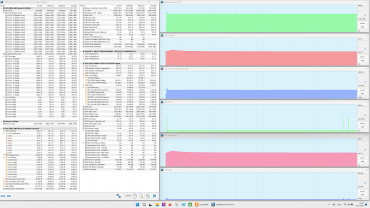
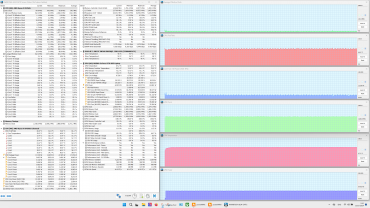
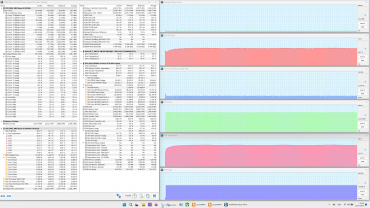
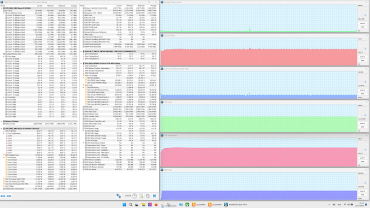
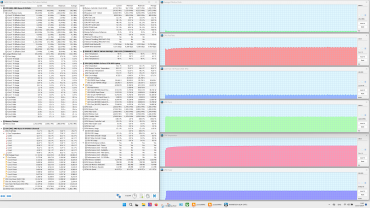
The profiles can be roughly divided into two groups: high-performance (1-3) and energy-saving (4 and 5). We tested the laptop in four scenarios with maximum load on the central processor, video card and both processors simultaneously, using the powerMax utility and the HWinfo application for measurements. The «Super Battery» profile is only activated when running on battery power, so testing in this mode was not carried out due to a significant limitation on the consumption of the computing devices.
Below is a table with data on consumption, temperatures and clock frequencies of the central processor and video card in different modes, as well as the rotation speed of the CPU and GPU fans. Maximum and steady-state values are indicated with a fraction sign.
| Load | CPU frequencies, GHz | CPU temperature, °C | CPU consumption, W | GPU frequency, GHz | GPU temperature, °C | GPU power consumption, W | CPU/GPU Coolers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inaction | 55 | 8 | 49 | 5 | 1600/1600 | ||
| MSI AI Engine | |||||||
| На CPU | 4,3/3,8 | 71/66 | 65/48 | 3200/3200 | |||
| On the GPU | 1,7 | 67 | 65 | 3200/3200 | |||
| На CPU+GPU | 4,2/2,8 | 83/68 | 65/28 | 2,0/1,6 | 70 | 67/62 | 3200/3300 |
| Extreme performance | |||||||
| На CPU | 4,4/4,0 | 79/70 | 65/54 | 3200/3200 | |||
| On the GPU | 2,2 | 74 | 105 | 4200/4200 | |||
| На CPU+GPU | 4,3/3,3 | 74 | 37 | 2,0 | 75 | 88 | 4200/4200 |
| Balanced | |||||||
| На CPU | 4,0/3,8 | 64 | 54/50 | 3200/3200 | |||
| On the GPU | 1,7 | 65 | 65 | 3200/3200 | |||
| На CPU+GPU | 4,0/2,8 | 67 | 54/40 | 1,6 | 68 | 61 | 4400/2100 |
| Silent | |||||||
| На CPU | 3,6/3,3 | 62/56 | 40/35 | 2700/2700 | |||
| On the GPU | 1,7 | 72 | 55 | 2700/2700 | |||
| На CPU+GPU | 3,5/2,8 | 77/73 | 68/58 | 2,2/1,5 | 75 | 68/54 | 2700/2700 |
When idle, the processor consumes 8 W of power and its temperature stabilizes at 55°C. The video card consumes 5 W and heats up to 49°C. Both coolers operate at 1600 rpm and are almost inaudible.
Maximum CPU load
In the Extreme Performance profile, the processor consumes 65 W at initial overclocking and reaches a clock frequency of 4.4 GHz, and after stabilization, the consumption drops to 54 W at 4.0 GHz. These values are the maximum in all tests. In turbo mode, the maximum temperature reaches 79 ° C, while overheating and throttling are not observed. In the MSI AI Engine mode, overclocking characteristics are slightly lower than in the extreme profile, and after stabilization — significantly less. In the profiles from balanced to silent, the indicators continue to decrease.
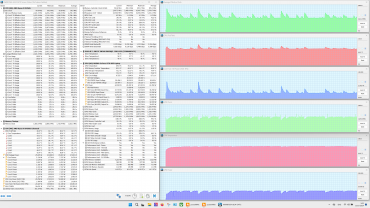
Maximum load on the video card
In the Extreme Performance profile, the graphics card consumes up to 105 W at maximum load and operates at 2.2 GHz, while the GPU temperature is stable at 74 °C throughout the entire test. In the MSI AI Engine mode and the Balanced profile, the graphics card consumes only 65 W, demonstrating a clock frequency of 1.7 GHz.
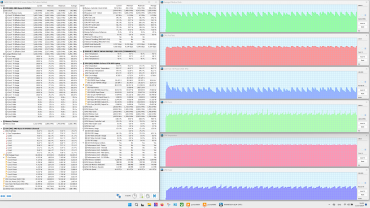
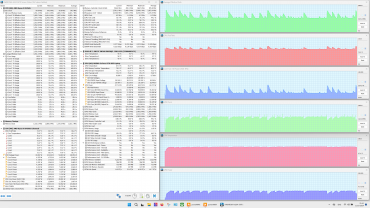
Maximum load on the CPU and video card simultaneously
All presets show a struggle for resources between the processors: sharp peaks in the graphs of changes in clock frequency, temperature and processor consumption are often accompanied by dips in the graphics card graphs. The «Extreme Performance» profile achieves maximum consumption and clock frequency with simultaneous load on both processors. No overheating or throttling was observed in the tests.
The cooling system works effectively, preventing overheating and throttling. The central processor easily exceeds the rated consumption values both in stable mode (54 W versus 35 W) and during overclocking (65 W versus 54 W), but does not reach 80 ° C (Tjmax 100 ° C). Its clock frequency in turbo mode is significantly lower than the maximum allowed (4.4 GHz versus 5.2 GHz), which indicates limited CPU efficiency. The graphics card, on the other hand, consumes the stated 105 W and reaches a maximum clock frequency 20% higher than the rated one (2.2 GHz versus 1.98 GHz), without any complaints about the discrete graphics accelerator.
Below are thermal images taken after the laptop had been running for a long time under maximum load on the CPU and GPU in the «Extreme Performance» profile:
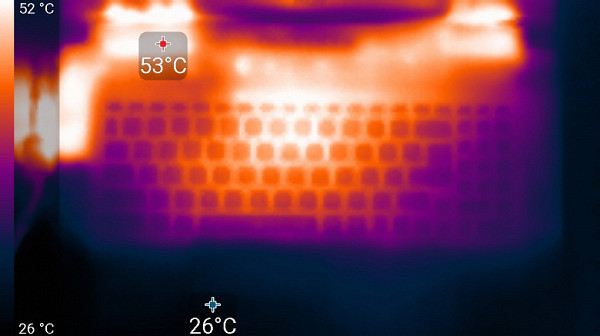
Above
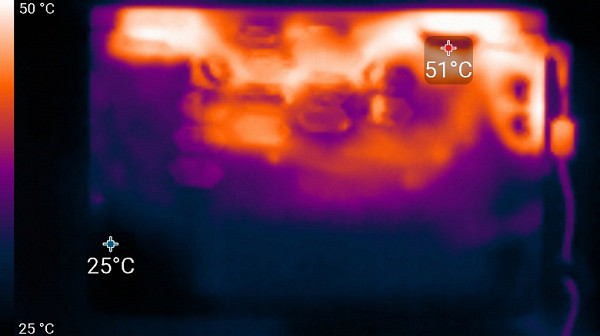
From below
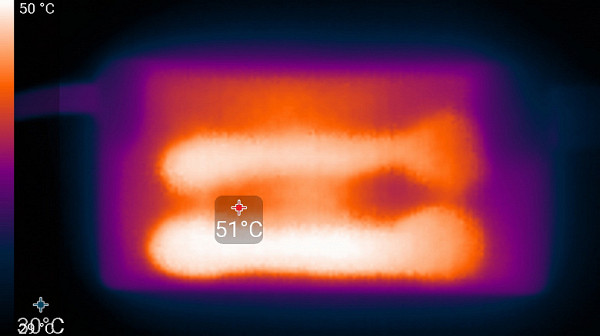
power unit
At maximum load, the keyboard is comfortable to use, as the area under the wrists hardly heats up. However, holding the laptop on your lap is uncomfortable due to the heating in the area of the lower part of the device, where it touches your lap. The power supply unit gets very hot, so when working for a long time at high performance, it is important to ensure that it is not covered by anything.
Noise level
We measure the noise level in a specially soundproofed and partially muffled chamber. The sound meter microphone is positioned to simulate a typical user head position: the screen is tilted back by 45 degrees (or the maximum possible angle if 45 degrees is not available), the microphone axis coincides with the normal from the center of the screen, the front end of the microphone is 50 cm from the plane of the screen, and the microphone is directed at the screen. We create the load using the powerMax program, the screen brightness is set to maximum. The room temperature is maintained at 24 ° C, but in the immediate vicinity of the laptop the temperature may be higher due to the lack of additional airflow. To assess real consumption, we also indicate the consumption from the network in some modes. Before testing, the battery is charged to 100%. In the utility settings, the «Extreme performance» or «Super battery» profile is selected.
| Load scenario | Noise level, dBA | Subjective assessment | Power consumption, W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Profile «Superbattery» | |||
| Inaction | background (16.0) | relatively silent | 26 |
| Extreme Performance Profile | |||
| Maximum load on the processor and video card | 43,6 | very noisy | 156 (maximum 172) |
If the laptop is not actively used, its cooling system in the «Super Battery» mode can operate in a completely passive mode under the specified conditions. Under significant load, the noise from the cooling system remains moderate. The noise is smooth and does not cause discomfort.
The spectrogram confirms subjective sensations — in the frequency range where sounds can be especially irritating, there are no pronounced peaks (the «Extreme Performance» mode at maximum load on the processor and video card).
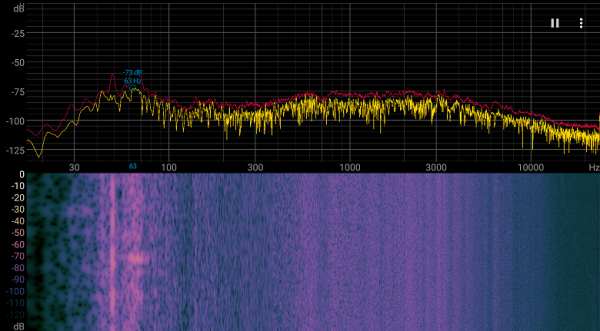
For a subjective assessment of the noise level, we use the following scale:
| Noise level, dBA | Subjective assessment |
|---|---|
| Less than 20 | relatively silent |
| 20—25 | very quiet |
| 25—30 | quiet |
| 30—35 | clearly audible |
| 35—40 | noisy |
| 40—45 | very noisy |
| 45—50 | loud |
| Above 50 | very loud |
Noise levels can be classified as follows:
- Below 20 dBA — the computer is relatively silent.
- From 20 to 25 dBA — the laptop is very quiet.
- From 25 to 30 dBA — the noise of the cooling system does not stand out against the background of ordinary office sounds.
- From 30 to 35 dBA — the noise is clearly audible.
- From 35 to 40 dBA — the noise begins to exceed the comfortable level for long-term work.
- From 40 to 45 dBA — the laptop works very noisily, it may require masking with background music.
- From 45 to 50 dBA — the noise level is extremely uncomfortable.
- Over 50 dBA — the noise is so loud that you need to use headphones.
This scale is conditional and does not take into account the individual characteristics of sound perception.
Wi-Fi
In our review, we consider the budget wireless adapter Mediatek (MT7922A22M), branded as AMD RZ616, as opposed to the more advanced adapters Intel AX or BE. To evaluate its performance, we will conduct tests in the network, using a dual-band router TP-Link Archer AX72 class Wi-Fi 6 AX5400 for access and distribution of data. As a control measurement, we use a desktop with a 2.5-gigabit PCIe adapter TP-Link TX201. On the PC for measurements, the iperf3 application is launched as a client, and on the tested device — as a server.
We will compare the results obtained by the Intel Killer BE1750 adapter in the laptop under review with the results of two other portable devices:
- MSI Vector 17 HX A14VGG with the Intel Killer BE1750 adapter
- MSI Titan GT77 HX 13VI with the Intel Killer AX1690i adapter
- Maibenben X639 with the Intel AX211 adapter
The measurements were taken under three connection conditions to the TP-Link Archer AX72 router:
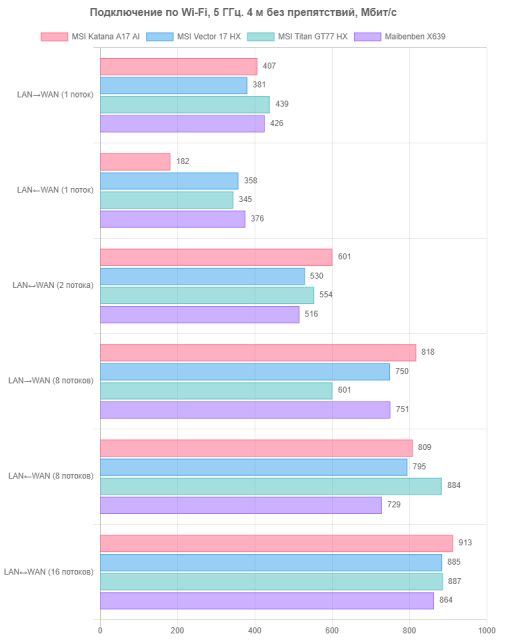
- At a distance of 4 m from the router in the line of sight (without obstacles);
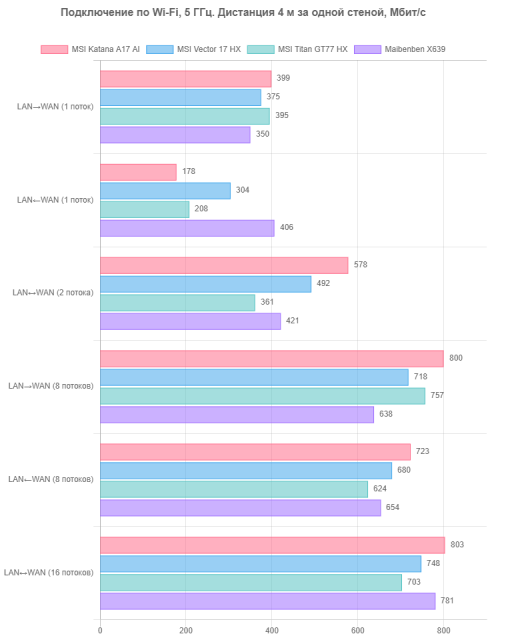
- At a distance of 4 m from the router with one brick wall as an obstacle;
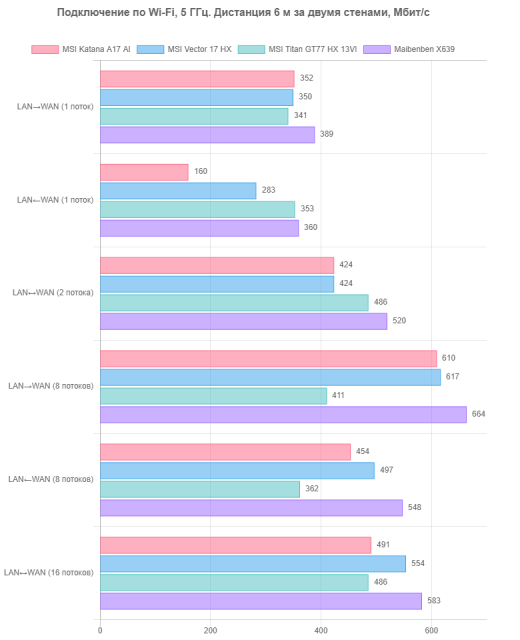
- At a distance of 6 m from the router with two brick walls as obstacles.
The client devices run the iperf3 application in server mode, and the measuring station (reference desktop) is connected to the router via UTP Cat5E cable and operates as a client. The results are presented in three tables for each of the specified locations.
The test results were quite encouraging. At a minimum distance from the router and without obstacles, the MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG demonstrates excellent speed performance, especially with two-, eight- and sixteen-stream duplex. However, when transmitting packets from WAN to LAN (incoming traffic) in single-stream mode, its performance is significantly inferior to competitors. With an increase in the distance to the router and the appearance of obstacles, the Wi-Fi connection speed for other types of transmission also drops noticeably. In practice, this can become a noticeable problem with a long-distance connection, although in close-range conditions the difference may not be so noticeable. As a result, the wireless adapter in the MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG is an interesting, but not the most preferable solution.
Performance
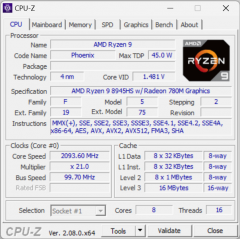
Before we move on to the main tests, let's check the operation of the available hardware components of the MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG and compare the results with the achievements of other models of portable PCs. For this, we use the CPU-Z utility to review the system characteristics.
RAM
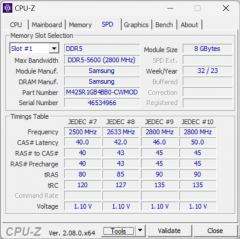
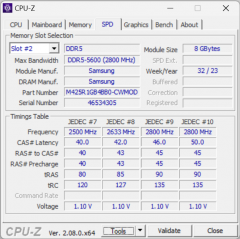
The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG is equipped with two 8GB DDR5-5600 SO-DIMM modules, enabling the RAM to operate in dual-channel mode. In tests using the built-in benchmark of the AIDA64 utility, the RAM showed the following results:
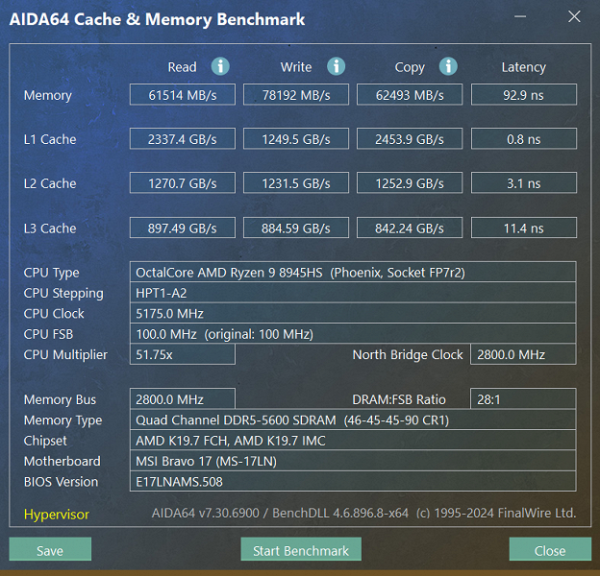
MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG (16 GB, dual-channel mode)
The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG's DDR5 RAM speeds aren't particularly impressive. For comparison, consider the similar figures for two other laptops that we previously mentioned as its competitors:
- MSI Vector 17 HX A14VGG — 16GB DDR5-5600 (2×8GB SK Hynix HMCG66AGBSA095)
- MSI Titan GT77 HX 13VI — 16GB DDR5-4800 (2×8GB Samsung M425R2GA3BB0)
Let's present the data on diagrams.
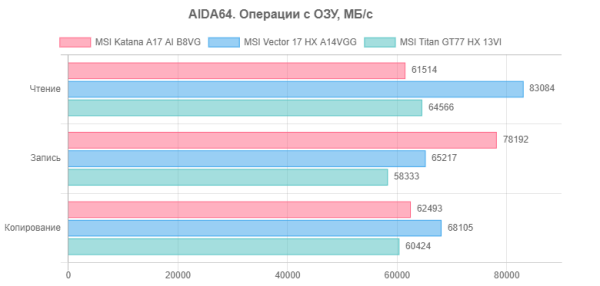
The hero of the review is ahead of both of its “teammates” in terms of memory write speed, but it is difficult to judge the value of this circumstance without taking into account practical activities.
System storage
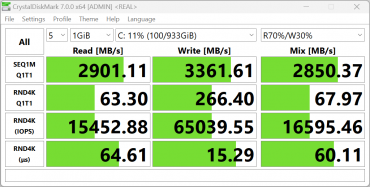
The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG uses a WD SN560 (SDDPNQE-1T00-1032) NVMe drive with a PCIe 4.0 ×4 interface to store programs and data. Let's run a quick test of this device using the popular CrystalDiskMark utility.
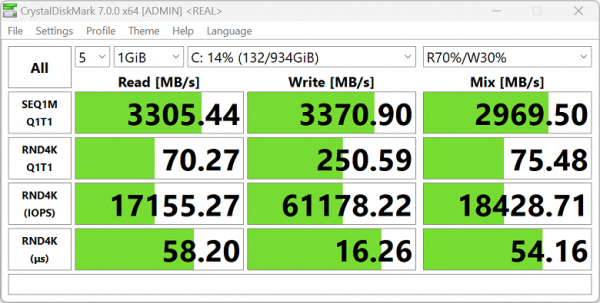
MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG
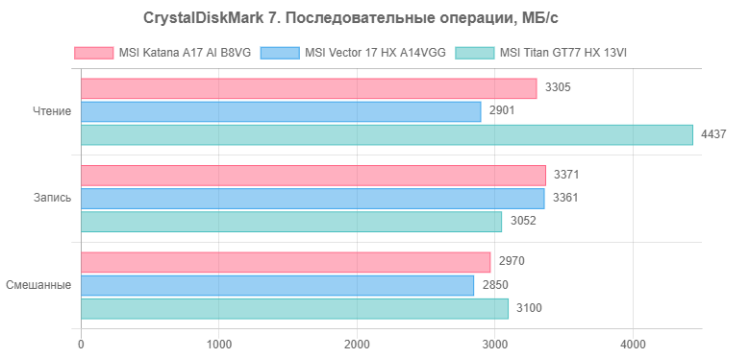
The speeds are not bad, but SSDs with PCIe 4.0 ×4 interface could show higher results. Let's compare the performance of the NVMe drive of the hero of the review with two other laptops:
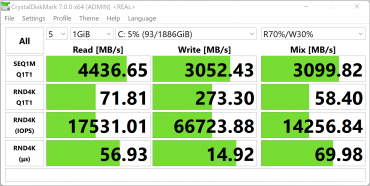
- MSI Vector 17 HX A14VGG — 1 TB WD SN560 SDDPNQE-1T00-1032 (PCIe 4.0 ×4)
- MSI Titan GT77 HX 13VI — 2 TB Micron Pyrite MTFDKBA2T0TFH (PCIe 4.0 ×4)
For ease of comparison, we present the corresponding diagrams.
The MSI Katana A17 AI B8VG system drive performs better than the similar SSD in the MSI Vector 17 HX A14VGG, but falls slightly behind the NVMe drive in the MSI Titan GT77 HX 13VI. However, the speed differences between these devices are small and may be barely noticeable in real-world use.