Google Pixel 8 is one of the few remaining compact flagships that offer high technical characteristics in a small size. Previously, such smartphones were rare due to the trend of “the more expensive, the bigger”, and after the disappearance of the “compact Sony”, the choice has decreased to units. Nevertheless, for fans of compact devices with excellent photo and video shooting, Google Pixel 8 is worth attention, even despite its unofficial presence on the Russian market.

Key Features of Google Pixel 8
- SoC Google Tensor G3, 9 processor cores (1×Cortex-X3 @3.0 GHz + 4×Cortex-A715 @2.45 GHz + 4×Cortex-A510 @2.15 GHz)
- GPU Immortalis-G715s MC10
- OS Android 14
- Touchscreen Super AMOLED, 6.2″, 1080×2400, 20:9, 428 ppi, 120 Hz
- RAM 8 GB, internal memory 128/256 GB
- No microSD support
- Support Nano-SIM (1 pc.) + e-SIM
- Networks 2G GSM, 3G WCDMA, 4G LTE, 5G
- GPS (L1+L5), Glonass (G1), Galileo (E1+E5a), QZSS (L1+L5)
- Wi-Fi 6e/7
- Bluetooth 5.3, A2DP, LE, aptX HD
- NFC
- USB 3.2 Gen1 (USB 3.0) Type-C, USB OTG
- no 3.5 mm audio output for headphones
- Cameras 50 MP + 12 MP (wide-angle), video 4K@60 fps
- Front camera 10.5 MP
- Proximity and light sensors, magnetic field, accelerometer, gyroscope
- Fingerprint scanner (under the screen)
- Battery 4575 mAh, charging 27 W, wireless charging 18 W
- Dimensions 151×71×8.9 mm
- Weight 187 g
Appearance and ease of use
The Google Pixel 8 smartphone comes in a minimal, hard cardboard box, as it does not come with any accessories, only a connecting cable.

The Google Pixel 8 body has a well-thought-out design. The sides of the smartphone are wide enough to comfortably hold in your hand, while the transitions on them are slightly rounded, which prevents discomfort. The smartphone is already compact, and thanks to the tactilely pleasant roundings it feels even more miniature.

The Google Pixel 8 body has a well-thought-out design. The sides of the smartphone are wide enough to comfortably hold in your hand, while the transitions on them are slightly rounded, which prevents discomfort. The smartphone is already compact, and thanks to the tactilely pleasant roundings it feels even more miniature.
The design of the rear cameras certainly raises different opinions. The protruding «squiggle» may not seem like a suitable solution for an expensive flagship to everyone. However, despite this, this design has its advantages: the protruding cameras lift the smartphone when it is lying on a hard surface, and since this block covers the entire width of the back, the device does not wobble when working with the screen.

The side buttons on the Google Pixel 8 are conveniently placed on one edge, easily accessible by finger. They have a crisp and firm stroke. However, the power button is surprisingly located above the volume rocker, which is a rare placement for smartphones on the market.

A single front camera lens is installed behind a round cutout in the screen matrix in the center of the top edge.
The fingerprint scanner is located under the bottom of the screen glass. The sensor is optical, located low, this solution is less convenient and faster than the scanner in the side button.

The tray accepts a Nano-SIM card. There is no provision for a microSD memory card.

The bottom end houses a speaker, microphone and USB Type-C connector.

The top end is given over to an additional microphone.

Google Pixel 8 is available in several color options: pink, gray, black, and recently added mint (Obsidian, Hazel, Rose, Mint). The smartphone body is fully protected from moisture and dust according to the IP68 standard.
Screen
The Google Pixel 8 features a 6.2-inch Super AMOLED display with a resolution of 1080×2400 pixels (aspect ratio of 20:9) and a density of 428 ppi. The screen is protected by flat Corning Gorilla Glass Victus and supports a refresh rate of 120 Hz.
The front surface of the Google Pixel 8 display is a glass panel with a mirror-like, smooth surface that is resistant to scratches. The anti-glare properties of the screen are better than those of the Google Nexus 7 (2013), and the oleophobic coating significantly improves the oil repellency, which makes it easier to remove fingerprints and slows down their appearance.
The maximum long-term brightness of the screen with manual adjustment and displaying a white field reaches about 970 cd / m², if the device is cool enough. In HDR mode, the maximum brightness can reach about 1400 cd / m² for small areas of white (2%) and for the entire screen. The minimum brightness is 1.8 cd / m². High maximum brightness and excellent anti-glare properties provide good readability even in sunlight, and in complete darkness, the brightness can be reduced to a comfortable level. Automatic brightness control works based on the light sensor, which is located under the screen. In automatic mode, the screen brightness is adjusted depending on external conditions: in complete darkness up to 5 cd/m², with artificial office lighting up to 120 cd/m², and in bright sunlight up to 970 cd/m². If necessary, the user can adjust the brightness manually, obtaining values of 15, 120 and 970 cd/m² for these conditions.
The screen also exhibits brightness modulation with a frequency of 240 Hz, which is observed at all brightness levels.
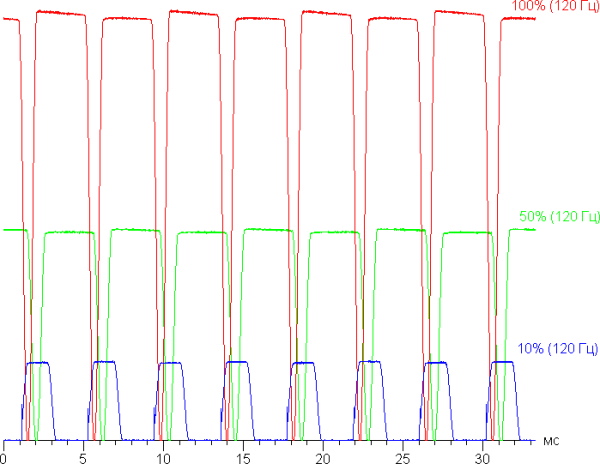
At maximum and medium screen brightness, the modulation has a low duty cycle, which eliminates visible flickering. However, when the brightness is reduced, modulation with a high duty cycle becomes noticeable, which can be seen in stroboscopic tests or with rapid eye movement. Depending on individual sensitivity, this flickering can cause fatigue. However, the high modulation frequency and phase differences across the screen area reduce the negative impact of flickering.
A mode with a refresh rate of up to 120 Hz is available in the screen settings.
In the 120Hz refresh rate mode, the smoothness of scrolling, for example when moving lists in the menu, is significantly improved.
The display uses a Super AMOLED matrix based on organic light-emitting diodes. The color image is formed by subpixels of three colors — red ®, green (G) and blue (B), while the red and blue subpixels are half the size of the green ones. This can be designated as RGBG, which is confirmed by a fragment of a microphotograph.
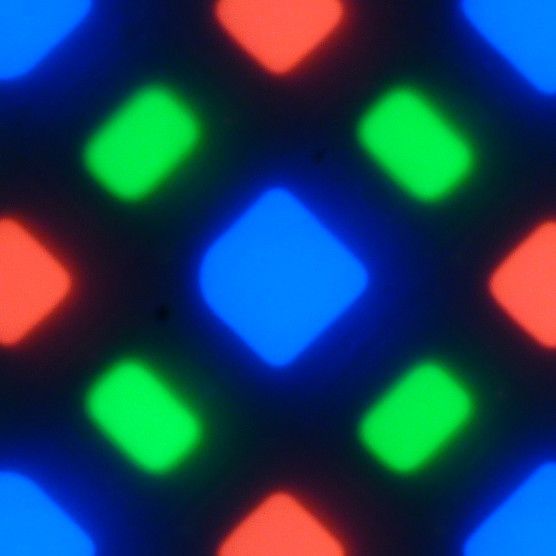

The fragment shows that the screen contains 4 green subpixels, 2 red (including 4 halves) and 2 blue (1 whole and 4 quarters). These fragments can be repeated across the entire screen without gaps or overlaps. For such matrices, Samsung uses the PenTile RGBG designation. The screen resolution is calculated by green subpixels, and for other colors it is slightly lower.
The screen provides excellent viewing angles. Brightness decreases when viewed at an angle on both screens, but this decrease is much less pronounced on the smartphone compared to the Nexus 7. Therefore, the smartphone screen seems brighter at any viewing angle. Although white takes on a slight bluish tint at a significant deviation, black remains deep and saturated at any angle. For comparison, photographs with a white field are provided, in which the screens of the smartphone and another device display the same images, with a brightness of about 200 cd / m² and a color balance set to 6500 K.
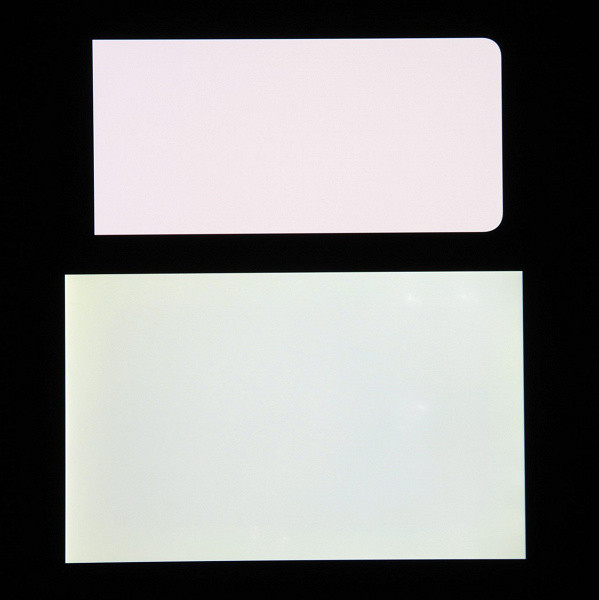

Note the good uniformity of brightness and color tone of the white field.
And the test image (Natural [colors] profile):
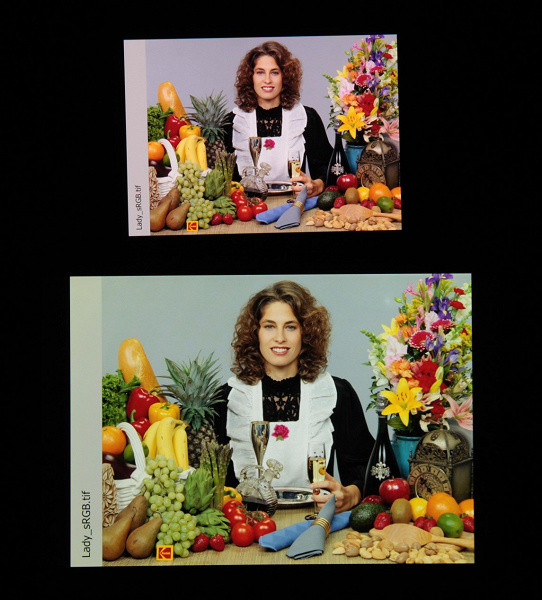

The screen has good color rendering: the colors are saturated, the color balance of the screens is slightly different. It should be remembered that the photo does not always accurately reflect the quality of color rendering and is used for illustration purposes only. For example, the reddish tint of white and gray in the photos of the smartphone screen is not noticeable when looking directly, which is confirmed by hardware tests using a spectrophotometer. This is due to the fact that the spectral sensitivity of the camera matrix does not fully match the characteristics of human vision.
In the photo shown, the screen is set to the active profile «Natural colors», out of two available profiles.

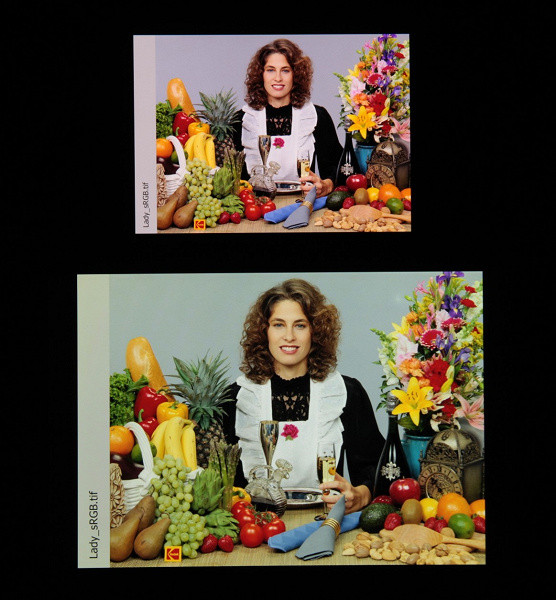
The Adaptive profile (selected by default) features slightly increased color saturation:

Switching of the matrix elements state occurs almost instantly, but at the switching front there may be a step of about 17 ms (which corresponds to a screen refresh rate of about 60 Hz) or about 8 ms (120 Hz). For example, this is what the change in brightness from black to white looks like:
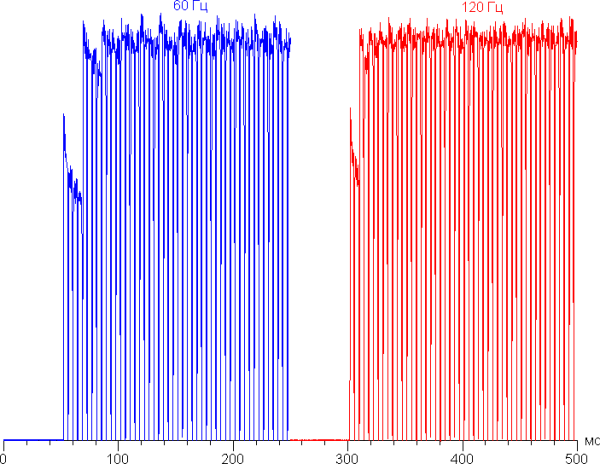
In some conditions, the presence of such a step can lead to the appearance of trails that follow moving objects.
The gamma curve of grayscale plotted using 32 points shows the absence of significant distortions in both light and dark areas. The approximating power function has an exponent of 2.27, which is slightly higher than the standard value of 2.2. At the same time, the real gamma curve generally corresponds to the power dependence.
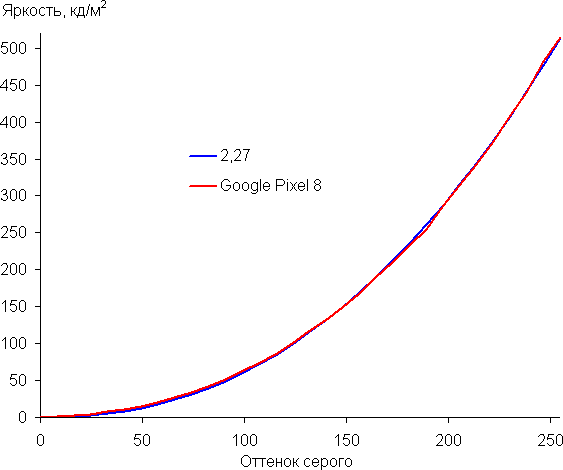
Let us recall that in OLED screens the brightness of individual image fragments changes dynamically depending on the overall nature of the image — it decreases slightly for light images. Therefore, the dependence of brightness on hue (gamma curve) most likely does not completely coincide with the gamma curve for a static image, since the measurements were taken with sequential output of gray shades to most of the screen.
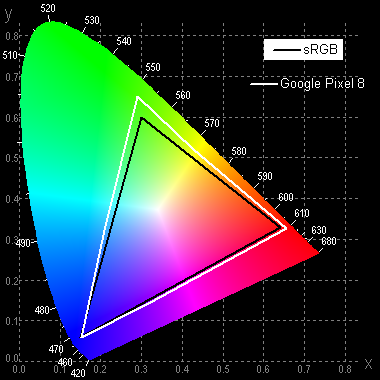
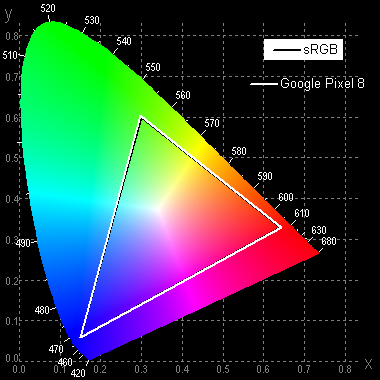
The color gamut in the «Adaptive adjustment» profile is slightly wider than sRGB, while in the «Natural» profile it is close to sRGB.
Let's look at the spectra (Natural profile):
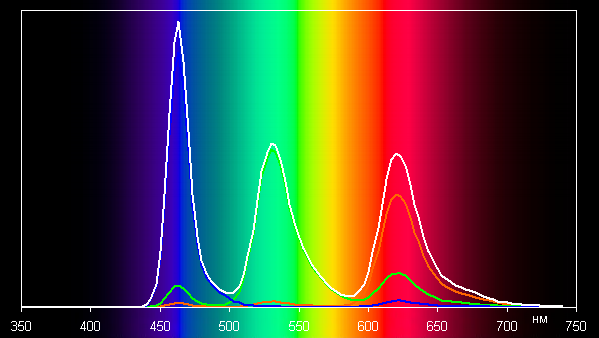
Such spectra are typical for OLED matrices — the components are well separated, which provides a wide color gamut. In this case, the color gamut is precisely limited by the sRGB boundaries, which makes the colors visually natural and saturated.
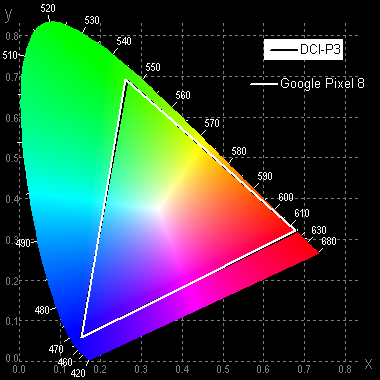
These results were obtained when displaying images in the Google Chrome browser. When using the Google Photos program with images in the Display P3 profile, the color gamut was wider than sRGB and close to DCI-P3.
Let's look at the spectra in the case of test images in this case:
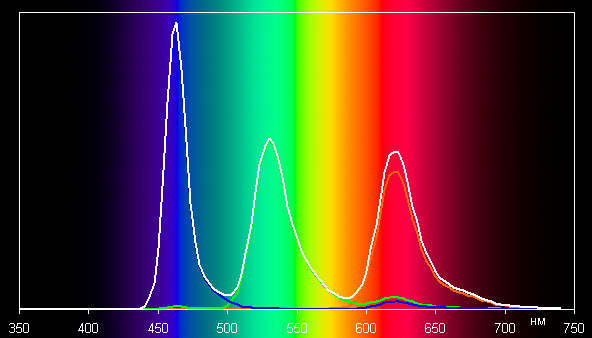
It is noted that there is a slight cross-mixing of components, indicating that the color space of the screen is slightly wider than DCI-P3.
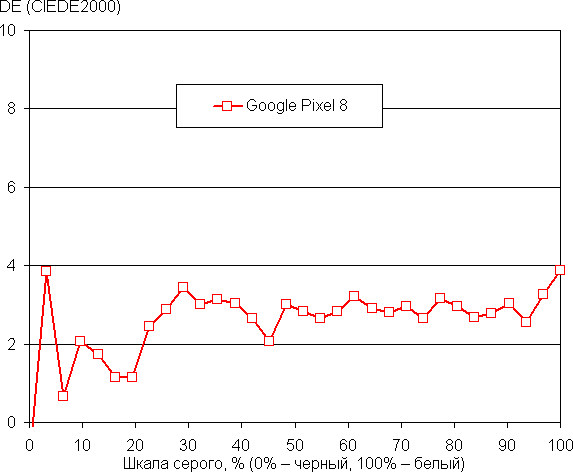
The balance of shades on the gray scale is good, since the color temperature is close to the standard 6500K, and the deviation from the black body spectrum (ΔE) is below 10 — which is an excellent result for a consumer device. The color temperature and ΔE remain stable across different shades, which has a positive effect on the color balance. The darkest parts of the gray scale can be ignored, since the color balance is not so important in these areas, and also due to the significant measurement error at low brightness.
Of course, there is a function to reduce the intensity of the blue component:
The description of the Night Light mode contains some misleading information about eye strain, although there are some good points. It is true that bright light can disrupt the daily (circadian) rhythm, but this can be solved by reducing the brightness to a comfortable level. Reducing blue light does not make much sense for improving perception.
Apparently, this device does not support DisplayPort Alt Mode over USB Type-C, which limits the ability to output images and sound to external devices via this port.
To summarize, it can be noted that the screen has a very high maximum brightness (up to 970 cd / m²) and excellent anti-glare properties, which makes it comfortable to use the device even in direct sunlight. In complete darkness, the brightness can be reduced to a comfortable level (up to 1.8 cd / m²). The automatic brightness adjustment mode works adequately. The screen also features an effective oleophobic coating, supports the sRGB and DCI-P3 color gamut (in combination with Google Photos software), has a good color balance, and supports a dynamic refresh rate of up to 120 Hz. The advantages of OLED screens include true black color and less loss of brightness when viewed at an angle compared to LCD screens. The disadvantages include screen flickering at low brightness, which can cause increased fatigue in sensitive users. Overall, the quality of the screen is very high.
Camera
The Google Pixel 8 smartphone has two rear cameras and one front camera:
- 50 MP, 1/1.31″, 1.2 µm, f/1.7, 25 mm, dual pixel PDAF, Laser AF, OIS (main)
- 12 MP, 1/2.9″, 1.25 µm, f/2.2, 126˚, AF (wide-angle)
- 10.5 MP, 1/3.1″, 1.22 µm, f/2.2, 20 mm (selfie)
The main camera takes photos with a resolution of 12.5 MP by default thanks to the pixel binning function. The quality of the photos is one of the best on the market. Google has always been a leader in the field of computational photography, and the current smartphone models fully realize this potential. Photos are highly detailed, clear, sharp and have good contrast. The dynamic range ensures the development of all halftones without overexposure. There is no blurring, and the color rendition is close to natural. The quality of the photos is truly flagship.
Examples of photos taken with the main camera in auto mode:
The main camera takes photos with a resolution of 12.5 MP by default thanks to the pixel binning function. The quality of the photos is one of the best on the market. Google has always been a leader in the field of computational photography, and the current smartphone models fully realize this potential. Photos are highly detailed, clear, sharp and have good contrast. The dynamic range ensures the development of all halftones without overexposure. There is no blurring, and the color rendition is close to natural. The quality of the photos is truly flagship.
Examples of photos taken with the main camera in auto mode:
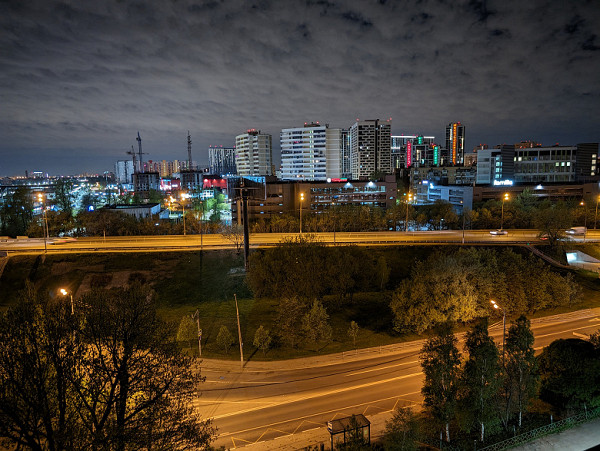

There is no dedicated zoom lens like the Pro version, so you have to rely on digital zoom. It is not entirely clear whether this is purely digital zoom or whether the sensor simply cannot provide more detail when cropping a 50-megapixel image, but there is no or minimal improvement in detail. However, at 2x zoom the image looks quite decent.
The wide-angle module, thanks to excellent processing, effectively hides its inherent shortcomings, such as low detail and blurring at the edges. The images are good, with adequate sharpness (excluding extreme corners) and contrast. Color rendering is comparable to the main camera.
Video can be shot in 4K at 60 fps, which provides flagship quality. The image is bright, rich and contrasty, with excellent detail. Stabilization works great, providing smoothness even when shooting on the move, without a noticeable stroboscopic effect. Reducing the resolution to 1080p is impractical, since in 4K@60 fps mode the quality is high, although the color rendition may be overly saturated. Sound is recorded in high quality.
Telephone and communications
The Google Pixel 8 smartphone supports mobile networks up to 5G, ensuring stable operation within the city limits of Moscow. It reliably holds the signal and quickly restores the connection after interruptions. The device is equipped with the latest wireless adapter with Wi-Fi 7 support, and also supports Bluetooth 5.3 and NFC. Built-in e-SIM support is also present.
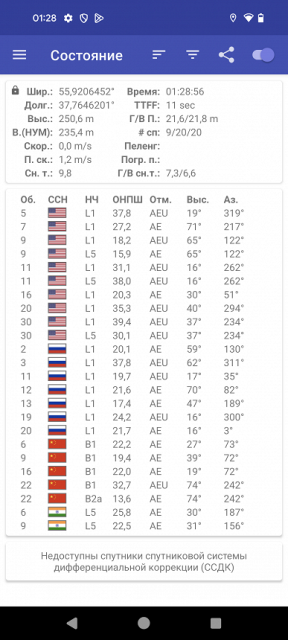
Satellite navigation works with GPS (L1 + L5), GLONASS (G1), Galileo (E1 + E5a) and QZSS (L1 + L5). Satellites are found quickly even with a cold start, positioning accuracy is at a high level. All the necessary sensors, including a gyroscope, are also present.
The voice of the interlocutor in the speaker is clear and loud, and the vibration motor works pleasantly and noticeably.
Software and multimedia
Google Pixel 8 runs on pure Android 14 OS without additional shells. Pixel smartphones are the first to receive Android updates and support them longer than others — up to 7 years. All Google services are fully supported here, and the Google Play Store is also installed.
The Android interface is optimized for smooth and fast operation. In the «pure» version of Android, the notification curtain is presented as a single telescopic menu, without dividing it into two parts. The new version of the OS offers advanced customization options: widgets and wallpapers can be manually configured so that they change depending on the time of day and weather. Attention is also paid to AI-based functions, which are constantly evolving.
The sound of the smartphone is bright, loud and clear. A2DP, LE and aptX HD protocols are supported for wireless headphones.
Performance
Google Pixel 8 is equipped with Google Tensor G3 SoC with nine processor cores and Immortalis-G715s MC10 GPU. The device has 8 GB of RAM and built-in storage of 128 or 256 GB. A memory card cannot be installed. External devices can be connected via the USB Type-C port in USB OTG mode.
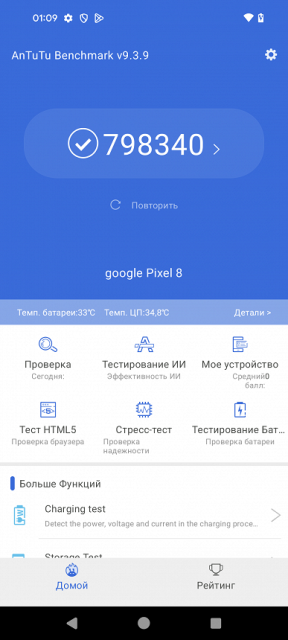
The platform is powerful, at a sub-flagship level and is manufactured using a 4 nm process technology. In AnTuTu, it scores about 800 thousand points, although the throttling level is high. The smartphone shoots 4K video at 60 fps without any problems. This provides high performance for most tasks, but is not specifically designed for gaming: the screen is small, throttling is noticeable, and the performance is average. For example, Genshin Impact does not work as smoothly as we would like even at medium settings.
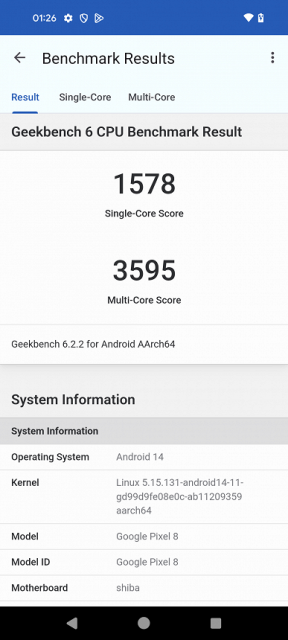
Testing in complex tests AnTuTu and GeekBench:
We have collected the smartphone test results in the latest versions of popular benchmarks and presented them in tables for convenience. The tables also include data on several other devices from different segments, tested on the same versions of benchmarks, to give a visual assessment of the results obtained. Unfortunately, due to comparison limitations, not all models that were tested on previous versions of programs can be presented in one comparison. Therefore, some relevant and worthy devices remain out of the frame.
| Google Pixel 8 (Google Tensor G3) | Realme GT 6T (Qualcomm Snapdragon 7+ Gen3) | Oppo Reno11 5G (MediaTek Dimensity 7050) | Huawei nova 12s (Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G) | Redmi Note 13 Pro+ (Mediatek Dimensity 7200 Ultra) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AnTuTu (v9.x) (bigger is better) | 798340 | 1003157 | 509328 | 546957 | 669583 |
| GeekBench 6 (bigger is better) | 1578/3595 | 1716/4369 | 1091/2571 | 996/2453 | 1126/2643 |
Testing the graphics subsystem in GFXBenchmark gaming tests:
| Google Pixel 8 (Google Tensor G3) | Realme GT 6T (Qualcomm Snapdragon 7+ Gen3) | Oppo Reno11 5G (MediaTek Dimensity 7050) | Huawei nova 12s (Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G) | Redmi Note 13 Pro+ (Mediatek Dimensity 7200 Ultra) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFXBenchmark Aztec Ruins OpenGL (Onscreen, fps) | 42 | 117 | 30 | 34 | 50 |
| GFXBenchmark Aztec Ruins Vulkan (Onscreen, fps) | 105 | 129 | 26 | 38 | 55 |
| GFXBenchmark Car Chase ES 3.1 (1080p Offscreen, fps) | 76 | 94 | 26 | 33 | 43 |
| GFXBenchmark Manhattan ES 3.1 (1080p Offscreen, fps) | 138 | 163 | 45 | 56 | 74 |
| GFXBenchmark T-Rex (1080p Offscreen, fps) | 316 | 400 | 106 | 133 | 191 |
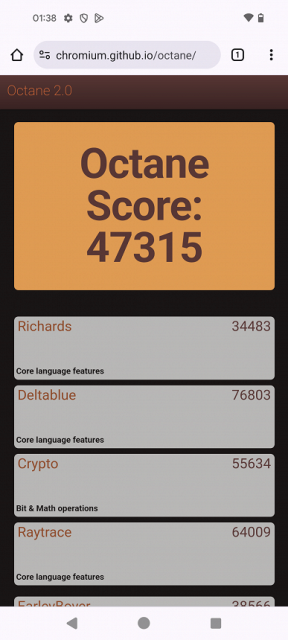
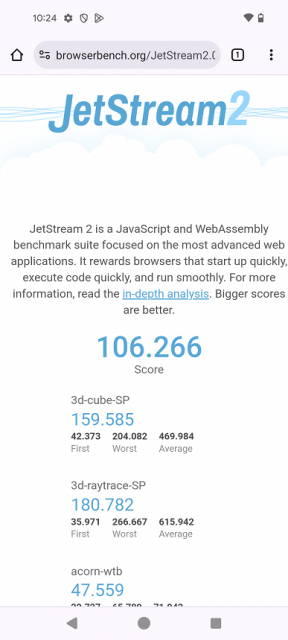
Testing in browser cross-platform tests:
| Google Pixel 8 (Google Tensor G3) | Realme GT 6T (Qualcomm Snapdragon 7+ Gen3) | Oppo Reno11 5G (MediaTek Dimensity 7050) | Huawei nova 12s (Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G) | Redmi Note 13 Pro+ (Mediatek Dimensity 7200 Ultra) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Octane 2 (bigger is better) | 47315 | 34829 | 7118 | 24923 | 39276 |
| JetStream (bigger is better) | 106 | 82 | 29 | 67 | 79 |
Memory speed test results:
Heat
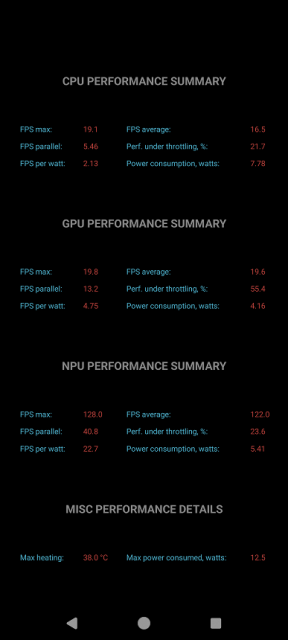
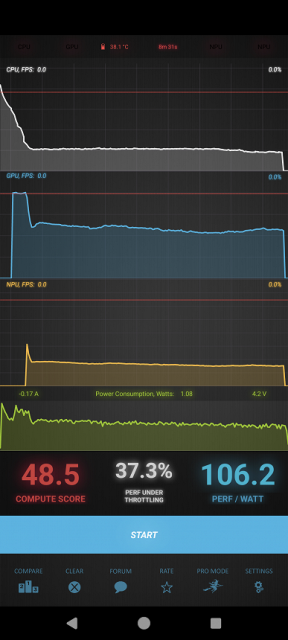
We test for performance degradation when heating using the Burnout Benchmark program, which allows you to load the CPU, GPU and NPU:
| Load on | Heating performance, as a percentage of maximum |
|---|---|
| CPU | 22% |
| GPU | 55% |
| NPU | 24% |
Battery life
The Google Pixel 8 smartphone is equipped with a 4575 mAh battery, which results in a low level of autonomy in tests.
Testing was carried out at a standard level of power consumption, without activating power-saving functions, although such functions are present in the device. Test conditions: minimum comfortable screen brightness (about 100 cd / m²). The tests included: endless reading in the Moon + Reader application (with a light theme), continuous viewing of HD video (720p), and the Injustice 2 game with automatic graphics settings.
| Battery capacity | Reading mode | Video mode | 3D gaming mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Pixel 8 | 4575 mAh | 18:00 | 14:00 | 6:00 a.m. |
| Realme GT 6T | 5500 mAh | 32 h 00 m | 29 h 00 m | 8:00 a.m. |
| Oppo Reno11 5G | 5000 mAh | 27:00 | 25:00 p.m. | 8:00 a.m. |
| Vivo V30e | 5500 mAh | 29 h 00 m | 26 h 00 m | 8:00 a.m. |
| Infinix Note 40 | 5000 mAh | 18:30 | 15:00 | 6 h 30 min |
| Tecno Spark 20 Pro+ | 5000 mAh | 18:00 | 14:00 | 6:00 a.m. |
| Vivo V30 | 5000 mAh | 23:00 | 21:00 | 8:00 a.m. |
| Vivo V29 | 4600 mAh | 21:00 | 19:00 | 8 h 30 min |
| Infinix GT 10 Pro | 5000 mAh | 20:30 h. | 18:00 | 8 h 30 min |
These results represent the maximum figures obtained under ideal conditions, including no SIM cards installed. Any changes in the usage scenario may result in a decrease in autonomy.
The smartphone does not come with a wall charger in the box, so the charging speed will depend on the charger used. The maximum supported charging power is 27 W, which means that even with chargers supporting Power Delivery 3.0, a full charge will take more than an hour and a half. Wireless charging is supported, but also has a power limit of 18 W.
Results
The Google Pixel 8 is a great smartphone with high technical specifications in all aspects: screen, sound, case materials, network capabilities and, above all, photo and video quality. It is quite deservedly comparable to the iPhone, especially with compact format models such as the basic iPhone 15. The main problem with both devices is the low level of autonomy compared to large flagships with large batteries. However, for those looking for a top-end compact Android smartphone, the Google Pixel 8 has virtually no competitors.