General information about GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super
At CES 2024 earlier this year, Nvidia introduced three new graphics card models, all equipped with Super specifications, which imply improvements over previous versions. These new products bring freshness to the product line ahead of the upcoming release of the next generation. Today we will look at the middle of this trio — GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, which appeared on the market on January 24.
This model attracts attention because it is based on a new GPU model, which distinguishes it from its predecessor. Previously, we reviewed the GeForce RTX 4070 Super video card, which showed a significant increase in performance compared to the base GeForce RTX 4070 — about 15%. On the other hand, the GeForce RTX 4080 Super turned out to be almost the same as the GeForce RTX 4080, but at a more affordable price. But the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is somewhere in the middle: it is clearly ahead of the regular GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, but the speed increase is not so great. However, the new model has the added benefit of increased video memory — 16 GB for the Super version compared to 12 GB for the regular version. This additional capacity could be useful for future games at high resolutions and maximum graphics settings, although many projects will likely be sufficient with 12 GB of the base GeForce RTX 4070 Ti. Despite improved performance over the regular version, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super remains noticeably slower than the GeForce RTX 4080, and both older models are fading from the scene.

In terms of performance, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is more than capable of gaming at 2560x1440 resolution, including high refresh rate monitors and at all graphics settings. This model is also capable of providing acceptable performance on 4K monitors, but to achieve 60 FPS with ray tracing enabled you will have to resort to technologies such as DLSS and other optimization methods. Comparing the performance of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super with the GeForce RTX 3090 Ti, you can see that the new product provides similar characteristics, but at a more affordable price — $799.
Unsurprisingly, AMD responded by lowering the price of the Radeon RX 7900 XT, with this multi-manufacturer model now available for around $700 at major North American retailers. If initially the Radeon RX 7900 XT and GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super were positioned as direct competitors in price, now the AMD video card turns out to be more affordable. Improvements to Nvidia's new graphics card, such as upgrading the GPU to an AD103, adding 4GB of memory, increasing the bus width by 64-bit, and increasing compute performance by 10%, make the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super a very attractive model for the same $799 price. However, a closer look at these improvements will reveal how effective they really are.

| GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super graphics accelerator | |
|---|---|
| Chip code name | AD103 |
| Production technology | 5 nm (TSMC 4N) |
| Number of transistors | 45.9 billion |
| Core area | 378.6 mm² |
| Architecture | unified, with an array of processors for stream processing of any type of data: vertices, pixels, etc. |
| DirectX hardware support | DirectX 12 Ultimate, supporting Feature Level 12_2 |
| Memory bus | 256-bit: 8 independent 32-bit memory controllers supporting GDDR6X memory |
| GPU frequency | up to 2610 MHz |
| Computing blocks | 66 (out of 80) streaming multiprocessors, including 8448 (out of 10240) CUDA cores for INT32 integer and FP16/FP32/FP64 floating point calculations |
| Tensor blocks | 264 (out of 320) tensor cores for matrix calculations INT4/INT8/FP16/FP32/BF16/TF32 |
| Ray tracing blocks | 66 (out of 80) RT cores for calculating the intersection of rays with triangles and BVH bounding volumes |
| Texturing blocks | 264 (out of 320) texture addressing and filtering units with support for FP16/FP32 components and support for trilinear and anisotropic filtering for all texture formats |
| Raster Operation Blocks (ROPs) | 12 (out of 14) wide ROP blocks of 96 (out of 112) pixels with support for various anti-aliasing modes, including programmable ones and for FP16/FP32 frame buffer formats |
| Monitor support | HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 1.4a support (with DSC 1.2a compression) |
| GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super graphics card specifications | |
|---|---|
| Core frequency | 2340/2610 MHz |
| Number of universal processors | 8448 |
| Number of texture blocks | 264 |
| Number of blending blocks | 96 |
| Effective memory frequency | 21 GHz |
| Memory type | GDDR6X |
| Memory bus | 256 pages |
| Memory | 16 GB |
| Memory Bandwidth | 672 GB/s |
| Compute Performance (FP32) | up to 44.1 teraflops |
| Theoretical maximum fill rate | 251 gigapixels/s |
| Theoretical texture sampling rate | 689 gigatexels/s |
| Tire | PCI Express 4.0 x16 |
| Connectors | according to the manufacturer's choice |
| Energy consumption | up to 285 W |
| Additional food | one 16-pin connector |
| Number of slots occupied in the system case | according to the manufacturer's choice |
| Recommended price | $799 |
The name of the new model, GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, follows the company's traditions and indicates improvements over the previous version, GeForce RTX 4070 Ti. This video card becomes a significant step forward in the line, surpassing the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti in performance and approaching the characteristics of the GeForce RTX 4080. The only drawback may be the complex name of the new product, which includes two suffixes at once.
Given that the AD104 GPU in the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti was already fully utilized, upgrading to the AD103 chip found in the GeForce RTX 4080 and GeForce RTX 4080 Super was the only way to achieve improvements in the Super series. The AD103 brings the benefits of a 256-bit bus and 16GB of memory to the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, which represents a 33% increase over the base GeForce RTX 4070 Ti. In addition, the new product received an improvement in computing performance by 10% and an increase in the speed of ROP blocks by 20%. These technical characteristics significantly exceed the capabilities of the regular GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, but the GeForce RTX 4080 still remains more powerful with its 9728 CUDA cores, larger L2 cache and number of ROP blocks.
The recommended price for the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super remained at $799, thus maintaining the price point of its predecessor. The new model completely replaces the base GeForce RTX 4070 Ti on the market, leaving the latter with only remnants. While the base GeForce RTX 4070 Ti price may have seemed high at launch, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super brings an additional 16GB of memory and a slight performance boost for the same price. However, being placed between the GeForce RTX 4070 Super for $599 and the GeForce RTX 4080 Super for $999, the new product finds itself in the mid-price segment, where the competition with the Radeon RX 7900 XT video card from AMD with a price of around $700 is noticeable.
The choice of 16 GB of video memory for the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is based on the wide 256-bit bus of the AD103 chip, which represents the optimal amount at the moment. This memory headroom is ideal for most use cases, even the most demanding 4K games where 12GB may not be enough at times. Considering that the main purpose of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is gaming at a resolution of 2560x1440, 16 GB of memory should be enough for many years to come.
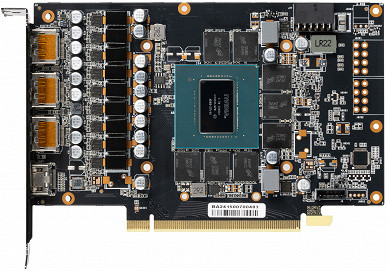
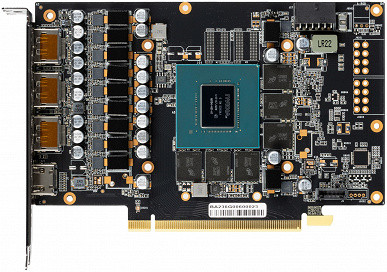
Unlike the previous GeForce RTX 4070 Super and GeForce RTX 4080 Super models, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is not represented by Nvidia's own Founders Edition and is only available from the company's partners. However, the overall appearance of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super follows typical solutions from various manufacturers — a three-fan cooling system that requires three slots in the case, one 16-pin 12VHPWR power connector, three DisplayPort connectors and one HDMI. This is a large video card, comparable in size to the GeForce RTX 4080.
As for power consumption, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super does not increase it compared to the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, remaining at 285 W, which is 35 W less than the GeForce RTX 4080. In games, the new product consumes 10-20 W more on average than the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, but is noticeably ahead of its competitors in terms of energy efficiency: the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super consumes 70-75 W less than the Radeon RX 7900 XTX, and 30-50 W less than the RX 7900 XT. However, it outperforms both AMD graphics cards in most complex scenarios, such as ray tracing games.

Nvidia partners have introduced and launched various versions of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super graphics card with unique designs. The assortment includes overclocked models with improved cooling and power systems, mostly equipped with triple fans, taking into account the tendency for increased heat generation of this video card. These updated graphics accelerators are already available from various manufacturers, including Asus, Colorful, Gainward, Galaxy, Gigabyte, Innovision 3D, MSI, Palit, PNY, Zotac and others.
Architecture Features
The GeForce RTX 40 line of graphics accelerators uses AD10x GPUs, which are based on the Ada Lovelace architecture. Nvidia engineers designed this graphics architecture to improve the performance of ray tracing and machine compute on Tensor Cores. The transition to a modern process technology from the Taiwanese company TSMC also had a significant impact, allowing a large number of execution units to be integrated into the chips. New GPUs are more complex, but they also run at higher clock speeds than previous models.
The AD103 GPU, which powers the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, includes all the features of the flagship AD102. This includes Gen 3 RT Cores and Gen 4 Tensor Cores, providing support for all of the ray tracing improvements and performance enhancing technology of DLSS 3.5. The AD103 crystal inside the new video card provides high performance comparable to the flagship solution of the previous generation — GeForce RTX 3090 Ti, with lower power consumption and a recommended price.
Like all Nvidia GPUs, the AD103 chip contains large Graphics Processing Clusters (GPCs). They combine several Texture Processing Clusters (TPCs), including Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs), ROPs, and memory controllers. The GPC cluster independently performs the main calculations within itself, including the Raster Engine, as well as four to six TPC clusters consisting of twice the number of SM multiprocessors. Let's look at the structure of the GPU in the configuration used specifically in the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super.
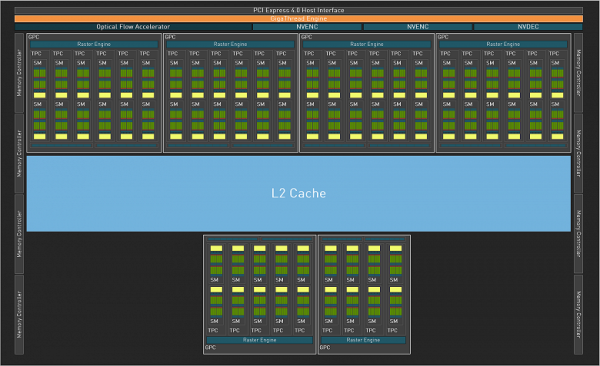
Unlike the fully unlocked chip used in the GeForce RTX 4080 Super with 80 SM multiprocessors and 10240 CUDA cores, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super version remains locked. The AD103-275-A1 GPU modification includes six of the seven GPC compute clusters, 66 SM multiprocessors, 8448 CUDA cores, 264 TMU texture units, 96 ROP units, 264 tensor cores and 66 ray tracing acceleration units. The base and turbo frequencies of the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super are 2340 and 2610 MHz, respectively, while the regular GeForce RTX 4070 Ti is 2310 and 2610 MHz — that is, the figures are quite close. However, in games frequencies up to 2800 MHz are reached.
Like other graphics cards based on this GPU, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is equipped with 16 GB of GDDR6X memory running at an effective frequency of 21 GHz and connected over a 256-bit bus, providing an impressive 672 GB/s of video memory bandwidth. Compared to the regular GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, which has 12 GB of GDDR6X memory and a 192-bit bus, memory bandwidth is 504 GB/s — which is a significant increase for the Super model. The large 48 MB cache also benefits many complex computing tasks, such as hardware ray tracing and rasterization, especially in games and benchmarks with a large number of translucent objects and particles.
All architectural improvements of the Ada Lovelace family were discussed in detail in a theoretical review, which described changes in the RT cores of the new architecture, including the Opacity Micromap Engine and Displaced Micro-Mesh Engine hardware units, as well as an additional Shader Execution Reordering scheduler for changing the order of shader execution. In terms of video capabilities, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is the same as the flagship model, supporting AV1 video encoding, which improves efficiency by 40% to 50% over H.264, and provides support for 8K video decoding at 60 FPS.
Software technologies
The first graphics cards in the GeForce RTX series were introduced in mid-2018, and despite the fact that the development of the GeForce RTX ecosystem did not proceed as quickly as many expected, it turned out to be important for the industry. Hardware-accelerated ray tracing brings significant improvements to the realism of lighting and reflections in games and professional applications. DLSS technology has become a key tool for accelerating graphics algorithms. Currently, more than 500 games and applications use various RTX technologies, including ray tracing, DLSS and other artificial intelligence applications.
DLSS became not only a resolution scaling technology, but also the ability to insert additional frames, optimizing the frequency and smoothness of video footage, as well as improving complex ray tracing through information accumulation and reconstruction. This capability gives current Nvidia solutions an additional advantage over competitors and previous generations. DLSS 3.5 supports frame generation and ray reconstruction.
Together with the release of new Super models of the GeForce RTX 40 line, Nvidia introduced an update to the RTX Video HDR software. It enables faster conversion of standard dynamic range (SDR) videos to high dynamic range (HDR) using tensor cores. This process also brings improvements in image quality using artificial intelligence. Despite the rise in original HDR videos, many previously created videos only exist in SDR format. Tensor Core technology in GeForce RTX GPUs enables efficient HDR conversion, improving brightness, contrast, and color reproduction.
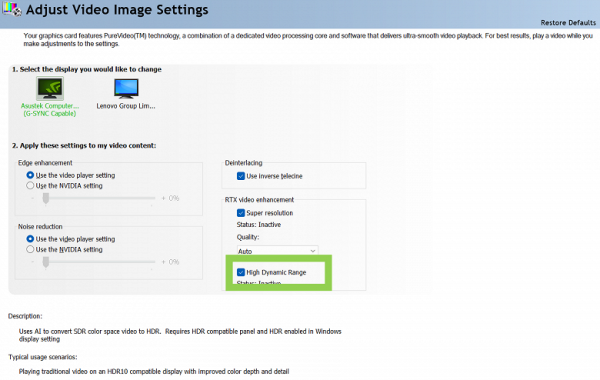
Modern graphics cards from Nvidia offer the ability to simultaneously use RTX Video HDR and RTX Video Super Resolution technologies to improve detail, dynamic range and other aspects of video content. This is available in Chromium-based browsers such as Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. Activation of RTX Video HDR and Video Super Resolution requires an HDR10-compatible display, the latest video drivers installed, HDR mode enabled in the operating system settings, and the corresponding settings in the Nvidia Control Panel, available in the «Adjust Video Image Settings» section.
The GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super graphics card allows for effective use in professional digital content creation tasks. Its high performance at a reasonable price, tensor cores for accelerated work with artificial intelligence tools, and hardware blocks for accelerated ray tracing are supported in various 3D packages and engines, such as Blender Cycles, Redshift, V-Ray, Octane and many others. These features help you render complex scenes faster and make your projects more efficient than comparable previous-generation graphics cards.
Preliminary Performance Assessment
Let's make a theoretical comparison of the characteristics of all three new models of GeForce RTX 40 series video cards, based on various chips from the AD10x line, with some previous models from the same family. This will allow us to clearly evaluate the differences between all the company's solutions.
| GeForce RTX 4070 | GeForce RTX 4070 Super | GeForce RTX 4070 Ti | GeForce RTX 4070 Super | GeForce RTX 4080 | GeForce RTX 4080 Super | GeForce RTX 4090 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPU | AD104 | AD104 | AD104 | AD103 | AD103 | AD103 | AD102 |
| Number of SM multiprocessors | 46 | 56 | 60 | 66 | 76 | 80 | 128 |
| Number of CUDA cores | 5888 | 7168 | 7680 | 8448 | 9728 | 10240 | 16384 |
| Number of TMUs | 184 | 224 | 240 | 264 | 304 | 320 | 512 |
| Number of ROP blocks | 64 | 80 | 80 | 96 | 112 | 112 | 176 |
| L2 cache volume, MB | 36 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 64 | 64 | 72 |
| Base frequency, MHz | 1920 | 1980 | 2310 | 2340 | 2205 | 2295 | 2235 |
| Turbo frequency, MHz | 2475 | 2475 | 2610 | 2610 | 2505 | 2550 | 2520 |
| Texturing speed, Mtex/s | 455 | 554 | 626 | 689 | 762 | 816 | 1290 |
| Fill rate, Mpix/s | 158 | 198 | 209 | 251 | 281 | 286 | 444 |
| Memory capacity, GB | 12 | 12 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 24 |
| Memory bus, bit | 192 | 192 | 192 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 384 |
| Memory frequency, GHz | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 22.4 | 23 | 21 |
| PSP, GB | 504 | 504 | 504 | 672 | 736 | 736 | 1008 |
| Energy consumption, W | 200 | 220 | 285 | 285 | 320 | 320 | 450 |
| Price, $ | 599 | 599 | 799 | 799 | 1199 | 999 | 1599 |
Based on theoretical data, it is clear that the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super brings several significant improvements over the previous model, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti. Increasing the number of SM multiprocessors to 66 and increasing the bus width of the AD103 chip to 256 bits brings a noticeable increase in computing and memory performance, which in theory should be reflected in real-world performance in games and other computing tasks.
However, in practice, the performance increase of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super turned out to be somewhat more moderate than expected. Despite the 10% increase in computing power, the new product demonstrates an acceleration of only 7% compared to the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti. It remains not close enough to the GeForce RTX 4080, falling short of the latter by 10%-12%. Increasing the memory size and increasing the L2 cache, although important characteristics, do not always have a significant impact on performance, especially when most users are satisfied with the current values.
Despite this, updating the graphics card line between generations is a profitable move for Nvidia and its partners. Super models provide more attractive options for upgrading systems, especially those with older GPUs. For example, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super offers a significant performance boost over the previous generation and is even comparable to the GeForce RTX 3090 Ti, which could be a significant selling point for users considering upgrading their graphics cards.
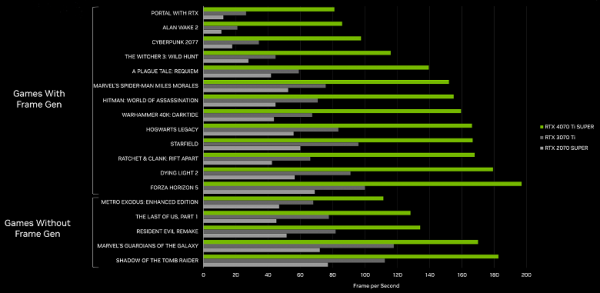
According to tests from Nvidia, the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is significantly superior to its predecessors from the previous two generations. According to the company, the performance of the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super exceeds the GeForce RTX 3070 Ti by more than one and a half times, and when using DLSS 3 technology, even by 2.5 times. This is an important update for owners of GeForce RTX 3060 (Ti) graphics cards, especially considering the new DLSS 3 frame generation, which is only available on the new model.
In terms of energy efficiency, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super confirms good performance, close to the regular GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, despite the increased video memory and larger GPU. Consumption up to 285 W makes the graphics card an efficient solution, which is a characteristic feature of Nvidia products.
Compared to its competitors, especially the Radeon RX 7900 XT, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super outperforms it in rasterization and by more than 15%-20% in active ray tracing conditions. This graphics card performs better in ray-traced games, making it an attractive option for those who value high performance in such environments. Despite the Radeon RX 7900 XT's better price, most buyers will likely prefer the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super for its improved ray tracing capabilities and DLSS 3.5 support.
However, despite the significant upgrade from the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super compared to its predecessors, the performance gains do not always live up to high expectations. It is only 6%-7% compared to the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti, and the main incentive to choose this model may be the increased video memory of up to 16 GB. This may be relevant for future memory-intensive games and applications. However, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is a good upgrade, delivering strong performance and an improved experience for gamers and professionals.
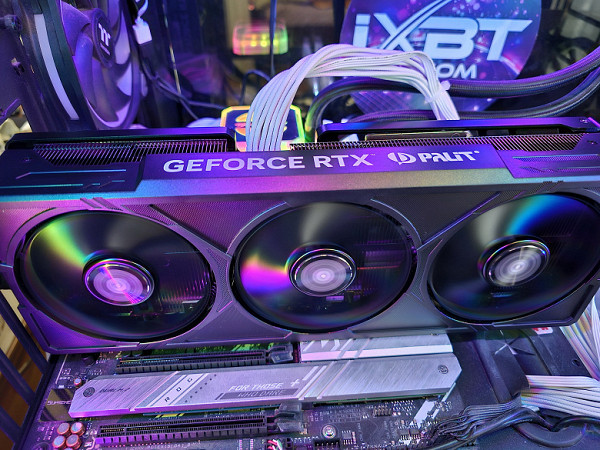
Palit GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super JetStream OC 16 GB video card
Palit Microsystems was founded in 1988 in the Republic of China (Taiwan) and is the parent company of the Palit brand. Headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan, with a major logistics center in Hong Kong and an additional sales office in Germany. There are also production facilities in China. On the Russian market since 1995, Palit began its journey with sales of unnamed products (Noname), and products appeared under the Palit brand after 2000. In 2005, the company acquired the Gainward brand and assets after its bankruptcy, which led to the creation of the Palit Group holding company. An additional office was also opened in Shenzhen, focused on the Chinese market. Palit Group includes several other brands.
The object of the study is the commercially available Palit GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super JetStream OC video card with 16 GB of GDDR6X video memory and a 256-bit bus.


| Palit GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super JetStream OC 16 GB 256-bit GDDR6X | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Meaning | Nominal value (reference) |
| GPU | GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super (AD103) | |
| Interface | PCI Express x16 4.0 | |
| GPU operating frequency (ROPs), MHz | 2640(Boost)—2790(Max) | 2610(Boost)—2805(Max) |
| Memory operating frequency (physical (effective)), MHz | 2625 (21000) | 2625 (21000) |
| Memory bus width, bits | 256 | |
| Number of computational units in the GPU | 66 | |
| Number of operations (ALU/CUDA) in block | 128 | |
| Total number of ALU/CUDA blocks | 8448 | |
| Number of texturing units (BLF/TLF/ANIS) | 262 | |
| Number of rasterization units (ROP) | 96 | |
| Number of Ray Tracing blocks | 66 | |
| Number of tensor blocks | 268 | |
| Dimensions, mm | 330×130×65 | 310×130×70 |
| Number of slots in the system unit occupied by a video card | 4 | 4 |
| PCB color | black | black |
| Peak power consumption in 3D, W | 272 | 285 |
| Power consumption in 2D mode, W | 40 | 40 |
| Energy consumption in sleep mode, W | eleven | eleven |
| Noise level in 3D (maximum load), dBA | 29.4 | 34.0 |
| Noise level in 2D (video viewing), dBA | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| Noise level in 2D (idle), dBA | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| Video outputs | 1×HDMI 2.1, 3×DisplayPort 1.4a | 1×HDMI 2.1, 3×DisplayPort 1.4a |
| Multiprocessing support | No | |
| Maximum number of receivers/monitors for simultaneous image output | 4 | 4 |
| Power: 8-pin connectors | 0 | 0 |
| Power: 6-pin connectors | 0 | 0 |
| Power: 16-pin connectors | 1 | 1 |
| Weight of the card with delivery set (gross), kg | 1.95 | 2.5 |
| Card weight (net), kg | 1.44 | 2.0 |
| Maximum resolution/frequency, DisplayPort | 3840×2160@144 Hz, 7680×4320@60 Hz | |
| Maximum resolution/frequency, HDMI | 3840×2160@144 Hz, 7680×4320@60 Hz |
Memory

The graphics card is equipped with 16 GB of GDDR6X SDRAM video memory, which is distributed among 8 chips installed on the front side of the printed circuit board. Memory chips represented by Micron models (MT61K512M32KPA-21/D8BZC) are designed for a nominal operating frequency of 2625 (21000) MHz.
Card features and comparison with Palit GeForce RTX 4070 Ti JetStream (12 GB)
We compare this video card with a model of the same manufacturer and series, but of a lower level, and observe the expected results: both cards are almost identical, differing only in the installation of two additional memory chips. This is because all PCBs designed for modern Nvidia GPUs with a 192-bit memory bus are actually routed for a 256-bit bus. The reduced bus width is achieved due to the absence of two memory chips.
The graphics core is designated AD103-275, and the release date falls on the 48th week of 2023.
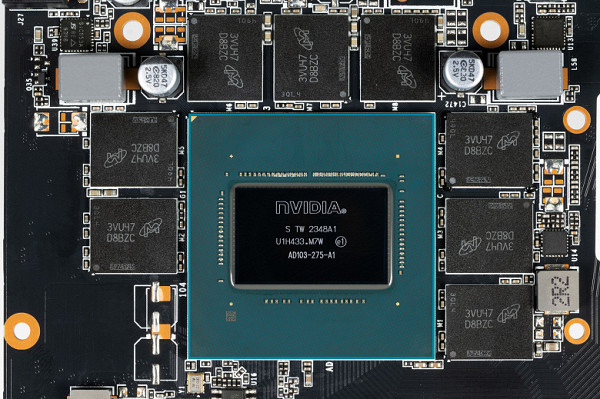
On the right side of the video card we notice installed footprints similar to the 8-pin power connectors. In fact, these places are intended for connecting powerful external fans in systems using professional versions of such video cards. It is worth noting that gaming and professional video cards are often based on the same GPUs, and the differences can only be in the amount of memory, configuration of work units and software.
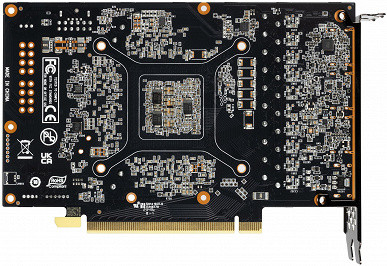
The total number of power phases for both Palit cards is 11 (9+2).
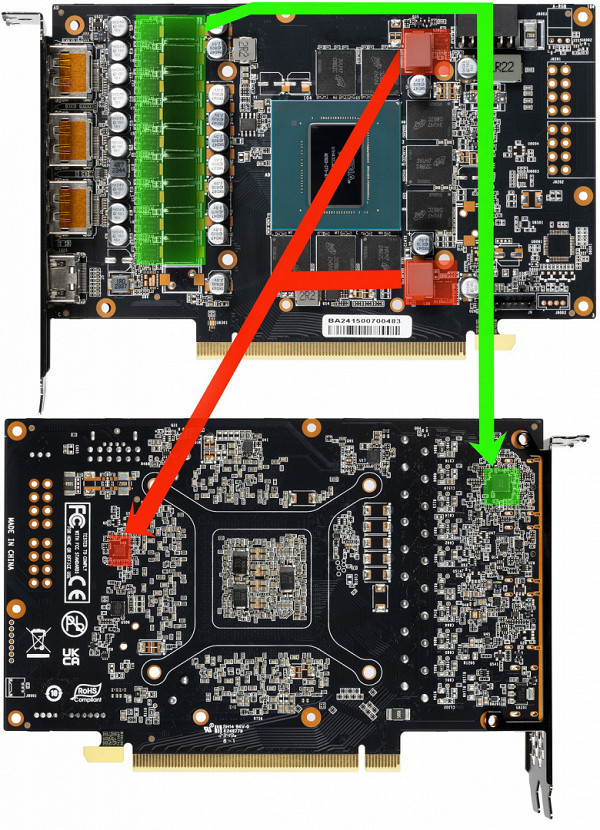
The core power supply circuit is indicated in green, and the memory circuit in red. All pulse width modulation (PWM) controllers are located on the reverse side of the printed circuit board.
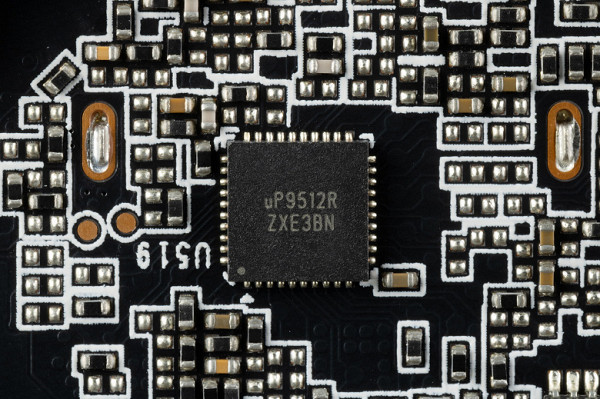
The nine power phases for the core are controlled by the uP9512R PWM controller from uPI Semiconductor, which is capable of providing up to 12 phases.
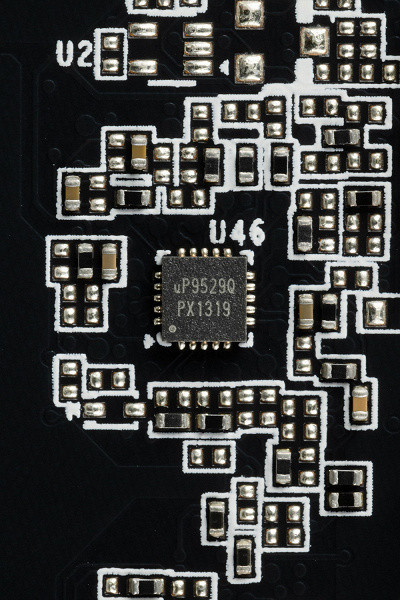
The power supply for the memory chips is controlled by the uP9529Q PWM controller (uPI Semiconductor).
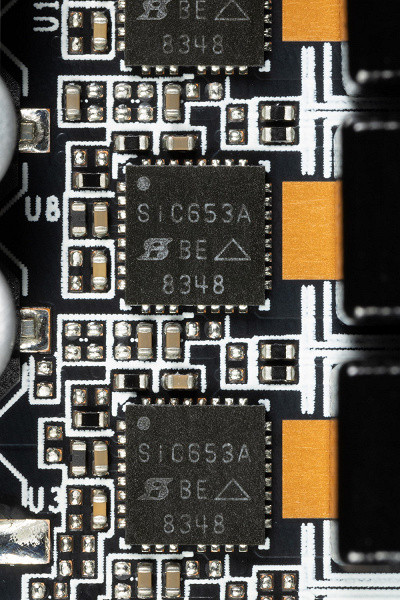
For the power converter, as is customary in Nvidia video cards, DrMOS transistor nodes are used. This example uses SiC653A modules from Vishay Intertechnology, each of which is designed for a maximum current of up to 50 A.
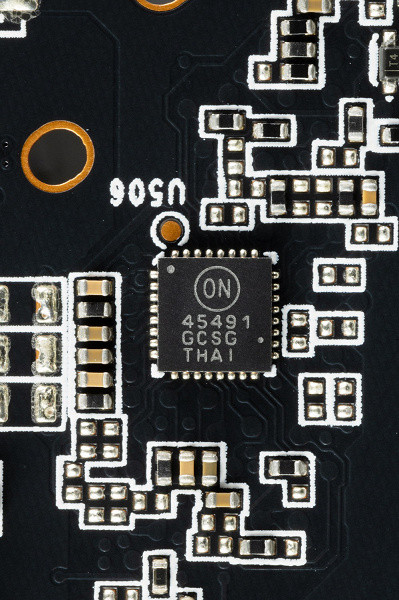
Also on the back of the board there is an NCP45491 (On Semi) controller, which is responsible for monitoring the card (monitoring voltages and temperatures).
There is no built-in backlight on the card, therefore there is no corresponding controller.
Factory memory frequencies coincide with the reference values, the core Boost frequency is slightly higher than the reference value, and the maximum value is slightly lower. The suffix «OC» does not make sense in this case. The performance difference between this stock clocked Palit card and the reference clocked card is only 0.2%, which can be considered negligible.
The power consumption of the Palit card in tests reaches 272 W.
The inability to increase the power consumption limit on this card eliminates the possibility of manual overclocking.
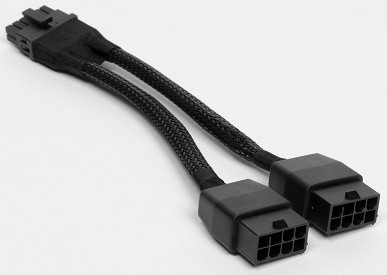
The Palit card is powered via a 16-pin PCIe 5.0 (12VHPWR) connector.
The card is supplied with an adapter for such a connector from two ordinary 8-pin ones (well known to everyone).
Despite the relatively low power consumption and light load on the adapter, it is recommended to use full-fledged power supplies of the ATX 3.0 form factor with a 12VHPWR connector and a cable equipped with 16 pins for connecting new generation video cards.
It is worth noting the significant dimensions of the card, especially its thickness, which is 6.4 cm. As a result, the video card occupies 4 slots in the system unit.

The GeForce RTX 4070 Ti does not support multi-graphics configuration via SLI technology, and also does not have a special connector for this purpose on the top end.
The functionality of the card is controlled using the proprietary Thunder Master utility. The test version from the Palit website (4.14) at the time of testing was not fully compatible with the new Super line, but all operations were performed correctly.

The overclocking panel allows you to adjust card frequencies and also set auto overclocking
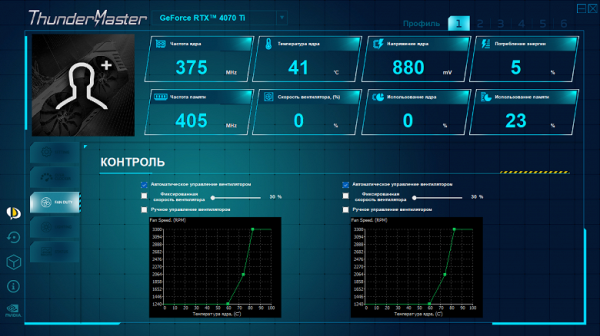
Fan control panel: three fans are divided into 2 blocks (2 outer + 1 central), they can be controlled separately
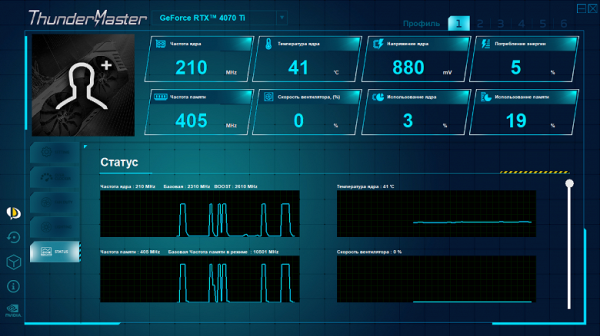
Card Status Dashboard
Heating and cooling
We are seeing the use of a cooler designed around the concept of pass-through airflow through the rear of the heatsink. The basis of the cooling system is a massive multi-section nickel-plated radiator with heat pipes that effectively distribute heat over the entire surface of the radiator.
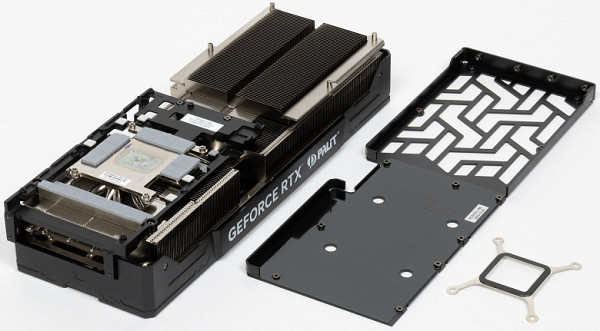
The heat pipes are hard-soldered to a large nickel-plated copper plate, which effectively cools both the graphics core and memory chips (through the use of thermal pads). To effectively cool the VRM power converters, a separate sole is provided, mounted on a massive frame, which is screwed to the radiator (the frame itself also serves as reinforcement for the entire structure).

The back plate functions solely as a protection element for the PCB and is an integral part of the overall design concept.
Above the radiator there is a casing equipped with three fans with a diameter of 100 mm, each of which is equipped with 9 blades and operates at the same speed (default). It is important to note that through the ThunderMaster program you can individually adjust the rotation speed for the central fan and the two outer fans.

The radiator fins are designed using YFormula Fins, which means different angles depending on their location in the radiator. This design optimizes airflow and increases the overall contact area between the air and the radiator fins.

The fans automatically stop when the load on the graphics card is low, provided that the GPU temperature drops below 50 degrees and the memory chip temperature drops below 80 degrees. When the computer starts, the fans begin to function, but after loading the video driver, the operating temperature is monitored, as a result of which they automatically turn off. A video on this topic is available below.
Temperature monitoring:
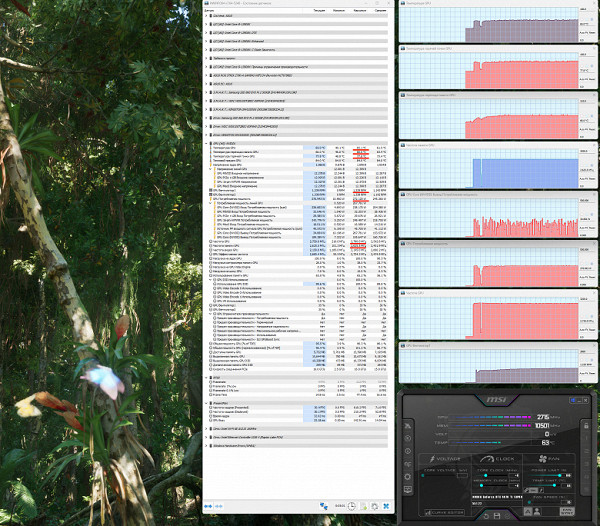
After two hours of testing under maximum load, the core temperature did not exceed 65 degrees, reaching a maximum of 78 °C at the hottest point. The temperature of the memory chips was 68 degrees, which is an excellent result for video cards of this level. The card's power consumption in tests reached 272 W, given that the safe heating limit for GDDR6X memory is 105 °C.
Recording and playback of the 8-minute test, accelerated 50 times, is available in video format.
The maximum heating was observed near the PCIe slot, as well as near the power connector.
Noise
The noise measurement technique used assumes that the room is equipped with sound insulation and sound-absorbing materials, which minimizes reverberation. The system unit, which includes the video card, does not contain fans and is not a source of mechanical noise. The background noise level in the room is 18 dBA, including the level of the sound level meter. Measurements are taken at a distance of 50 cm from the video card, at the level of the cooling system.
Measurement modes:
- Idle mode in 2D: An Internet browser with a website, a Microsoft Word window, and several Internet communicators are loaded.
- 2D mode with movie viewing: Uses SmoothVideo Project (SVP) for hardware decoding with insertion of intermediate frames.
- 3D mode with maximum load on the accelerator: The FurMark test is used.
The noise level rating is as follows:
- Less than 20 dBA: relatively silent.
- 20 to 25 dBA: very quiet.
- From 25 to 30 dBA: quiet.
- From 30 to 35 dBA: clearly audible.
- From 35 to 40 dBA: loud, but tolerable.
- Above 40 dBA: very loud.
In idle mode in 2D, the temperature did not exceed 36°C, the fans were turned off, and the noise level was equal to the background level — 18 dBA.
There were no changes when watching a movie with hardware decoding.
At maximum load in 3D, temperatures reached 65/78/68 °C (core/hot spot/memory). The fans operated at a frequency of 1339 rpm, the noise level increased to 29.4 dBA, which remains within the quiet operating mode.
The noise spectrogram shows a smooth picture without pronounced peaks that can cause irritation.
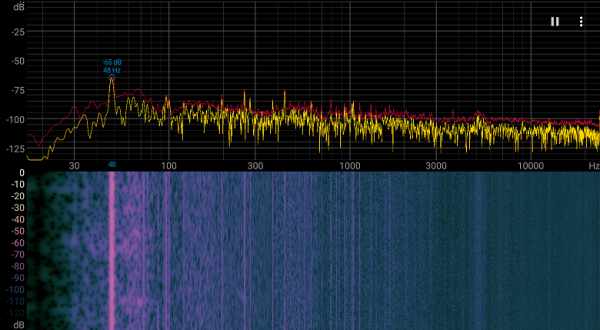
Do not forget that the heat generated by the card remains inside the system unit, so using a case with good ventilation is highly desirable.
Backlight

The map is not backlit.
Delivery and packaging
In addition to the traditional quick start guide, the package includes a power adapter.
Testing: synthetic tests
We tested the updated Nvidia graphics card at standard frequencies in our set of synthetic tests. The test suite is constantly being improved, sometimes new tests are added, and outdated ones are gradually removed. It is important for us to expand and improve the set of synthetic tests, and if you have clear and reasonable suggestions, we will be grateful for your feedback in the comments to the article or in private messages.
We've implemented several additional benchmarks to measure ray tracing performance and use resolution scaling and performance enhancement technologies: DLSS, FSR, and XeSS. We also included several subtests from the popular 3DMark suite in our semi-synthetic tests, such as Time Spy, Port Royal, DX Raytracing, Speed Way and others. However, it was decided to exclude sample DirectX 11 and 12 applications included in various SDKs, as they often gave incorrect results, making the analysis meaningless.
In our synthetic tests we used the following video cards:
- GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super with standard parameters.
- GeForce RTX 4070 Ti with standard parameters.
- GeForce RTX 4080 with standard parameters.
- GeForce RTX 3090 Ti with standard parameters.
- Radeon RX 7900 XTX with standard parameters.
- Radeon RX 7900 XT with standard parameters.
To analyze the performance of the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super model, we compared it with three other video cards from this manufacturer. The RTX 3090 Ti is the flagship model of the previous generation, while the RTX 4080 and RTX 4070 Ti are the base models of the current family. In addition, to determine whether the price of Nvidia’s new product is justified, we took the Radeon RX 7900 XT, which, although it costs a little less, can serve as an analogue in price, and the top-end Radeon RX 7900 XTX. Comparison with these Radeon models will help you understand how competitive the new graphics card is.
3DMark Vantage tests
For many years, we have been closely studying the legacy synthetic benchmarks in 3DMark Vantage because they often provide unique information that is not found in more modern benchmarks. Feature tests of this set support DirectX 10 and remain relatively up-to-date, which allows you to draw useful conclusions when analyzing the results of new video cards.
Feature Test 1: Texture Fill
This test aims to measure the performance of texture fetch units. It involves filling a rectangle with values read from a small texture using multiple texture coordinates that change on each frame.
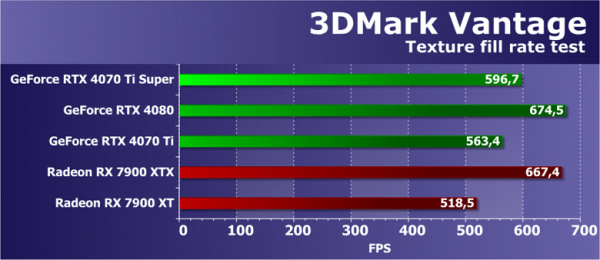
The performance of AMD and Nvidia video cards in the Futuremark texture test usually demonstrates high performance, close to theoretical values. However, sometimes the results may be a little low for some GPUs. In the case of the RTX 4070 Ti Super, which uses a cut-down version of the AD103 GPU compared to the AD104, performance in this test is slightly reduced. The RTX 4070 Ti Super turned out to be closer to the RTX 4070 Ti, superior to the first by only 6% and inferior to the older one by 12%. This slight difference in texturing speed raises some red flags.
Comparison with competitors from AMD shows the advantage of GeForce video cards. Previous generations of AMD graphics cards were stronger in this test, but the effective texturing speed of the new Radeon family has decreased slightly. As a result, Nvidia solutions that are close in price have overtaken and, sometimes, surpassed AMD. The RTX 4070 Ti Super not only outperformed the Radeon RX 7900 XT, but also came close to the flagship XTX, although the latter is more in line with the more powerful RTX 4080.
Feature Test 2: Color Fill
The second test measures color fill rate. It uses a simple pixel shader that is not a performance bottleneck. The interpolated color results are written to an off-screen buffer using alpha blending. The test uses a 16-bit off-screen buffer in the FP16 format, often used in games with HDR rendering, making the test modern and relevant.
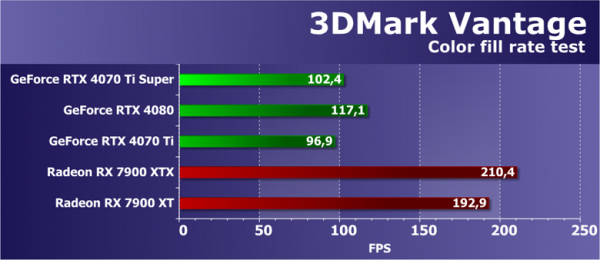
The results of the second subtest of 3DMark Vantage demonstrate the performance of ROP units without taking into account video memory bandwidth. The test measures the effectiveness of the ROP subsystem, while the impact of the memory bandwidth is usually minimal. For the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, the situation is approximately the same as in the previous test, especially when compared with the base model RTX 4070 Ti. In theory, they differ in the speed of the ROP subsystem, but the results are similar. Also, the RTX 4080 shows about the same performance increase as in the previous subtest.
However, all three Nvidia video cards are inferior to two AMD video cards in this test — Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX. The latter outperform all Nvidia solutions in this task by about half. Despite this, GeForce video cards are usually inferior to their competitors in synthetic tests in terms of peak scene fill rate. Therefore, these results may not always translate unambiguously to real-world applications, and similar results in this subtest are not surprising.
Feature Test 3: Parallax Occlusion Mapping
This test is one of the most interesting feature tests, since the Parallax Occlusion Mapping technique has been used in games for a long time. This test maps a single quad (or rather, two triangles) using the Parallax Occlusion Mapping technique to simulate complex geometry. The test involves resource-intensive ray tracing operations and the use of a high-resolution depth map. The surface is also shaded using a heavy Strauss algorithm. This test is a complex test of the GPU, involving multiple texture samples in ray tracing, dynamic branching, and complex Strauss lighting calculations.
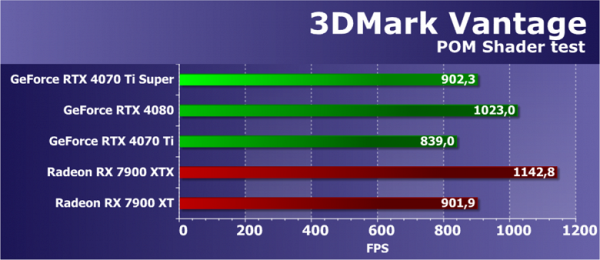
The results of this test from the 3DMark Vantage package depend not only on the speed of mathematical calculations, the efficiency of branch execution and the speed of texture fetches, but also on several parameters simultaneously. The correct balance of the GPU and the efficiency of executing complex shaders is important. This test is a useful benchmark because its results often correlate with performance in gaming tests, more than is the case with some other synthetic benchmarks.
In this case, the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super model showed a result 8% higher than the base RTX 4070 Ti model. This is a bit of a departure from the theoretical difference between the two, given that the new one was supposed to be faster. The RTX 4080, running a more powerful version of the same GPU, also sees a 12% performance boost. However, the new product turns out to be closer to the RTX 4070 Ti than to the RTX 4080. It is also important to compare with competing solutions, such as Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX video cards, where the RTX 4070 Ti Super shows results close to the younger AMD model, comparable in price.
Feature Test 4: GPU Cloth
The fourth test is interesting because it simulates physical interactions (fabric simulation) using the GPU. It uses vertex simulation with a combination of vertex and geometry shaders, as well as multiple passes. Use stream out to pass vertices between simulation passes. Thus, the test evaluates the execution performance of vertex and geometry shaders, as well as the data transfer speed through stream out.
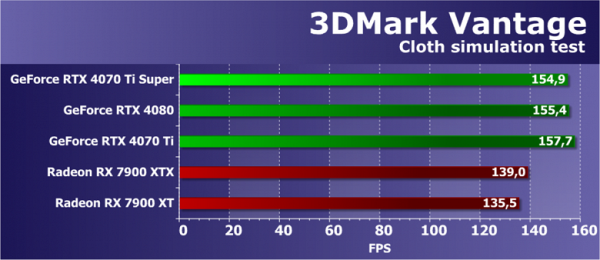
Rendering speed in this test depends on several parameters, primarily geometry processing performance and geometry shader execution efficiency. In the past, the strengths of Nvidia chips should have been evident, but the test has a long history of producing incorrect results. At first, this only affected GeForce, but over time, Radeon graphics cards also encountered this situation. Newer AMD drivers resulted in poor results, and therefore all GPUs show incorrect results in this test, not meeting theoretical expectations in any respect. This is likely due to a lack of driver optimizations for the legacy test suite.
Feature Test 5: GPU Particles
This test presents a physics simulation of effects based on particle systems calculated by the GPU. A vertex simulation is used, where each vertex represents a separate particle. Stream out is also used to transfer data between simulation runs. The test calculates several hundred thousand particles, each one is animated individually, and their collisions with the height map are also taken into account. A geometry shader is used to render particles, creating four vertices from each point to form a particle. The largest load is represented by shader units with vertex calculations, and stream out is also tested.
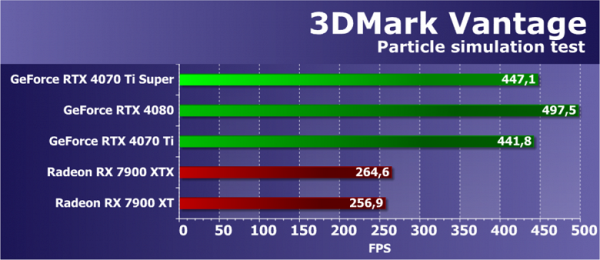
The second geometry test from 3DMark Vantage also shows results that are far from theoretically expected. However, they are closer to reality compared to the previous subtest of this benchmark. If we consider the results correct, then the Super-line video card showed almost the same result as the base Ti model. While the RTX 4080 turned out to be noticeably faster. The Radeon pair, which competes with the video card in question, also loses to Nvidia video cards in this subtest, which is likely due to insufficient optimization of AMD drivers. However, the results as a whole are also questionable.
Feature Test 6: Perlin Noise
The last feature test from Vantage is a mathematically intensive GPU test that calculates several octaves of Perlin noise in a pixel shader. Each color channel uses its own noise function to create additional mathematical load on the video chip. Perlin noise is a standard algorithm widely used in procedural texturing, and it involves a lot of mathematical calculations.
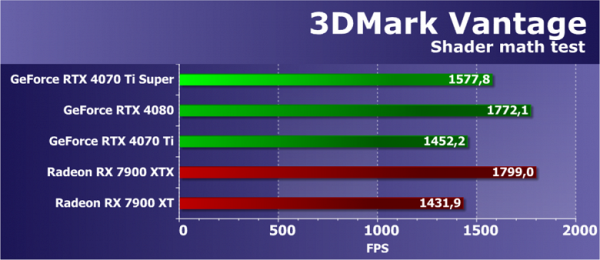
In this mathematical test, the performance of all solutions, although not fully consistent with theory, is usually close to the peak performance of video chips in extreme tasks. The test includes floating point operations, and the new Ada Lovelace and RDNA3 architectures were supposed to reveal some of their unique capabilities in dual execution of the corresponding instructions. However, it should be noted that this test is outdated and is not fully capable of identifying the new capabilities of modern GPUs, as the comparative results suggest.
The middle model of the Super line in the GeForce RTX 40 family demonstrated the expected result, being between the base model and the older version with the same GPU. At the same time, the RTX 4070 Ti outperformed the base model by only 5%, which is again lower than the theoretical difference, and in comparison with the older RTX 4080 model, based on a more powerful chip, the new product lagged behind significantly — by 14%. As for competing Radeon models with similar price positioning, the new Nvidia model showed speeds approximately in the middle between the RX 7900 XT and XTX. In the next section, we'll look at more modern synthetic benchmarks that put more strain on the GPU.
Direct3D 12 tests
We decided to exclude examples from Microsoft's DirectX SDK and from AMD's SDK that use the Direct3D12 graphics API from our tests, since they have long shown incorrect results in most cases. In this section, the only computational test with Direct3D12 support that remains is the well-known Time Spy benchmark from 3DMark. We are interested not only in the general comparison of GPU power, but also in the difference in performance when the asynchronous computing capabilities introduced in DirectX 12 are enabled and disabled. To confirm the accuracy, we tested the video cards in two graphics tests.
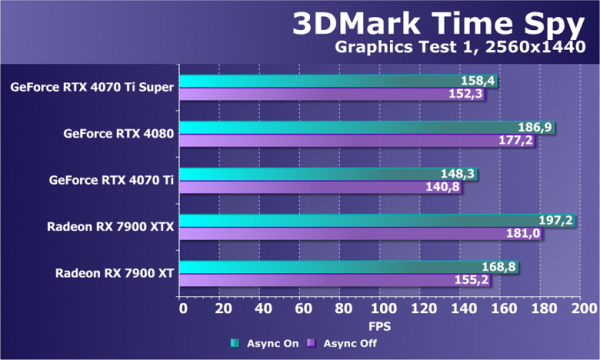
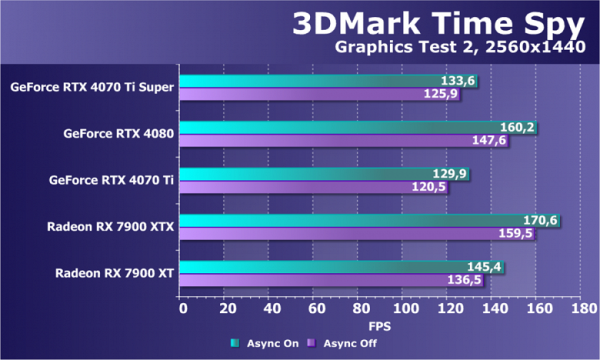
If we look at the performance of the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super in this task compared to the base RTX 4070 Ti video card, it is noticeable that the improved video card was only slightly faster — the increase was 3%-8%. This is significantly lower than the theoretical difference between them. The older RTX 4080 model showed more significant progress, possibly due to differences in maximum power consumption: 320 W for the RTX 4080 versus 285 W for the RTX 4070 Ti Super. It may be because of this limitation that the new model was unable to achieve higher performance.
Radeon video cards in this test usually perform better than competing GeForces in terms of price, but this is not always reflected in actual gaming performance. In this case, the more affordable Radeon RX 7900 XT showed slightly higher performance, which may indicate that AMD solutions may be more effective in rasterization. Next up are ray tracing tests, where GeForce traditionally shows its strength.
Ray tracing tests
One of the earliest tests of ray tracing performance is the Port Royal benchmark from the creators of the famous 3DMark tests. This benchmark is compatible with GPUs that support the DirectX Raytracing API. We tested several graphics cards at 2560x1440 resolution with various settings, including calculating reflections using ray tracing in two modes, as well as the traditional method used for rasterization.
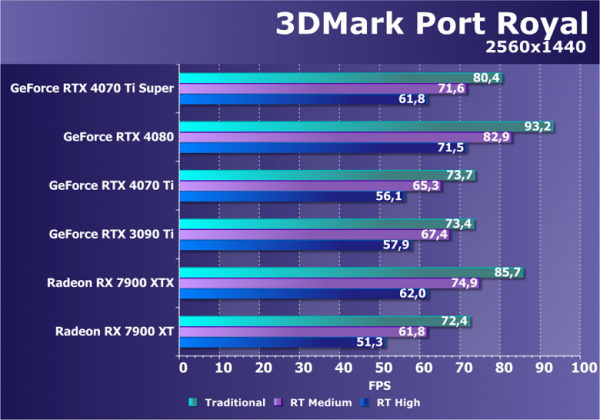
The benchmark only partially demonstrates the basic capabilities of ray tracing through the DXR API, using algorithms for rendering reflections and shadows using the technology. The test is not perfectly optimized and puts a significant load on even powerful GPUs. However, it is suitable for comparative analysis of the performance of different GPUs in the field of ray tracing.
The test results clearly demonstrate the differences in the approaches of AMD and Nvidia to hardware acceleration of ray tracing. Despite some improvement in RDNA3 from AMD, the difference remains noticeable. The RTX 4070 Ti Super is positioned between the RTX 4070 Ti and RTX 4080, approaching the former. An interesting point is a comparison with the previous flagship RTX 3090 Ti, which was inferior to the new product in all modes. AMD's solutions are still lagging behind, but handle ray tracing quite well, especially the flagship RX 7900 XTX, which demonstrates similar performance to the RTX 4070 Ti Super in this test. Comparatively, the RX 7900 XT lags, as expected.
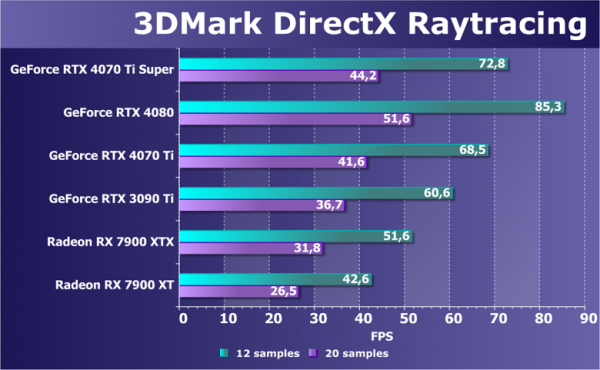
In this ray tracing test, the hardware support level is especially important. GeForce demonstrates high efficiency thanks to dedicated RT cores, which do much of the work and remain more versatile. When ray tracing is enabled, Nvidia generally remains noticeably faster with these RT cores compared to competitor AMD's Ray Accelerator cores and regular SIMD cores. However, in real games, where the load on the RT units is less, the difference may be less pronounced, and the Radeons are not so inferior.
The new RTX 4070 Ti Super showed a slight increase in performance compared to the base RTX 4070 Ti model, only about 6%, which was lower than preliminary expectations. The RTX 4080 demonstrated noticeably higher performance. The older RTX 3090 Ti lagged behind new solutions, highlighting progress in technology. AMD video cards, in turn, were significantly inferior to the RTX 4070 Ti Super, especially the older Radeon model. In synthetic tests of this kind, the results may not fully correspond to real-world conditions, for example in games where ray tracing is used more effectively.
With the release of new generations of GPUs in 2022, another test has been added to the 3DMark suite called Speed Way, which represents a more realistic ray tracing load similar to those heavily used in modern games. This test is interesting for a more accurate assessment of GPU performance under active ray tracing conditions.
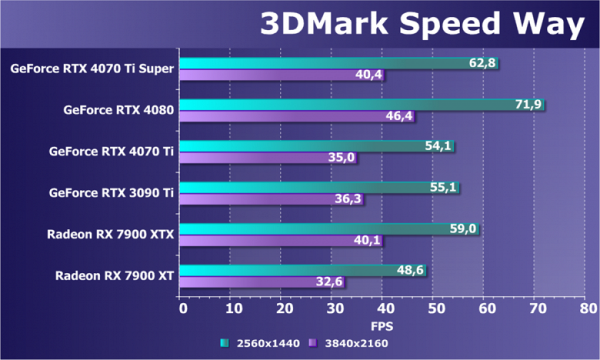
The selected resolutions in the tests showed acceptable frame rates only for the most powerful GPUs. The difference between Radeon and GeForce video cards has noticeably decreased, while AMD models are not so much inferior to their competitors in price. The RTX 4070 Ti Super sits midway between the base RTX 4070 Ti and the higher-end RTX 4080 in the test, with the RTX 4080 coming out ahead by a small margin. It's interesting to note that the RTX 3090 Ti is ahead of the RTX 4070 Ti in this test, but the new model outperforms both cards. It is important that not only the Radeon RX 7900 XT, but also the RX 7900 XTX are slightly inferior to the RTX 4070 Ti Super, even at a higher resolution.
Let's look at another benchmark on a real game engine. Boundary, a Chinese project with support for DXR and DLSS technologies, provides a test with a serious load on the GPU. This benchmark makes heavy use of ray tracing for complex reflections, soft shadows and global illumination. Please note that DLSS technologies cannot be used in tests with Radeon.
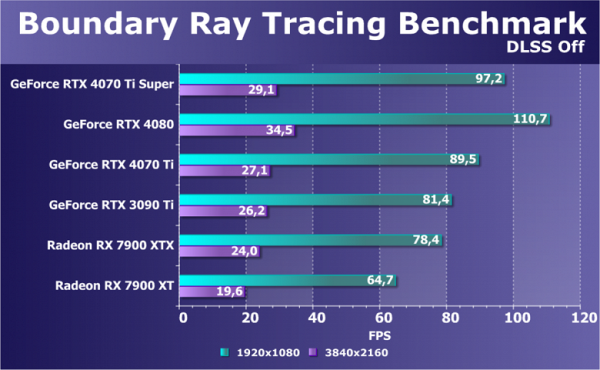
4K resolution turned out to be unplayable without scaling enabled on all video cards reviewed. Even in Full HD resolution without using DLSS technology, only sufficiently powerful GPUs show acceptable performance. In this scenario, even the top-end graphics card from AMD is inferior to all GeForce graphics cards, including the base RTX 4070 Ti and the previous top-end RTX 3090 Ti. The Nvidia graphics card we're reviewing today is only slightly ahead of the base model RTX 4070 Ti and noticeably inferior to the RTX 4080. However, the RTX 3090 Ti is again ahead by a margin.
The speed performance of Radeon video cards again emphasizes that AMD solutions are not able to keep up with Nvidia GPUs in ray tracing tests. In such tasks, the RTX 4070 Ti Super is significantly ahead of even the most powerful Radeon RX 7900 XTX, not to mention a competitor that is closer in price.
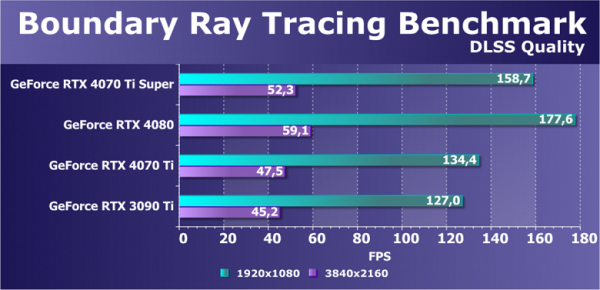
With resolution scaling enabled via DLSS, even the flagship RTX 30 series graphics card is able to provide sufficient frame rates for 4K gaming, although even the GeForce RTX 4080 does not reach 60 FPS. The new RTX 4070 Ti Super boasts a more than 10% performance increase over the RTX 4070 Ti, allowing you to enjoy gaming even at 4K resolution, despite Nvidia recommending a 2560x1440 resolution for this graphics card. The RTX 4080, although slightly faster than the new product, is already outdated and has been discontinued, giving way to the RTX 4080 Super.
Let's look at another benchmark written on a Chinese game — Bright Memory. It is interesting to note that both tests show similar results and image quality, despite the differences in subject matter. However, this benchmark turns out to be more demanding, especially in terms of ray tracing performance. Unfortunately, it does not work on AMD graphics cards, requiring specifically an Nvidia GeForce RTX card.
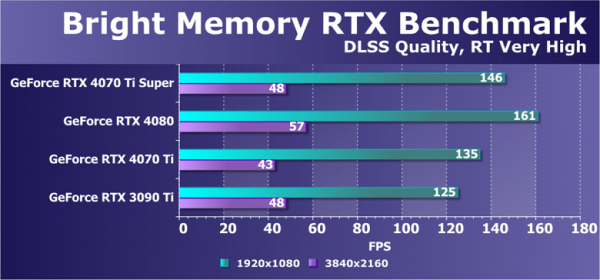
In this test, the updated Ti Super model, based on a stripped-down version of the AD103 GPU, scores between the base RTX 4070 Ti and the more powerful RTX 4080. This is a slight change from previous data. However, the RTX 3090 Ti also performs very well in this test, especially at high resolutions. What is important here are the parameters of memory bandwidth (surface area per second) and the amount of video memory, which are usually cut down in modern video cards. The RTX 4070 Ti Super adds 8% to 10% over the RTX 4070 Ti and outperforms the RTX 3090 Ti at low resolutions while delivering identical results at 4K — which represents a very high level of performance.
Computational tests
We continue our research to find benchmarks that use OpenCL to solve modern computing problems. Our goal is to include them as part of our synthetic test suite. At the moment, this section presents a rather old and unoptimized ray tracing test (not hardware) — LuxMark 3.1. This cross-platform oriented test is based on LuxRender and uses OpenCL.
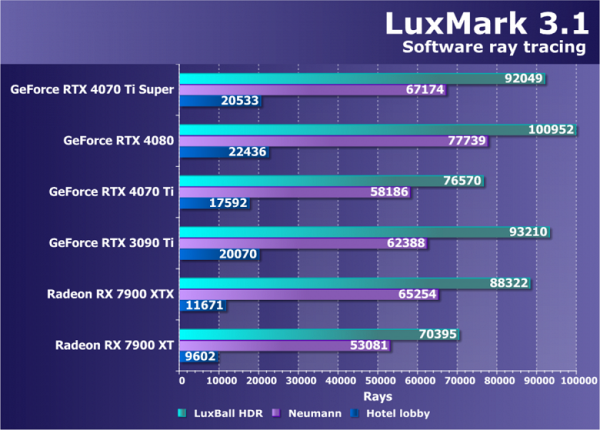
The new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super model, built on the basis of a stripped-down version of the AD103, has a significant number of computing units. Unsurprisingly, it significantly outperformed the base model RTX 4070 Ti, although the difference between the two is again lower than expected according to theory. All modern GPUs are limited by the power consumption limit, which for the new product does not exceed the level of the RTX 4070 Ti. As for the older model of the RTX 4080 graphics card, its higher power consumption limit also contributes to higher performance. However, the RTX 4070 Ti Super is confidently ahead of even the once flagship RTX 3090 Ti. AMD graphics cards historically do not perform their best in this test, and even the Radeon RX 7900 XTX is inferior to the new Super model from Nvidia in question.
Let's consider another test of the computing performance of GPUs — V-Ray Benchmark. This non-hardware-accelerated ray tracing test reveals the potential of the GPU in complex calculations and can demonstrate the benefits of new graphics cards. Previously, we used different versions of the benchmark, providing results in the form of time spent on rendering and the number of millions of paths rendered per second. However, in our current tests, only the first version, which measures rendering time, remained.
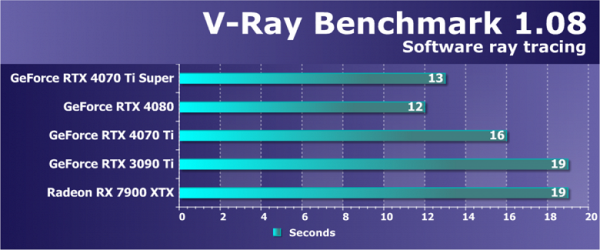
This test, also based on software ray tracing calculations, revealed that the new GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super is not only significantly ahead of the RTX 3090 Ti and the base RTX 4070 Ti, but is also approaching the performance level of the RTX 4080. Power consumption is likely a factor here. The GPU does not reach its maximum limit, and the cache and main video memory have a significant impact, as we previously noted. It is extremely important that even the flagship AMD Radeon graphics card lags far behind.
Let's move on to another rendering application — OctaneRender. This popular renderer supports CUDA and RTX technologies, and the OctaneRender 2020.1.5 version now supports the Ampere architecture. In the OctaneRender-based benchmark, you can disable RTX acceleration and test performance in several scenes with different loads. Unfortunately, this test does not support OpenCL. Here is the total number of points:
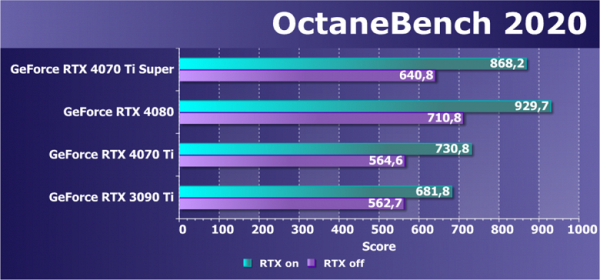
The updated GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super continues to demonstrate its excellent performance, outperforming even the previous flagship representative of the line. This is an expected result, especially with RTX hardware acceleration enabled, which significantly improves results using the Ada Lovelace architecture. In compute performance tests, the new RTX 4070 Ti Super performs closer to the RTX 4080 than the RTX 4070 Ti, with a noticeable advantage of 13% to 18%. Here the difference is most likely not due to power consumption limitations, but is probably due to different video memory bandwidth, which is noticeably higher in the new product than in the base RTX 4070 Ti. This could also be one of the reasons for the proximity to the RTX 4080.
A new version of the popular 3D rendering benchmark, Cinebench 2024 from Maxon, has recently been released. This benchmark provides an opportunity to evaluate the computing capabilities of both the processor and the video card, using complex algorithms and scenes adapted from the Cinema 4D program and the Redshift rendering engine. Test results can be compared with each other.
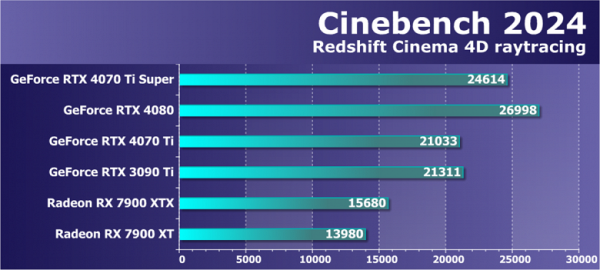
In the latest software ray tracing test, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super continues to demonstrate its outstanding performance, outperforming the base RTX 4070 Ti by a notable 17%. Even the more powerful RTX 4080 model, which left the market, is not significantly ahead of the new product. It's important to note that the previous flagship, the RTX 3090 Ti, was only able to beat the RTX 4070 Ti, but not the new RTX 4070 Ti Super.
Even more significantly, competing Radeon graphics cards showed noticeably lower results. The increased instruction rate of the new RDNA3 graphics architecture did not show up as expected in this test, and overall performance increased only slightly, remaining far from theoretically expected. The junior Radeon model is almost twice as slow, and the flagship Radeon has a significant speed gap over the RTX 4070 Ti Super.
Tests of DLSS/XeSS/FSR technologies
In this section, we conduct additional tests focused on performance-enhancing technologies. Initially, this only applied to resolution scaling technologies (DLSS 1.x and 2.x, FSR 1.0 and 2.0, XeSS). Later, they were added to the technology for generating intermediate frames — DLSS 3, and then version 3.5 with ray reconstruction using ray tracing.
We started by including DLSS benchmarks in our materials, although we have previously experimented with this technology in applications that use ray tracing. We came to the conclusion that conducting separate tests in this direction would be useful. The results of testing multiple GPUs at 4K resolution using various DLSS quality levels, including frame generation (denoted as FG), are presented in the chart.
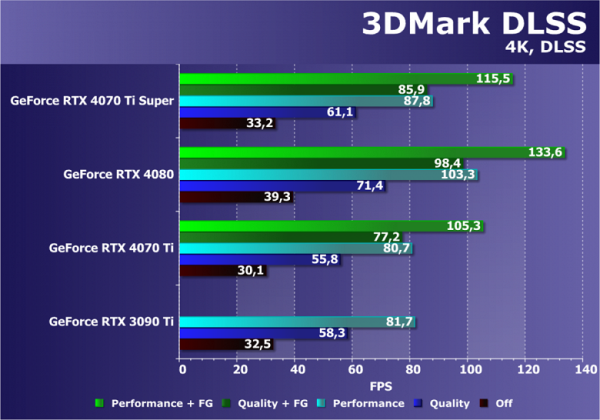
Without DLSS enabled, video cards rendered images at full resolution, which significantly reduced overall performance, bringing frame rates to 30-40 FPS in 4K resolution — a value insufficient for a comfortable gaming experience. However, when activating DLSS at the maximum performance level, the frame rate became more than sufficient, even for the top model of the previous generation RTX 3090 Ti, which does not have support for generating additional frames. The RTX 4070 Ti Super model in question demonstrated strong performance, exceeding the level of the RTX 3090 Ti without frame generation and noticeably ahead of it when it was turned on.
One of the strong competitive advantages of modern Nvidia video cards is support for DLSS 3.0 technology in the Ada Lovelace graphics architecture. This technology combines the functionality of DLSS 2.x with the generation of intermediate frames, which allows you to improve the smoothness of the video sequence with a slight increase in control latency. Enabling the generation of intermediate frames brings an increase in FPS by another factor of one and a half. Thus, with DLSS support, video cards can use higher rendering resolutions, improving performance in modes without and with frame generation.
XeSS is another performance technology offered by Intel that also uses lower resolution rendering and image scaling. This method, like DLSS 2.0, uses artificial intelligence to restore detail in the frame. A distinctive feature of XeSS is its compatibility with all modern GPUs, although efficiency on Intel cards may be higher. For testing, a specialized benchmark from the 3DMark package was used.
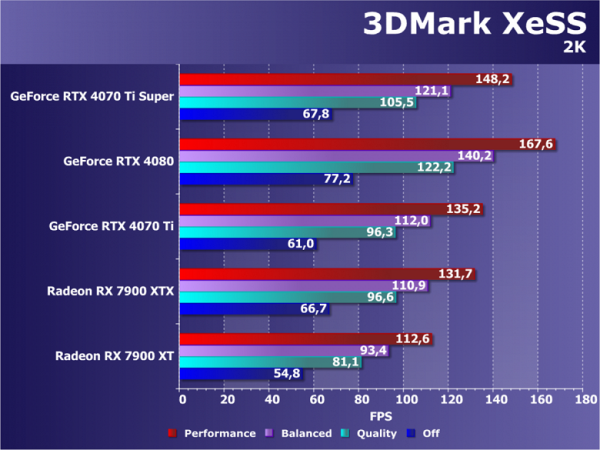
The inclusion of XeSS technology significantly increased the frame rate, reaching a level of two or more times. Due to its versatility, this technology deserves attention, given the presence of its own methods and accelerating blocks in each of the three companies. However, each technology has its drawbacks: DLSS, although the most advanced, works exclusively on Nvidia products; FSR, the most universal, is less advanced and does not use specialized blocks; XeSS, while versatile, lags behind DLSS in both quality and functionality.
In this test, the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super model, although it performs noticeably more efficiently than the base RTX 4070 Ti, which meets expectations, is closer to it than to the older RTX 4080. However, what is especially surprising and even striking is the ineffective performance of the Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX video cards. These AMD graphics cards are significantly inferior in this test, as the RTX 4070 Ti Super beats even Nvidia's more expensive flagship model. Perhaps the scene characteristics better match Nvidia's solutions.
Another member of the family of rendering scaling technologies is FSR 2.0 from AMD. For some reason, this particular technology became the last in the list of 3DMark subtests. Unfortunately, scenes using different scaling methods are mostly different, making direct comparisons difficult. We can only judge by performance gains, taking into account rendering resolution and quality differences, which is difficult to compare directly.
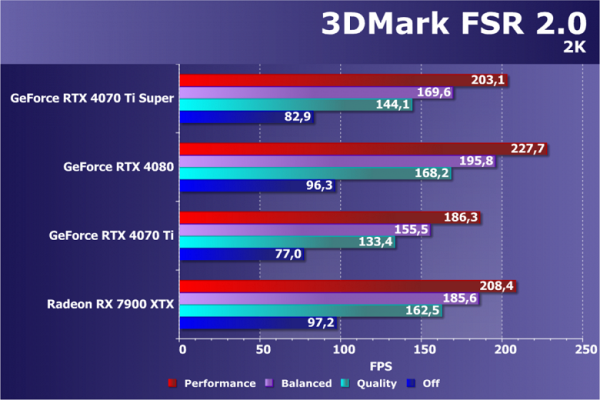
FSR is another generic technology that performs roughly the same on different GPUs, and there's nothing special to be found in the FSR 2.0 benchmarks. The Radeon RX 7900 XTX is much stronger, but it costs significantly more than the RTX 4070 Ti Super, which makes it more comparable to the GeForce RTX 4080 Super. Today's RTX 4070 Ti Super, while clearly inferior to AMD's top-end graphics cards, should outperform its closest competitor, the RX 7900 XT, especially in tests with FSR technology enabled. Now let's move on to gaming tests of the new Nvidia graphics card to assess how much the RTX 4070 Ti Super beats the base model without the «Super» suffix in real-world conditions, and not just in synthetic tests.
Testing: gaming tests
Test bench configuration
- Computer based on Intel Core i9-13900K processor (Socket LGA1700) :
- Platform:
- Intel Core i9-13900K processor (overclocked to 5.4 GHz on all cores);
- ЖСО Cougar Helor 360;
- Asus ROG Strix Z790-A Gaming WiFi D4 motherboard based on the Intel Z790 chipset;
- RAM TeamGroup Xtreem ARGB White (TF13D416G5333HC22ADC01, CL22-32-32-52) 32 GB (2×16) DDR4 5333 MHz;
- SSD Intel 760p NVMe 1 TB PCIe;
- SSD Intel 860p NVMe 2 TB PCIe;
- ThermalTake Toughpower GF3 1000W power supply ;
- Thermaltake Level20 XT case;
- operating system Windows 11 Pro 64-bit;
- TV LG 55Nano956 (55″ 8K HDR, HDMI 2.1);
- AMD drivers version 24.1.1;
- Nvidia drivers version 551.22;
- Intel drivers version 101.5125;
- VSync is disabled.
- Platform:
List of testing tools
All gaming tests used the maximum graphics quality in the settings.
- Marvel's Spider-Man Miles Morales (Insomniac Games/Sony Interactive)
- Cyberpunk 2077 (Softclub/CD Projekt RED), patch 2.01 (September 2023)
- God of War (Sony IE/Sony IE)
- Call of Duty: Modern Warfare II (Infinity Ward/Activision)
- Alan Wake 2 (Remedy/Epic Games)
- Ratchet and Clank: Rift Apart (Insomniac Games/Sony/Softclub)
- A Plague Tale: Requiem (Asobo Studio/Focus Entertainment)
- Hogwarts Legacy (Avalance Software/Warner Bros)
- Avatar: Frontiers of Pandora (Ubisoft)
- Atomic Heart (Mundfish/VK)
3D gaming performance in a nutshell
Before we provide more detailed tests, we will provide a brief performance assessment for this family of video cards, including the model in question, as well as its competitors. Our assessment is subjective and based on a scale of seven gradations.
Games without ray tracing (using classic rasterization technology):
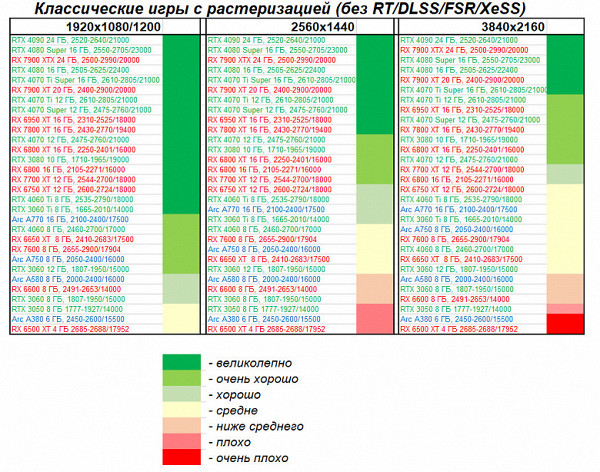
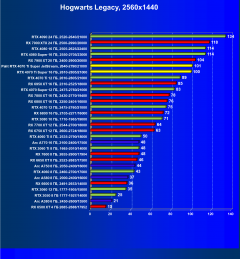
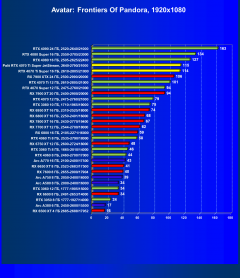
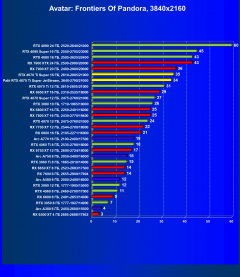
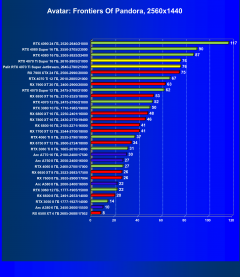
In many scenarios with 2K, 2.5K and even 4K resolutions in classic games, overall performance is often limited not only by the graphics card, but also by other system components, mainly the CPU. This also applies to the Palit graphics card in question (as well as all other cards based on the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super). With this card you can achieve complete comfort in games at any of the mentioned resolutions, even at maximum graphics settings (excluding RT and/or DLSS/FSR/XeSS).
Games using ray tracing and DLSS/FSR/XeSS technologies:
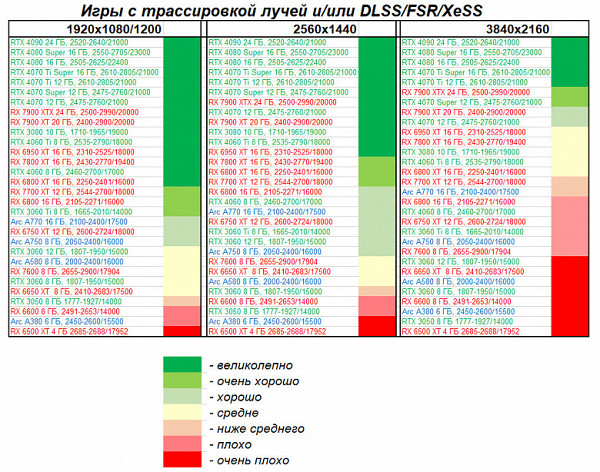
Enabling Ray Tracing (RT) reduces overall performance, but Nvidia's DLSS and AMD's FSR technologies (as well as Intel's XeSS), already widely used in many games, go a long way toward compensating for this performance hit. Thus, for powerful video cards such as the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super, all previous ratings remain valid. At the same time, even the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti (without the “Super” suffix) is ahead of AMD’s latest generation flagship, the Radeon RX 7900 XTX.

Test results in 3D games
Standard test results without hardware ray tracing at 1920x1080, 2560x1440, and 3840x2160 resolutions
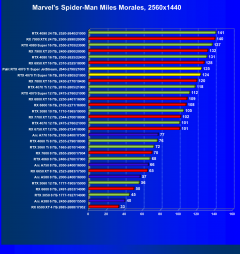
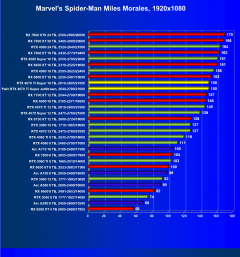
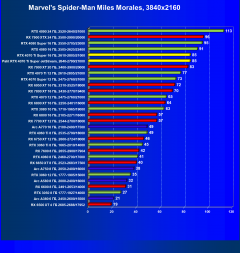
Marvel’s Spider-Man Miles Morales
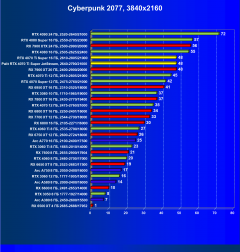
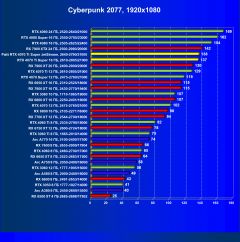
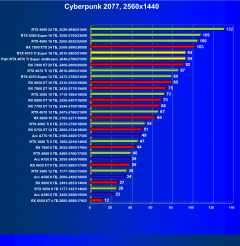
Cyberpunk 2077 2.01
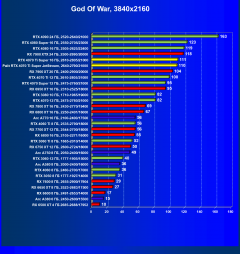
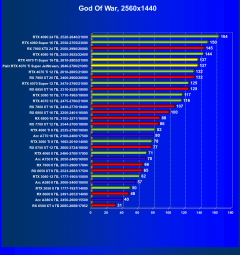
God of War
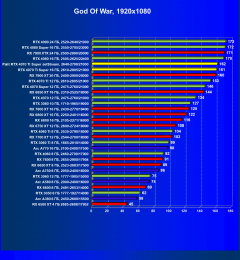
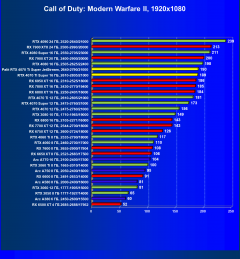
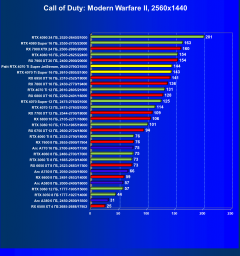
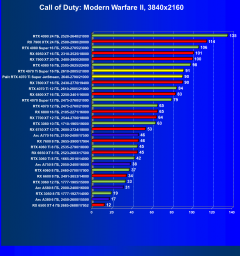
Call of Duty: Modern Warfare II
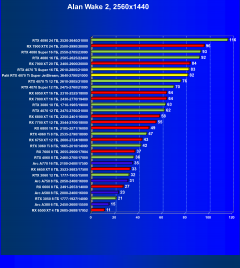
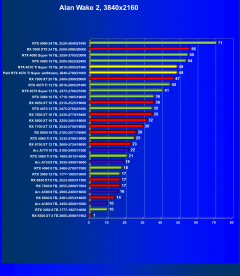
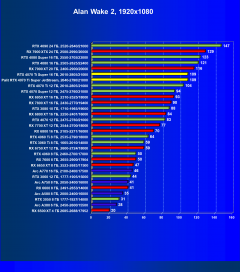
Alan Wake 2
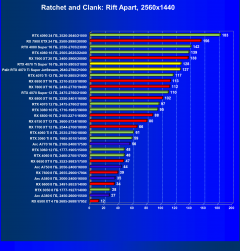
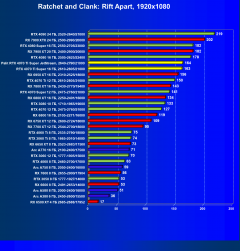
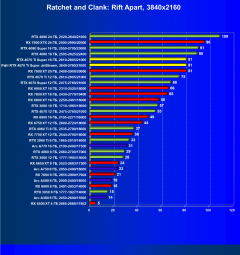
Ratchet and Clank: Rift Apart
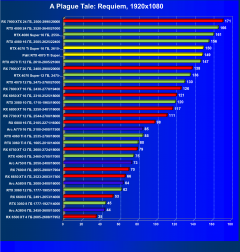
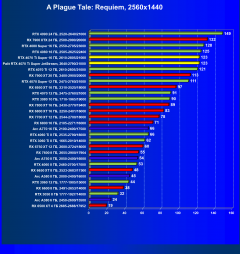
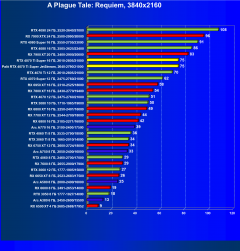
A Plague Tale: Requiem
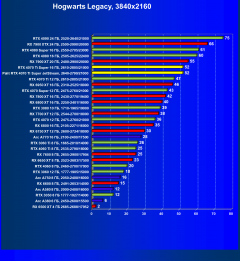
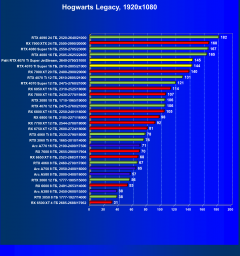
Hogwarts Legacy
Avatar: Frontiers of Pandora
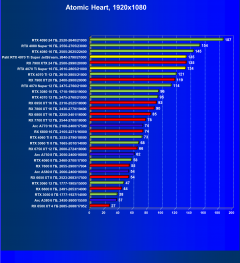
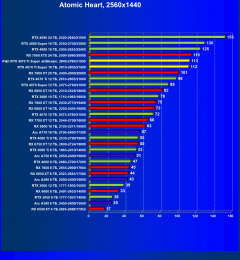
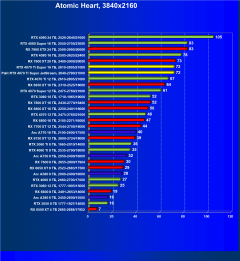
Atomic Heart
Conclusions and comparison of energy efficiency
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super (16GB) — Currently ranked fourth in performance among Nvidia's flagship gaming graphics cards. At higher positions are the GeForce RTX 4080, GeForce RTX 4080 Super and GeForce RTX 4090. However, given the withdrawal from the market of the GeForce RTX 4080 model (which the GeForce RTX 4080 Super replaces), the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super will soon take its place in the top three fastest gaming accelerators .
Its performance is somewhere between the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti and GeForce RTX 4080. Its main goal is to fill the gap between the new GeForce RTX 4070 Super and GeForce RTX 4080 Super models after they are released from the market