Among the Thunderobot gaming laptops (from the Chinese manufacturer Haier) that we tested, there are various models — from budget ones for budget users to advanced ones with the most modern processors and video cards that match the high price.
One of these relatively expensive, but not excessively expensive laptops is the Thunderobot Gravity 16 Max, which we will review.
Configuration and equipment
The following configuration is tested:
| Thunderbot Gravity 16 Max | ||
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i9-14900HX (8+16 cores/32 threads, 2.2-5.8/1.6-4.1 GHz, 45-55/157 W) | |
| RAM | 32 (2x16) GB DDR5-5600 (2 × Samsung M425AR2GA3BB0-CWMOD) both SO-DIMM slots occupied | |
| Video subsystem | discrete Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop (8GB GDDR6, claimed up to 140W), integrated Intel UHD Graphics (32EU) | |
| Screen | 16 inches, 2560×1600, IPS (BOE NE160QDM-NZ3), 240 Hz | |
| Sound subsystem | Realtek, 2 speakers | |
| Storage device | SSD 1 TB SSSTC CL6-8D1024, M.2 2280, NVMe, PCIe 4.0 x4 there is a free slot for a second SSD M.2 2280 | |
| Cartographer | No | |
| Network interfaces | Wired network | Realtek PCIe GbE 10/100/1000 Mbps |
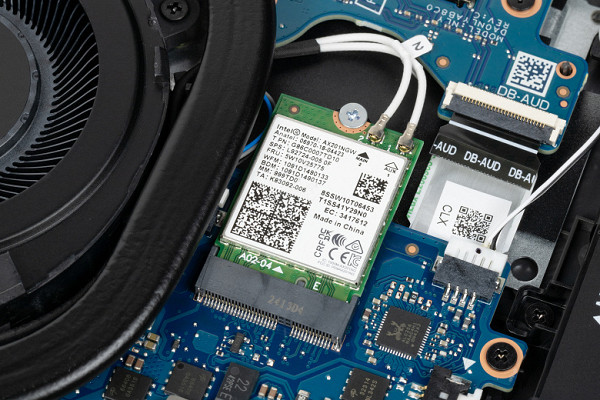
| Wireless Wi-Fi network | Wi-Fi 6 (Intel AX201NGW IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax, 2.4 and 5.0 GHz, MIMO 2×2, channel width 160 MHz) | |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.2 | |
| Interfaces and ports | USB | 1×USB3 Type-C (supporting Power Delivery 140W and video output) 2×USB3 Gen2 Type-A 1×USB3 Gen1 Type-A |
| RJ-45 | There is | |
| Video outputs | 1 × HDMI 2.1 1 × DisplayPort over USB Type-C | |
| Audio connectors | minijack | |
| Input Devices | Keyboard | with digital block and backlight |
| Touchpad | clickpad | |
| IP telephony | Webcam | 720p@30fps |
| Microphone | there are two) | |
| Fingerprint's scanner | No | |
| Battery | 63 Wh Lithium-Ion | |
| Dimensions | 358×267×37.8 mm (excluding legs: up to 32 mm) | |
| Weight without power supply | 2.7 kg | |
| Power adapter | 230 W (20 V, 11.5 A), weight 0.72 kg (with cables) | |
| operating system | Windows 11 Pro 23H2 | |
| Estimated cost | $2330 |
The product is packed in two cardboard boxes (one inside the other for better safety), the carrying handle is only on the inner one.
The laptop comes with a power supply unit with a replaceable input cable and a fixed output cable (1.7 m, with a Velcro fastener), a set of screws for attaching an additional storage device, which is a nice bonus, as well as printed materials in Russian.

Appearance and ergonomics
The case design, by the standards of gaming laptops, is rather strict: graphite-gray surfaces and a minimum of decorative elements, including an unobtrusive relief pattern, an illuminated logo on the top cover and two triangular raspberry-colored inserts on the rear end.
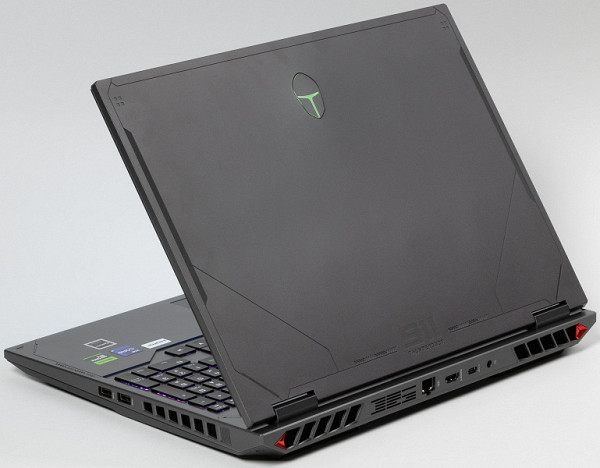

Although the description on the official website states that the case is made of «plastic and metal», the outer panels are made of plastic with a matte texture and slight roughness. There are small bevels on the end edges, and the corners are slightly rounded.
The design is not particularly rigid: the top panel of the case bends slightly under moderate pressure, and the torsional strength of the lid with the LCD screen is low.
Our measurements coincide with the officially declared length and width, but the thickness is different: the declared 24 mm corresponds only to the bevel of the front edge (actually 24.5 mm), and with the foot next to it — 30.5 mm. At the thickest point, closer to the rear end, the caliper shows 32 mm, and the rear foot increases it to 37.8 mm. Even for gaming laptops, this is quite a lot.
The black plastic frame around the screen is not too wide: 5.6 mm on the sides, 9.5 mm on top (where the webcam with an indicator, but without a curtain, and microphones are located), and 18.5 mm at the bottom to the hinge.

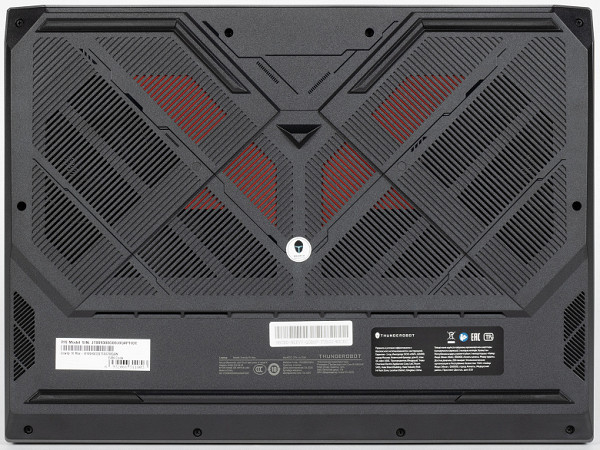
On the bottom, in addition to the legs (one in the front almost along the entire length and two curved ones at the back), there is a large lattice area closer to the rear edge. Air is drawn through this area to cool the components, so it is not recommended to place the laptop on a soft surface.

On the right and left sides of the back of the case, as well as on the side edges, there are grilles through which the ventilation system throws out heated air. The lower part of the screen does not heat up, since the screen is slightly extended forward relative to the back edge of the case.
The lid with the screen opens at an angle of up to 125-130 degrees and is accurately fixed in any position, starting from about 35 degrees. When closed, the fixation is slightly worse, since holding magnets are not provided.

The hinges are noticeable, but the lid can be opened with one hand without having to hold the bottom. You can hook it with your finger anywhere, as there are no special protrusions or cutouts for this.

The interface connectors are located on three sides.
On the back side there is a power connector with a charging indicator, USB3 Type-C ports (with support for Power Delivery and video output), HDMI and a full-size RJ-45. The specification on the website mentions «Mini DP 1.4», but there is no such connector. Probably, this means video output via USB Type-C, which makes the mention of a specific «Mini» connector unclear.

On the left is a USB3 Gen1 Type-A port and a «minijack» for an audio headset.

On the right side there are two USB3 Gen2 Type-A ports.

Both the set of ports and their placement are quite reasonable: at the back are those to which cables are usually connected permanently or for a long time. However, as for USB ports, three Type-A are enough, but one Type-C is not enough, and its location at the back is not always convenient. It would be better if another Type-C port was located on the left or right. Thunderbolt support would also be very desirable, since its absence is forgivable for inexpensive laptops, but not for this model.
There is no card reader or fingerprint scanner.
The keyboard is a membrane type with an island arrangement of keys and a full-fledged numeric block. The indents on the edges are small, only 12 mm.
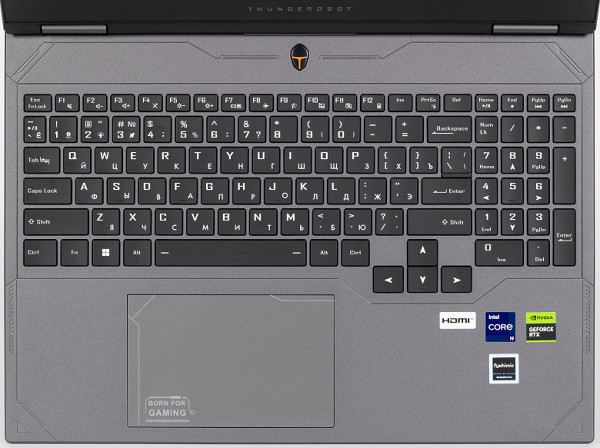

Most of the keys are the standard laptop size of 16 x 15.5 mm, the function keys are slightly smaller (13.7 x 9.9 mm). Both Shift keys are wide, and the Enter key is slightly smaller. All four arrow keys are an enlarged size of 17.5 x 15.5 mm, which is not so common.
The four-row numeric keypad has slightly smaller keys — 12.7 mm.
Typing is comfortable, and the sounds are quiet. Although the pressing force is a little high, you quickly get used to it. The full key travel is about 1.5-1.6 mm.
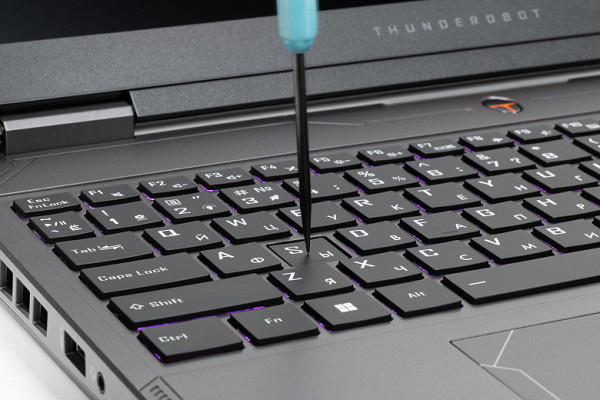

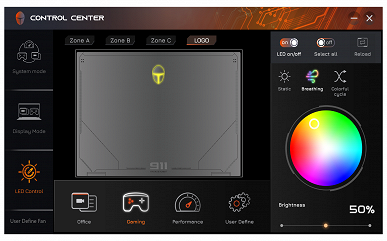
The laptop is equipped with RGB backlighting, which can be turned on and off, as well as switched between two brightness levels using the Fn combination and the button with the number two, which has a light bulb on it. Both the symbols (including Cyrillic) and the edges of the keys are illuminated. To select the color, you will need to install a proprietary utility (details below). There is no automatic backlight shutdown after a period of inactivity.

The logo on the outer surface of the lid with the screen also has a backlight. However, the person sitting at the laptop does not see it, and it is not accessible to others in all placement options.
The Power button is located behind the keyboard, closer to the screen, and is equipped with a built-in indicator. It is installed flush with the surface, which virtually eliminates accidental pressing, although in a semi-dark room it is difficult to notice when the laptop is turned off.

As already mentioned, the webcam is located above the screen. The camera resolution corresponds to budget laptops — 720p@30 fps. There is no shutter, only a key combination is provided for quick switching off.

The touchpad measures 125×80 mm and is almost not recessed into the case. There are no dedicated keys, but the left and right edges of the touchpad can function as the corresponding mouse buttons. There were no special complaints about its operation, but if necessary, it can be turned off and on again using a key combination.

Now about the design features.
To remove the bottom cover, you need to remove 11 screws, one of which is covered with a sticker. The company's representatives previously assured that if necessary, for example, to install a second SSD, the cover can be removed without negative consequences for the warranty.
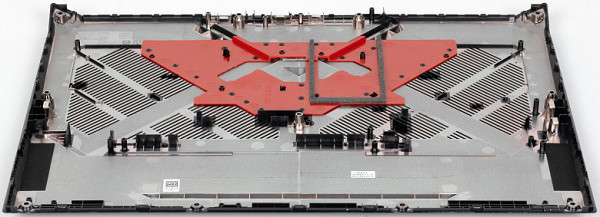
The most space inside the laptop is taken up by the system board with coolers, the rest is reserved for the battery, on the sides of which are the speakers.
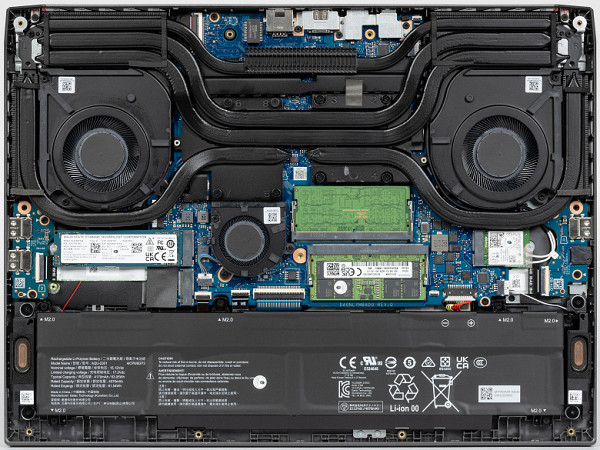

The board is covered with a flexible plate; if you remove it, the slots for SO-DIMM modules, the drive in the M.2 slot, and a free slot for a second similar SSD will become clearly visible (and easily accessible).
Another M.2 slot is equipped with a wireless communication module.

Software
Our laptop had nothing installed other than the operating system (the Recovery section of the disk contains only a «clean» OS, so it is possible that all additional materials were lost during reinstallation). At the time of testing, only the user manual could be downloaded from the «Support» page of the official website.

By the time the review was published, the page had been updated: drivers and the Control Center utility, familiar to us from other Thunderobot laptops, had appeared. It is extremely important to install it, since many useful functions remain unavailable without it.
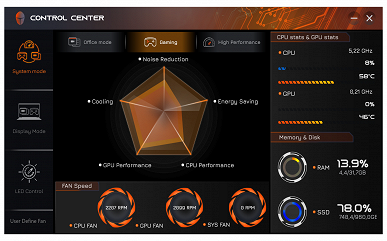
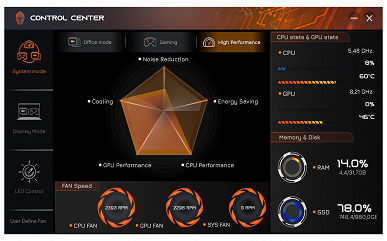
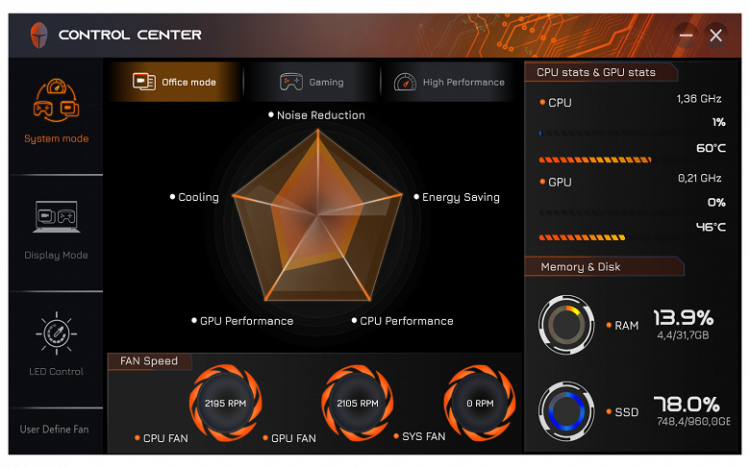
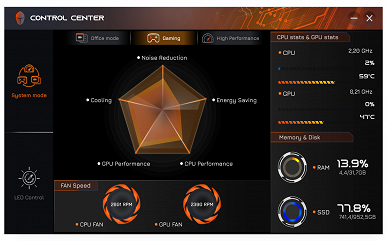
The Control Center utility (published by Leishen, judging by the name of the installation folder, but there is no information about this in the utility itself) implements basic monitoring functions, including displaying fan speeds (which is not available in other utilities, such as AIDA64). You can also choose one of three performance profiles: «Office mode», «Gaming» or «High Performance».
The change in fan status is displayed with a noticeable delay of up to 10-15 seconds. The minimum speeds for the CPU and GPU fans are around 2000 rpm, and the maximum (when pressing the Fn + 1 combination) reaches approximately 4800 rpm. The third fan, called the system fan (Sys Fan), varies in speed from zero to 6000 rpm.
You can set up custom profiles for the fans, specifying curves for the rotation speed (as a percentage of the maximum) versus the temperature (in degrees Celsius) separately for the CPU, GPU and Sys. These settings can be saved for later use.
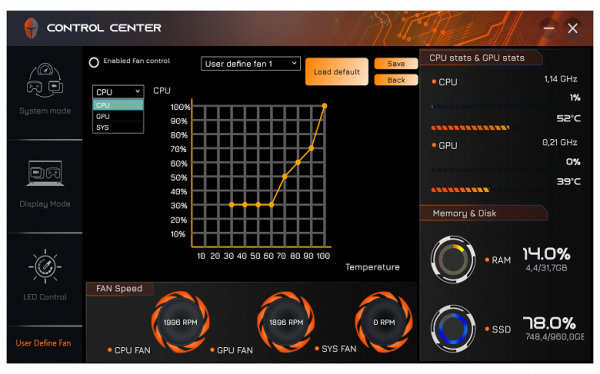
Just remember to put a «dot» in the upper left in the «Enabled Fan control» field, but then comes the following warning:
An important setting for selecting a video card is also available — discrete, integrated or hybrid mode (automatic selection depending on the needs of the application).
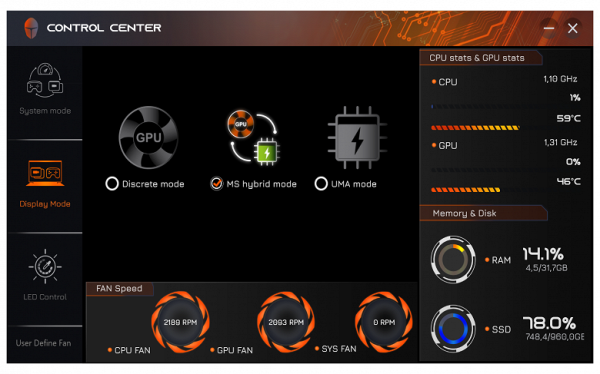
Changing the video card settings requires rebooting the laptop (with a request to do so).
Note that there are no external signs of using the selected video adapter, such as changing the color of the indicator on the Power button.
In addition, the Control Center utility allows you to control the RGB backlight, including three keyboard zones and the logo on the lid. You can choose colors, brightness, and various effects.
The Control Center utility does not provide general settings, such as changing the interface language or enabling autostart, which happens by default. However, changes to performance profiles and video modes are saved.
It is important to note that versions of Control Center downloaded from the Internet may not fully match the configuration of the laptop. For example, some versions do not have control over video cards, only two fans are displayed instead of three, and there is control over the backlight of elements that are not actually on this device.
Screen
The laptop uses a 16-inch IPS matrix with a resolution of 2560×1600 pixels

The matrix surface is black, hard and semi-matte with a pronounced mirror effect. There are no special anti-glare coatings or filters, and there is no air gap between the matrix and the glass. When powered from the mains or battery and manually adjusting the brightness (there is no automatic adjustment), the maximum brightness was 512 cd / m² in the center of the screen on a white background. This value allows you to comfortably use the laptop outdoors in sunny weather, provided that you avoid direct sunlight.
To assess the readability of the screen outdoors, the following criteria are used, based on testing screens in real conditions:
| Maximum brightness, cd/m² | Conditions | Readability assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Matte, semi-matte and glossy screens without anti-glare coating | ||
| 150 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | unreadable |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | barely readable | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work | |
| 300 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | barely readable |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | work comfortably | |
| 450 | Direct sunlight (more than 20,000 lux) | it's uncomfortable to work |
| Light shade (approx. 10,000 lux) | work comfortably | |
| Light shade and light clouds (no more than 7500 lux) | work comfortably |
These criteria are rather arbitrary and may be revised as more data is accumulated. Improved screen readability may be observed if the matrix has transreflective properties, in which part of the light is reflected from the substrate, allowing the image to be seen even when the backlight is off. Glossy matrices can sometimes be turned so that they reflect something dark and uniform (for example, the sky on a clear day), which improves readability, while matte matrices require protection from direct light to increase visibility. In rooms with bright artificial lighting (about 500 lux), working with the screen is possible even at a brightness below 50 cd / m², so in such conditions, the maximum brightness is not so critical.
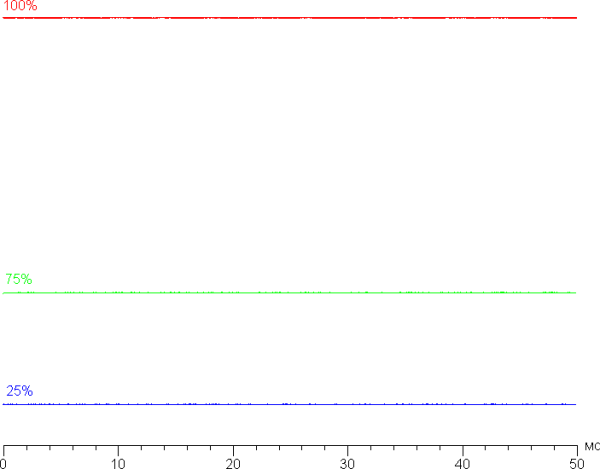
As for the tested laptop, when setting the brightness to 0%, the brightness decreases to 30 cd / m², which allows you to achieve a comfortable level in complete darkness. At any brightness level, there is no significant backlight modulation (PWM), which eliminates screen flickering. This is confirmed by the graphs of the dependence of brightness (vertically) on time (horizontally) at different brightness settings:
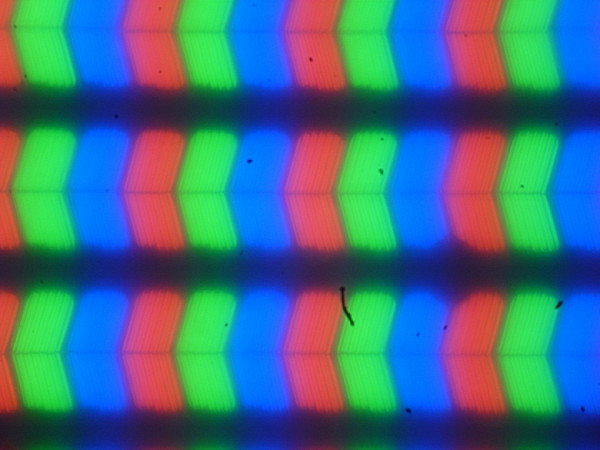
This laptop uses an IPS matrix. Microphotographs demonstrate the typical IPS subpixel structure (the black dots are dust on the camera matrix):
Focusing on the screen surface revealed randomly located microdefects on the surface, which are actually responsible for the matte properties:
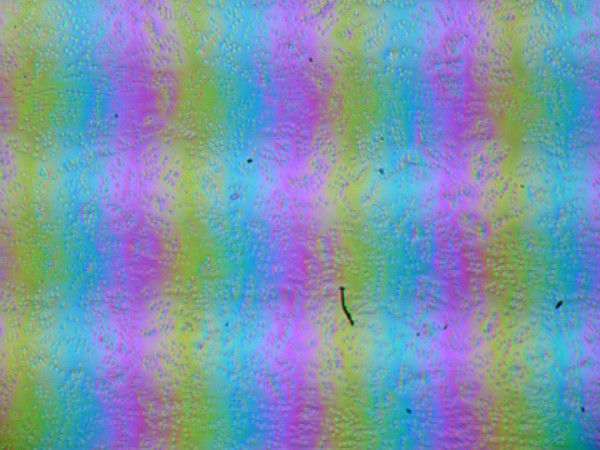
The grain size of defects is several times smaller than subpixels (the scale of the photographs is approximately the same), which makes microdefects and focus «jumping» across subpixels less noticeable, eliminating the «crystal» effect.
We measured the brightness at 25 screen points located at a step of 1/6 of the width and height of the screen (screen borders are not included). Contrast was calculated as the ratio of the brightness of the fields at these points.
| Parameter | Average | Deviation from the mean | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min., % | max., % | ||
| Black field brightness | 0.37 cd/m² | −12 | 12 |
| Brightness of white field | 500 cd/m² | −8,3 | 5,2 |
| Contrast | 1370:1 | −8,0 | 5,6 |
If you step back from the edges, the uniformity of all three parameters is good. The contrast is above the typical level for such matrices. The black field in places, especially closer to the edge, is slightly lightened, but this is noticeable only in very dark scenes and in complete darkness, which is not a significant drawback. The rigidity of the lid is not great, it is deformed with a slight application of force, which can affect the illumination of the black field.
The screen provides good viewing angles without significant color distortion even at large deviations from the perpendicular and without inverting shades. However, the black field is strongly lightened at diagonal deviation, but does not acquire a pronounced shade.
The response time for the black-white-black transition is 10 ms (5 ms on + 5 ms off), and the transition between gray halftones in total (from shade to shade and back) takes an average of 14 ms. The matrix is fast, but there is no obvious acceleration.
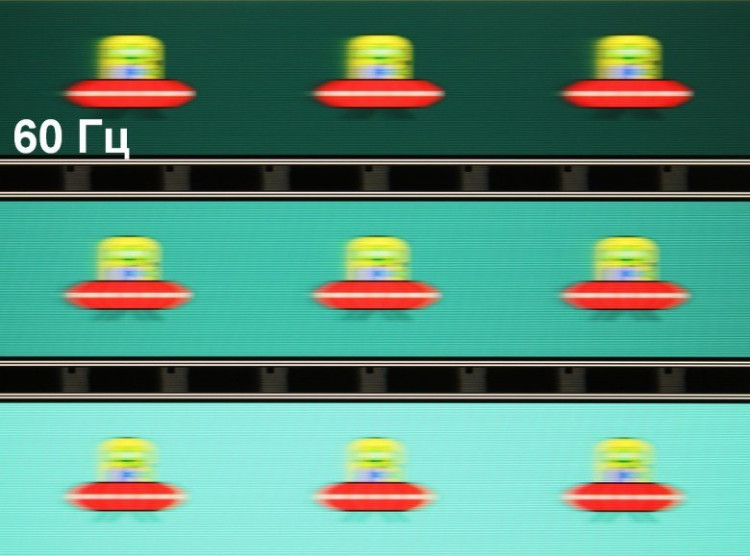
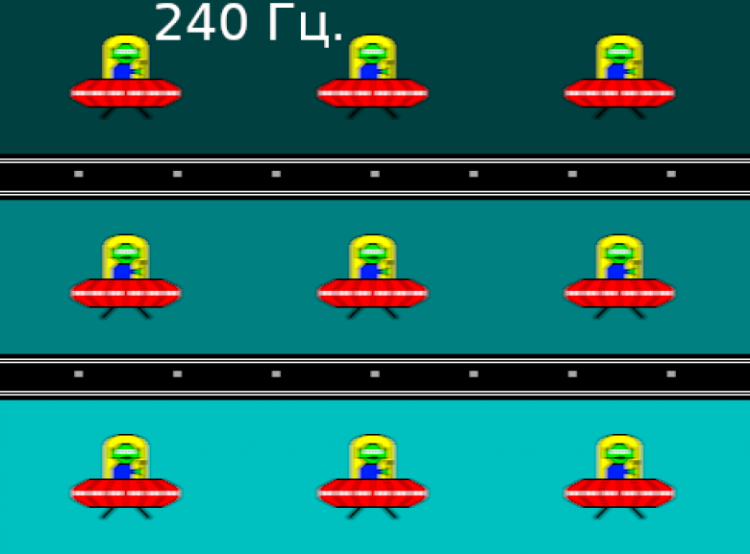
Let's check if this matrix speed is enough to display an image with a frequency of 240 Hz. Here is a graph of the dependence of brightness on time when alternating white and black frames at 240 Hz and 120 Hz.
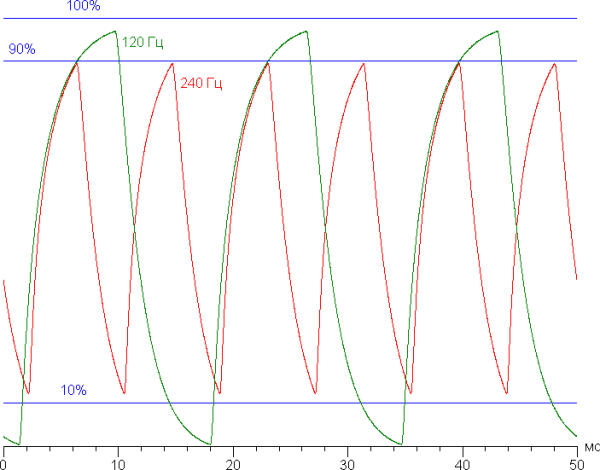
At 240 Hz, the maximum brightness of a white frame is less than 90% of the white level, and the minimum brightness of a black frame exceeds 10% of the black level. The resulting brightness amplitude is less than 80% of white. Thus, according to this formal criterion, the matrix speed is insufficient for full image output at 240 Hz. At 120 Hz, the amplitude already exceeds 80%, which makes 120 Hz quite workable.
To illustrate the practical consequences of such a matrix speed and possible acceleration artifacts, we will provide a series of photos taken with a moving camera. These photos demonstrate what a person sees when following a moving object on the screen with his eyes. The recommended parameters were used: movement speed of 960 pixels/s, shutter speed of 1/15 s. The refresh rate values are indicated in the photos.
It is clear that, all other things being equal, image clarity improves with increasing refresh rate, and artifacts are not observed.
Now imagine that we have a matrix with instant pixel switching. For such a matrix, at 60 Hz, an object moving at a speed of 960 pixels/s is blurred by 16 pixels, and at 240 Hz — by 4 pixels. Blurring occurs because the focus of vision moves at the specified speed, and the object is displayed on the screen for 1/60 or 1/240 of a second. For clarity, we will simulate a blur of 16 and 4 pixels.
The clarity of the real image is noticeably lower compared to the ideal matrix.
We measured the total output delay from switching the video buffer pages to the start of displaying the image on the screen. At a refresh rate of 240 Hz, the delay is 3 ms. This is a very small delay, which is not noticeable in normal work on a PC and does not affect the performance in dynamic games.
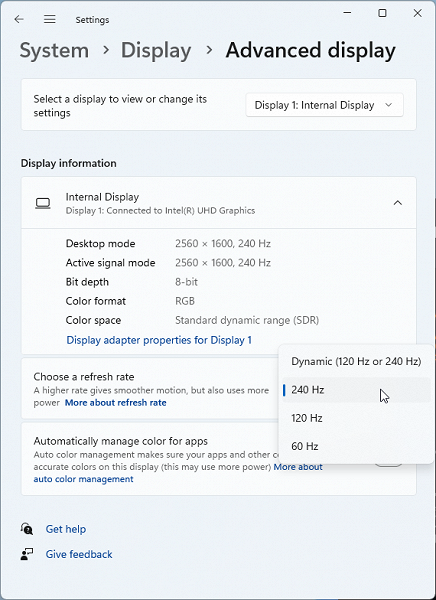
In the screen settings, three refresh rates are available: 60, 120 and 240 Hz, as well as automatic selection between 120 and 240 Hz.
The old design panel has more frequencies — 60, 75, 100, 120 and 240 Hz:
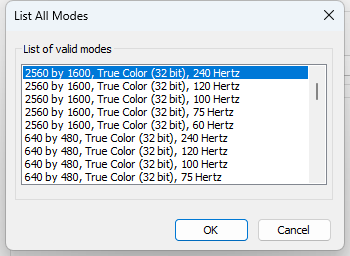
According to the EDID information, the screen supports refresh rates in the range of 60 to 240 Hz. Based on the data from the integrated video adapter control panel, it is also clear that the screen supports Adaptive Sync in the same range.
The output is done with a color depth of 8 bits per color.
Next, we measured the brightness of 256 shades of gray, from 0, 0, 0 to 255, 255, 255. The graph below shows the increase in brightness between adjacent halftones (not the absolute value!).
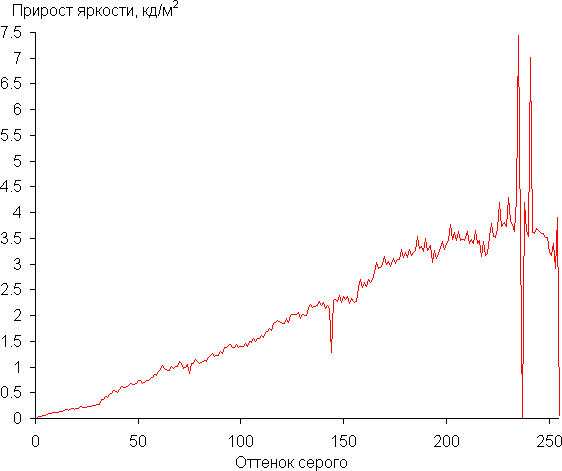
The increase in brightness on the gray scale is mostly uniform, with each subsequent shade being brighter than the previous one, with the exception of two pairs of shades in the bright areas. However, this does not affect the overall picture. In the darkest areas, shades are differentiated both by hardware and visually, which is excellent for a gaming laptop.
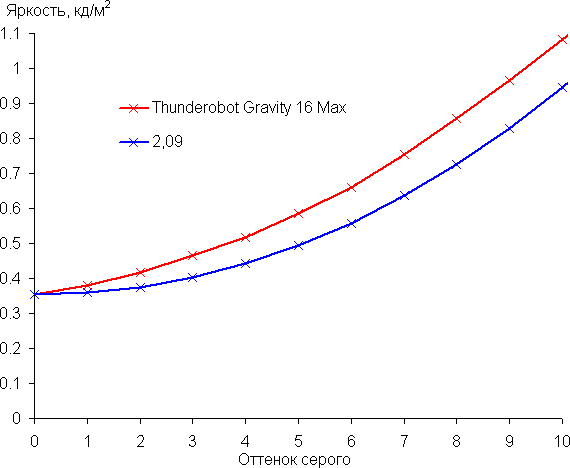
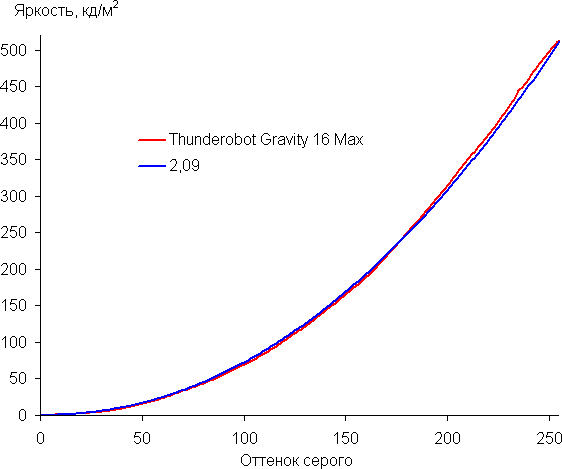
The gamma curve approximation showed a value of 2.09, which is slightly lower than the standard 2.2, so the image is slightly brightened. The real gamma curve also deviates slightly from the approximating power function.
The color gamut is close to sRGB:
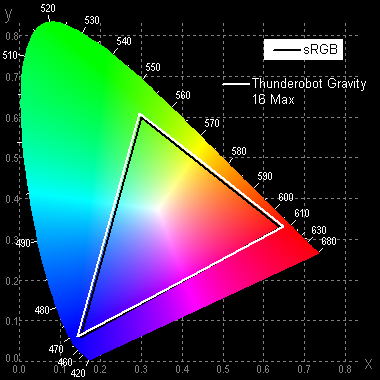
Therefore, the colors of images intended for the sRGB space appear naturally saturated on this screen. Below is the spectrum of the white field (white line) superimposed on the spectra of the red, green and blue fields (lines of the corresponding colors).
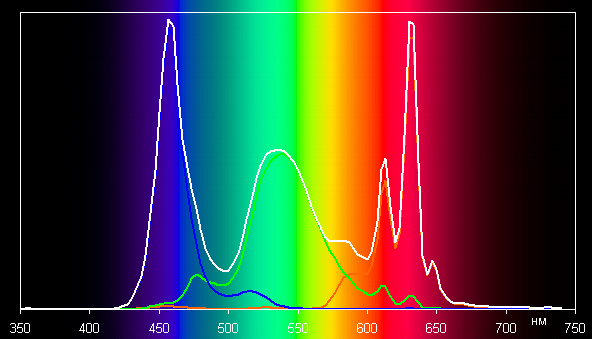
This display appears to use blue LEDs and phosphors for green and red (blue emitter and yellow phosphor are common). This solution provides good separation of components, and the red phosphor probably uses quantum dots. However, cross-mixing of components with color filters reduces the coverage to sRGB.
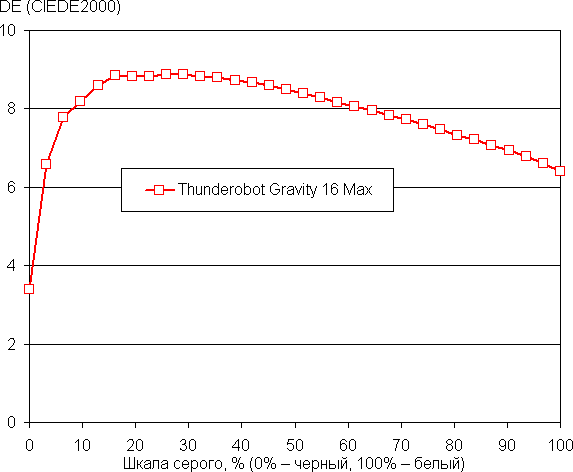
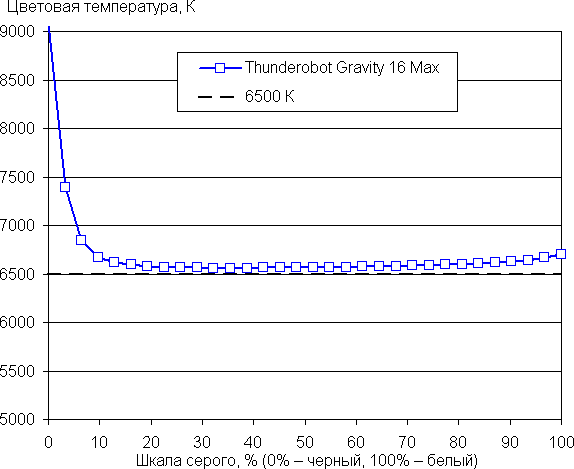
The grayscale balance is good: the color temperature is close to the standard 6500 K, and the deviation from the black body spectrum (ΔE) is below 10, which is considered acceptable for consumer devices. The color temperature and ΔE remain stable from shade to shade, which has a positive effect on the visual assessment of the color balance. The darkest areas of the grayscale can be ignored, since the color balance is less important there, and the measurement error at low brightness is large.
Let's sum it up. The laptop screen provides high maximum brightness (512 cd/m²), which allows you to comfortably use it outdoors during daylight hours, if you avoid direct sunlight. In complete darkness, the brightness can be reduced to a comfortable level (up to 30 cd/m²). The positive aspects of the screen include a high refresh rate (240 Hz), a fast matrix, low output lag (3 ms) and good color balance. The main drawback is the low stability of black color when deviating your gaze from the perpendicular to the screen. Overall, the screen quality is high, which justifies its use in gaming laptops.
Sound
The notebook's audio system uses the Realtek codec and consists of two speakers located on the sides of the bottom panel. Sound is transmitted through reflection from the surface on which the notebook is installed, which is a common solution for such devices.
The volume is subjectively average, but sufficient for individual use.
Battery operation
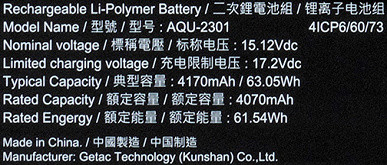
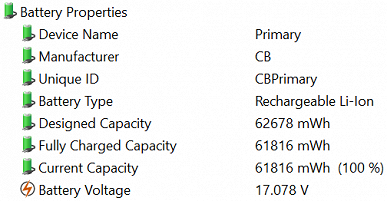
The declared battery capacity is 63 Wh, the same value is indicated on the battery itself, which is also confirmed by utilities.
We will evaluate the battery life using the Battery Benchmark v1.0 script, setting the screen brightness to 100 cd/m² (which corresponds to about 43% of the scale in Windows settings) to avoid the advantage of laptops with brighter screens.
In the Control Center utility, we select the Office mode profile, since when running on battery power, there is an automatic switch to this profile, and it is not possible to select another one.
| Load scenario | Operating time discharge from 100% to 1% |
|---|---|
| Keyboard backlight off, logo backlight on, video cards in hybrid mode | |
| Work with text | 4 h 37 min |
| Watch video | 2 hours 47 minutes. |
| Keyboard and logo backlighting is on maximum, video cards in hybrid mode | |
| Work with text | 3 h 35 min |
| Watch video | 2 h 29 min |
| Keyboard and logo backlight off, discrete graphics card | |
| Work with text | 2 h 33 min |
| Watch video | 1 hour 48 min. |
Enabling the keyboard backlight significantly reduces battery life when working in office applications, but has a lesser impact when watching videos. Battery life is reduced even more when forcibly using the discrete graphics card, which affects both scenarios.
While gaming laptops usually have short battery life, compared to other models in the same class, the Gravity 16 Max shows particularly poor results, almost reaching an anti-record, despite the presence of competitors with smaller battery capacities.
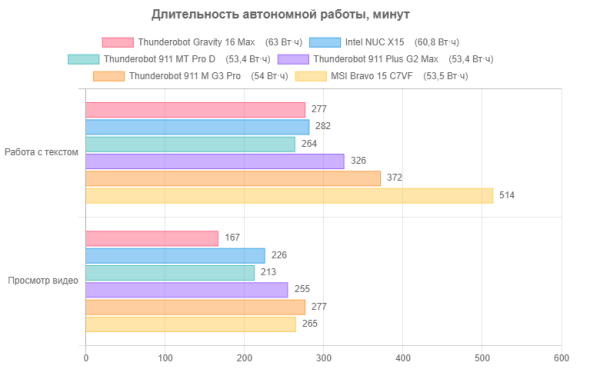
Now let's test the charge from the standard power supply after automatic shutdown at a level of 1%, in the table we provide the readings of the corresponding Windows equipment (the OS was loaded on the laptop):
| Charge level | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 95% | 100% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time, h:mm | 0:16 | 0:25 | 0:33 | 0:42 | 0:50 | 0:59 | 1:08 | 1:23 | 1:36 | 2:14 |
According to measurements, the battery of this capacity charges at the expected speed: 80% of the charge was reached in just over an hour, and after half an hour the indicator reached 95%. As usual, the last five percent of the charge took much longer — almost forty minutes, as a result of which a full charge took two hours and a quarter.
The ability to power from any adapter supporting Power Delivery technology is also declared, while consumption is said to be up to 140 W. We do not have such a powerful charger, so we had to make do with a 100-watt one, with which we tested the battery charge in a switched-off laptop.
| Time, h:mm | Start | 0:20 | 1:00 | 1:10 | 1:20 | 1:30 | 1:45 | 1:55 | 2:05 | 2:14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charging current, A | 2,25 | 2,38 | 2,55 | 2,1 | 1,2 | 0,83 | 0,48 | 0,33 | 0,22 | 0,01-0,02 |
At the beginning of charging, the current gradually increased, but did not reach values close to three amperes, which we observed in other laptops in similar tests. Then a rapid decline began, and after two and a quarter hours the current dropped to a minimum.
To charge a battery of this size, it is sufficient to use a regular 65-watt power supply with Power Delivery (PD) support. We had a 65-watt adapter that did not charge the laptop if a cable for up to 3 A (60-65 W) was used, but it worked with a 5 A cable (100 W). When using a 65-watt adapter, the laptop will work, but will «pump» the missing battery, which will lead to its gradual discharge, despite the display of the external power icon.
For reference, with a 100W adapter, a charged battery, wireless disabled, screen brightness at 40-45%, and keyboard backlight off, we recorded values up to 4.4A (temporarily) during Windows boot, even without performing heavy tasks. At either of the two PD adapter powers, only the Office mode profile is active in Control Center, as evidenced by the performance comparison for different profiles below.
The built-in battery management system (BMS) does not allow charging the battery when the remaining charge is 90% or more. To achieve a full charge, you must first discharge the battery to 89% or less.
Operation under load and heating
The laptop's cooling system includes two large radiators with fans located in opposite corners of the case. These radiators, connected to the processor and video card via heat pipes, are connected to each other, providing effective heat distribution.

This is a standard design, but what is unusual is the presence of an additional cooler, listed in the Control Center utility as Sys Fan. It is small in size, which allows it to spin faster than the main two fans.
As mentioned, air is sucked in through the slots in the bottom and expelled to the rear and sides (rear).
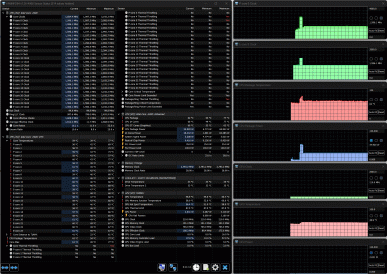
A table is provided to evaluate changes in the system operating parameters (temperature, frequency, etc.) under different loads. The table shows the maximum and steady-state values for each load scenario, with overheating modes highlighted in bold. The fans automatically adjust their speed as needed.
| Load scenario | CPU frequencies, GHz | CPU Temp, °C | CPU consumption, W | GPU frequency, GHz | GPU temperature, °C | GPU power consumption, W | CPU/GPU/Sys Fan Speeds, thousand rpm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inaction | 48-49 | 6-7 | 37-38 | 2-2,5 | 2,0/1,9/0 | ||
| High Performance Profile | |||||||
| Maximum CPU load | P: 3,8/3,2 E: 3,2/2,7 | 98/90-91 | 130/90 | 4,7/4,5/2,0 | |||
| Maximum load on the video card | to 72 | 12-13 | 2,5-2,52 | to 76 | 111-114 | 4,2/4,0/6,0 | |
| Maximum load on the processor and video card | P: 3,9/2,4-2,5 E: 3,4/2,0-2,1 | 98/87-90 | 127/51-56 | about 2.5 | to 88 | 106-124 | 4,7/4,5/6,0 |
| Profile Gaming | |||||||
| Maximum CPU load | P: 3,7/2,4 E: 3,2/2,0-2,1 | 98/75-77 | 119/55 | 2,7/2,6/2,0 | |||
| Maximum load on the processor and video card | P: 3,7/1,9 E: 3,2/1,7 | 97/87-88 | 128/45 | 2,15-2,25 | to 88 | 96-97 | 3,5/3,3/4,0 |
| Office mode profile | |||||||
| Maximum CPU load | P: 2,8/1,6 E: 2,4/1,6 | 77/61-63 | 70/35 | 2,4/2,3/0 | |||
| Maximum load on the processor and video card | P: 2,7/1,2-1,3 E: 2,3/1,6 | to 82 | 70/35 | 2,0-2,15 | to 82 | 80-81 | 3,0/2,8/4,0 |
First, select the High Performance profile.
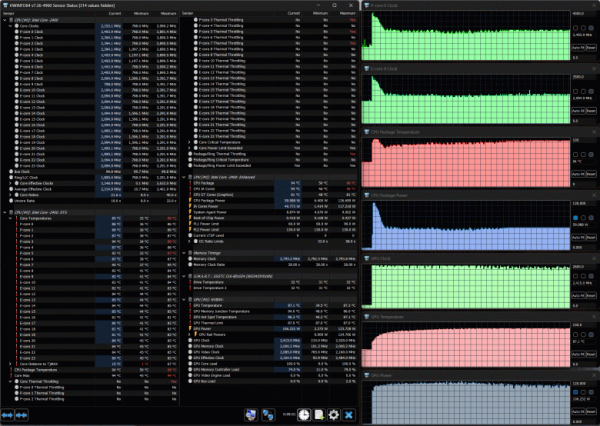
When applying a load (using the powerMax program), the Turbo Boost mode is activated on the CPU, in which the frequency of the P-cores reaches 3.8 GHz, and the E-cores — 3.2 GHz. The processor consumption increases to 130 W (although according to the specification it can be up to 157 W in turbo mode), and the temperature rises to 98 °C, which causes throttling on individual P-cores. The fans begin to quickly pick up speed, reaching almost maximum values. However, the frequencies quickly decrease and then gradually stabilize at 3.2 GHz for the P-cores and 2.7 GHz for the E-cores after two and a half minutes. The consumption drops to 90 W (which is more than the declared 45-55 W in normal mode), the temperature drops to 90-91 °C, and throttling disappears. CPU/GPU/Sys fans run at 4700/4500/2000 RPM. Once the load is removed, they slow down to a minimum after about a minute.
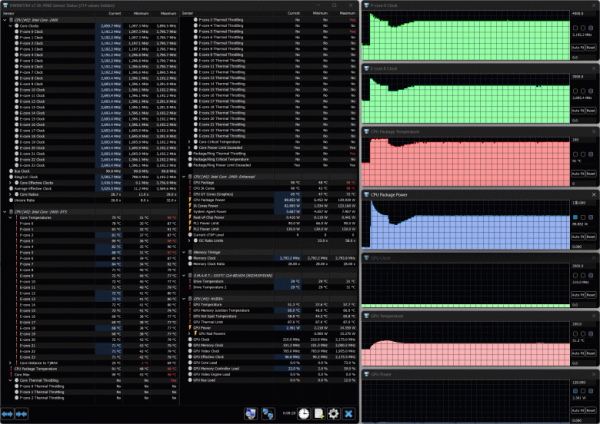
When the Nvidia video core is under load, the temperature slowly increases, the fans gradually increase their speed. As a result, the GPU temperature stabilizes at 76 °C, the frequency fluctuates around 2.5-2.52 GHz, and the consumption varies from 111 to 114 W with short bursts up to 122-123 W.
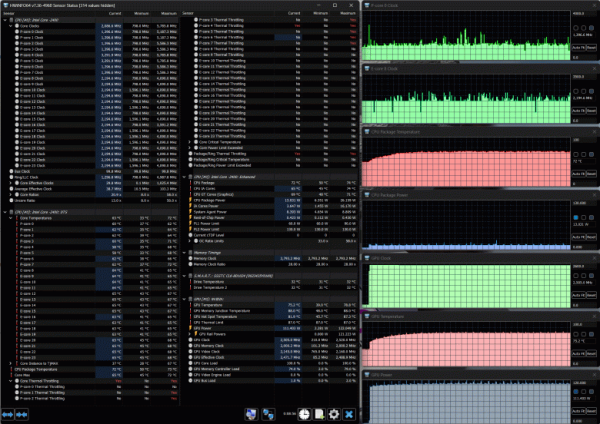
When both processors are loaded, the P-cores of the CPU initially overclock to 3.9 GHz, but then their frequency quickly drops to 2.4-2.5 GHz. The E-cores reach 3.4 GHz and stabilize at 2.0-2.1 GHz. The CPU temperature rises to 98 °C (throttling is observed), but with the fans turned on, it drops to 87-90 °C, and throttling disappears. Consumption reaches 127 W at peak and stabilizes at 51-56 W.
The GPU operates at a frequency of about 2.5 GHz, consumes 106-124 W, and the temperature does not exceed 88 °C.
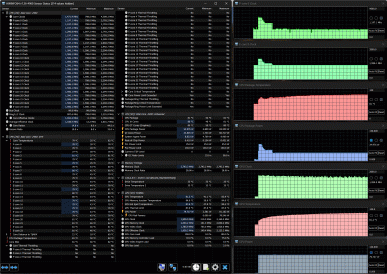
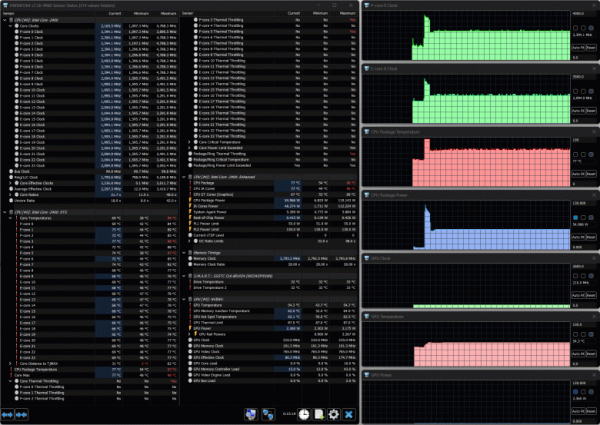
Switching to the Gaming profile.
When the processor is loaded in turbo mode, there is a more pronounced overclocking compared to the previous profile: the frequencies of the P- and E-cores reach 3.7 and 3.2 GHz, respectively, consumption is 119 W, the temperature is up to 97 ° C, and throttling begins on several P-cores. After 35-40 seconds, the frequencies drop, and Turbo Boost ends. In the steady state, the frequencies stabilize at 2.4 GHz for the P-cores and 2.0-2.1 GHz for the E-cores, consumption drops to 55 W, the temperature is down to 75-77 ° C (throttling disappears). The fans work noticeably quieter, their speeds do not exceed 2700/2600/2000 rpm.
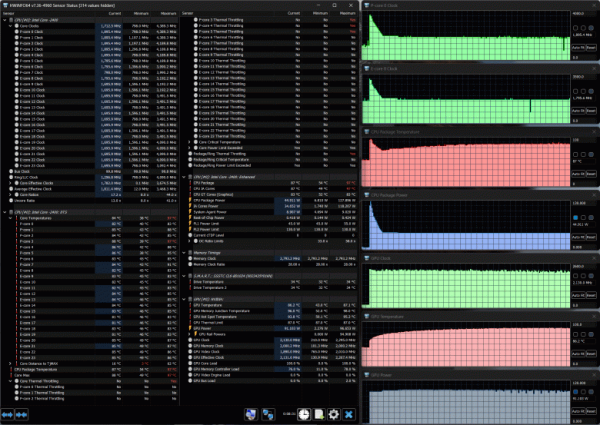
When both processors are loaded in the Gaming profile, the picture is generally similar to the previous profile, but with some differences in the values. The frequencies of the P- and E-cores of the processor are initially overclocked to 3.7 and 3.2 GHz, respectively, after which they quickly decrease and stabilize at 1.9 and 1.7 GHz. The processor temperature initially increases to 97 ° C with throttling, then decreases and stabilizes at 87-88 ° C, throttling stops. Consumption reaches 128 W at peak and decreases to 45 W in steady state.
The GPU operates at a frequency of about 2.15-2.25 GHz and consumes up to 96-97 W, the temperature does not exceed 88 ° C.
The fan speeds are increased and are 3500/3300/4000 rpm.
For Office mode, we provide screenshots, the numbers are in the table. Let's just say that the noise is significantly reduced, especially in comparison with the performance profile.
We did not conduct tests with forced maximum fan activation, since their speeds are already close to maximum in the High Performance profile and additional changes should not be expected. However, we checked: it is not possible to completely avoid short-term overheating with throttling at the beginning of the test.
Overall, the cooling system copes with the tasks quite well, providing only short-term overheating under some heavy loads, despite the fact that the processor can consume more than indicated in its specification.
The drive temperature in our tests did not exceed 35 ° C (according to the HWinfo utility).
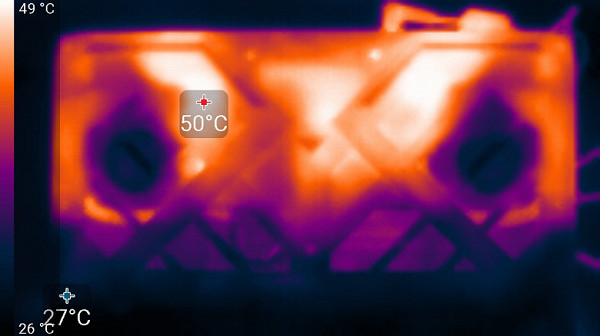
Below are thermal images taken after the laptop had been running for a long time under maximum load on the CPU and GPU in the High Performance profile.
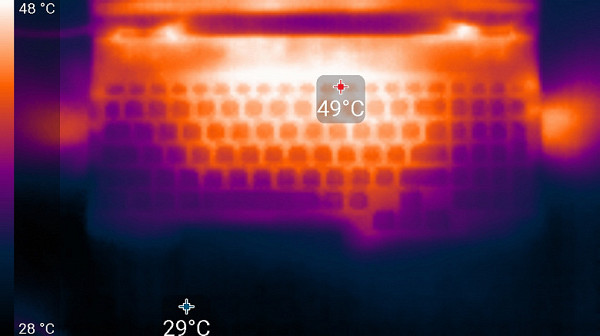
Above
From below
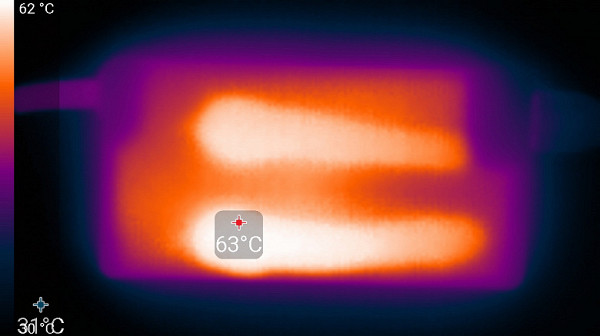
power unit
At maximum load, working with the keyboard remains comfortable, as the area under the wrists hardly heats up. However, holding the laptop on your lap is uncomfortable due to the heat in the areas of contact with the knees, which can cause discomfort and overheating. The knees can also cover the ventilation grilles, which further increases the risk of overheating. The power supply unit gets very hot, so when working for a long time at high performance, it is important to make sure that it is not covered and has sufficient ventilation.
Noise level
The noise level is measured in a soundproof chamber. The sound meter microphone is positioned to simulate the typical position of the user's head: the screen is tilted at 45 degrees (or at maximum if 45 degrees is not available), the microphone axis coincides with the normal emanating from the center of the screen, the front end of the microphone is 50 cm from the screen and directed at it. The load is created using the powerMax program, the screen brightness is set to maximum, the room temperature is maintained at 24°C, but the laptop is not additionally blown, so the air temperature nearby may be higher. To assess the actual consumption, we also indicate the power consumption. The battery is pre-charged to 100%, the Office mode or High Performance profile is selected in the utility settings.
| Load scenario | Noise level, dBA | Subjective assessment | Power consumption, W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Office mode profile | |||
| Inaction | 23,7 | very quiet | 45 |
| High Performance Profile | |||
| Maximum load on the processor and video card | 47,7 | loud | 250 (maximum 260) |
If the laptop is not loaded at all, the cooling system does not operate in passive mode even in Office mode, but the noise remains low. The noise character under high load is smooth and does not cause irritation. The spectrogram obtained under maximum load is also smooth, and in the frequency range where sounds can cause discomfort, there are no pronounced peaks.
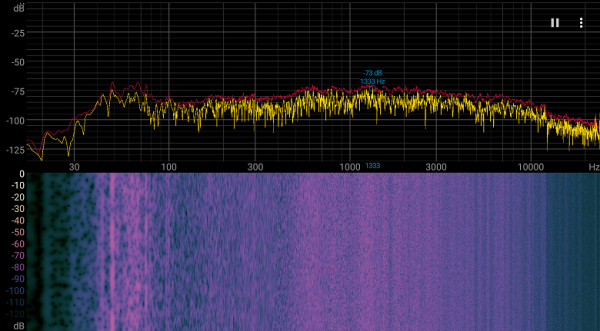
For a subjective assessment of the noise level, we use the following scale:
| Noise level, dBA | Subjective assessment |
|---|---|
| Less than 20 | relatively silent |
| 20—25 | very quiet |
| 25—30 | quiet |
| 30—35 | clearly audible |
| 35—40 | noisy |
| 40—45 | very noisy |
| 45—50 | loud |
| Above 50 | very loud |
Below are approximate noise levels for laptops:
- Below 20 dBA: relatively silent.
- From 20 to 25 dBA: very quiet.
- From 25 to 30 dBA: the noise from the cooling system does not stand out from the background of typical office sounds.
- From 30 to 35 dBA: the noise is clearly audible.
- From 35 to 40 dBA: the noise exceeds a comfortable level for long-term work.
- From 40 to 45 dBA: the laptop works very noisily, it is recommended to use background sounds to mask it.
- From 45 to 50 dBA: the noise level is very uncomfortable.
- Over 50 dBA: the noise is so loud that headphones are needed.
This scale is conditional and does not take into account the individual characteristics of the user and the nature of the sound.
Let's compare these values with other similar laptops, taking into account the maximum noise levels (excluding forced increase in fan speed, if any).
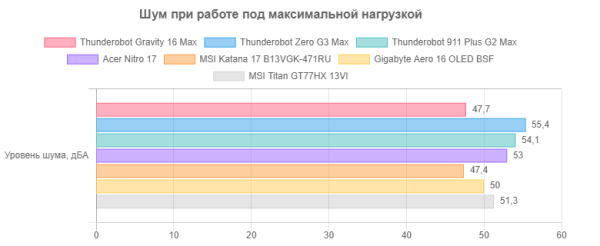
Although the noise level of our device is not the highest compared to other gaming laptops, it is still quite loud. However, the sound is uniform and is just the rustle of the outgoing air, without any additional annoying components.
Performance
The laptop is equipped with the latest Intel Core i9-14900HX processor, introduced in early 2024. It has 24 cores: eight of them are high-performance P-cores, supporting up to 5.8 GHz in Turbo Boost mode (base frequency of 2.2 GHz), and sixteen are energy-efficient E-cores, operating at frequencies of up to 1.6/4.1 GHz.
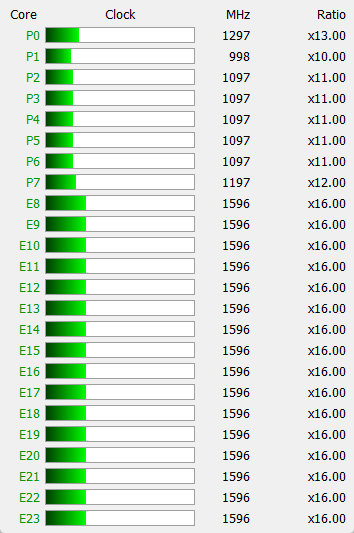
According to the specification, the TDP of the processor varies from 45 to 55 W in normal mode and can reach 157 W in Turbo Boost. However, in this laptop model, the actual consumption reaches 130 W in turbo mode and stabilizes at up to 90 W under long-term load.
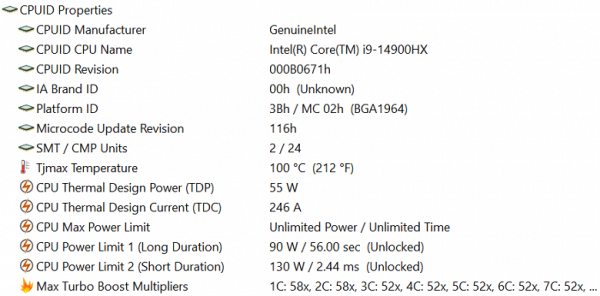
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop discrete graphics card, based on the Ada Lovelace architecture and introduced in spring 2021, operates at frequencies up to 2.175 GHz and has a power consumption of up to 115 watts.
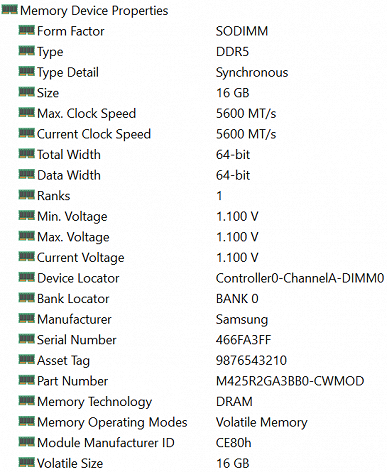
The RAM uses two DDR5-5600 Samsung M425AR2GA3BB0-CWMOD modules of 16 GB each in SO-DIMM slots, there are no free slots.

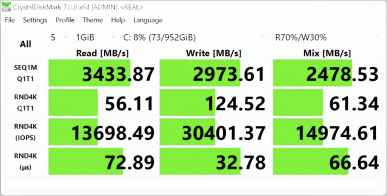
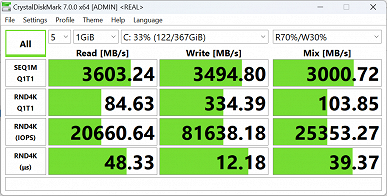
A 1 TB SSD drive with the designation SSSTC CL6-8D1024 and a PCIe 4.0 x4 interface is installed.
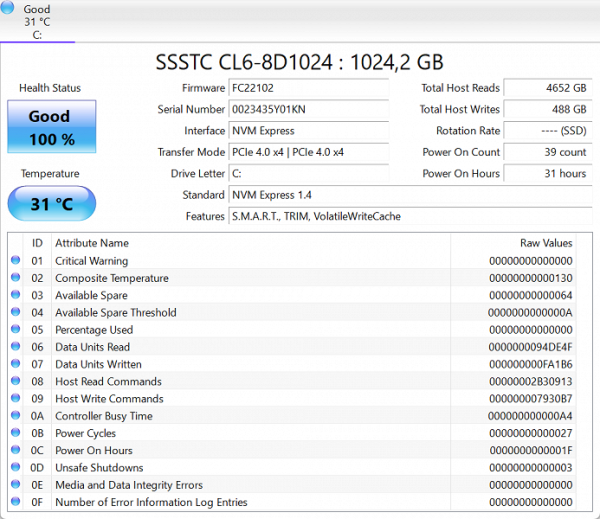
In the corresponding test, he showed the following results:
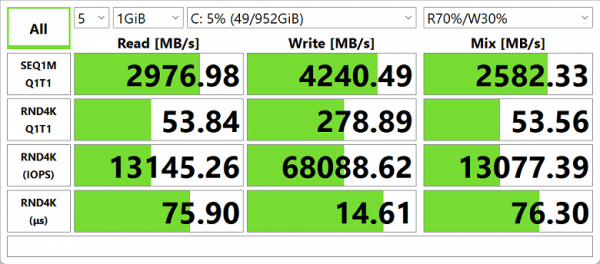
We suggest comparing the test results with two other SSDs with the PCIe 4.0 x4 interface: Western Digital SN560 (1 TB, installed in the Asus Zenbook Duo UX8406MA laptop) and Gigabyte AG470S (1 TB, installed in the Gigabyte Aorus 15 BSF-73KZ754SD laptop).
For clarity, we present the results in the form of diagrams:
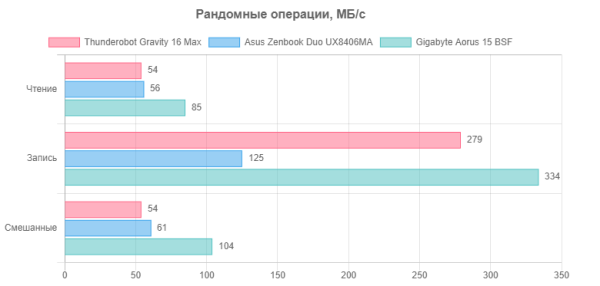
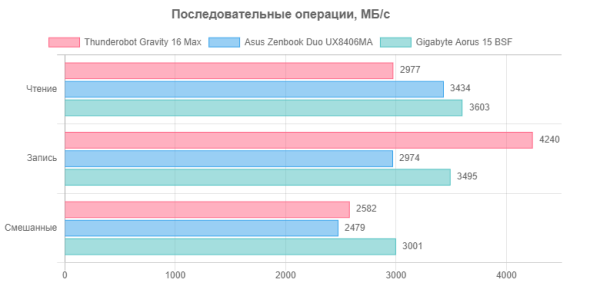
Let's move on to application tests, without using the Control Center utility at the first stage. For comparison, in addition to our reference desktop with a 6-core Intel Core i5-9600K, we also test the following laptops:
- Asus ROG Zephyrus G16 with an Intel Core Ultra 9 185H processor (6 P-cores/12 threads + 10 E-cores, up to 5.1 GHz, TDP 45-55/157 W), Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 Laptop graphics, 32 GB LPDDR5X and 1 TB Samsung PM9A1 PCIe 4.0 x4 SSD.
- Acer Nitro 17 with AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS processor (8 cores/16 threads, 4.0-5.2 GHz, TDP 35-54 W), Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop graphics card, 32 GB DDR5-5600 and 1 TB SSD SK Hynix PCIe 4.0 x4.
- Maibenben X639 with Intel Core i9-13900HX processor (8+16 cores/32 threads, up to 5.4 GHz, TDP 55-157 W), Nvidia GeForce RTX 4080 Laptop with 12 GB GDDR6, 32 GB DDR5-4800 and 1 TB SSD Kingston PCIe 4.0 x4 (results without using an external liquid cooling system).
| Reference result (Intel Core i5-9600K) | Thunderobot Gravity 16 Max (Intel Core i9-14900HX) | Asus ROG Zephyrus G16 (Intel Core Ultra 9 185H) | Acer Nitro 17 (AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS) | Maibenben X639 (Intel Core i9-13900HX) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video conversion, points | 100 | 238 | 207 | 213 | 256 |
| MediaCoder x64 0.8.57, c | 132,0 | 41,8 | 53 | 58 | 40 |
| HandBrake 1.2.2, c | 157,4 | 64,8 | 75 | 72 | 64 |
| VidCoder 4.36, c | 385,9 | 219,8 | 228 | 198 | 189 |
| Rendering, points | 100 | 307 | 239 | 226 | 270 |
| POV-Ray 3.7, с | 98,9 | 26,8 | 38 | 43 | 36 |
| Cinebench R20 | 122,2 | 34,8 | 47 | 51 | 46 |
| Vlender 2.79, p | 152,4 | 53,3 | 67 | 73 | 53 |
| Adobe Photoshop CS 2019 (3D rendering), c | 150,3 | 62,8 | 71 | 66 | 68 |
| Video content creation, points | 100 | 275 | 179 | 243 | 283 |
| Magix Vegas Pro 16.0, c | 363,5 | 107,4 | — | 121 | — |
| Adobe After Effects CC 2019 v 16.0.1, с | 468,7 | 187,7 | 221 | 219 | 192 |
| Photodex ProShow Producer 9.0.3782, c | 191,1 | 130,9 | 142 | — | 138 |
| Digital Photo Processing, Points | 100 | 249 | 212 | 202 | 173 |
| Adobe Photoshop CС 2019, с | 864,5 | 483,1 | 571 | 553 | 584 |
| Adobe Photoshop Lightroom Classic СС 2019 v16.0.1, c | 138,5 | 37,3 | 43 | 61 | 88 |
| Phase One Capture One Pro 12.0, c | 254,2 | 108,9 | 131 | 108 | 115 |
| Text recognition, points | 100 | 365 | 233 | 265 | 366 |
| Abbyy FineReader 14 Enterprise, c | 492,0 | 134,7 | 211 | 185 | 134 |
| Archiving, points | 100 | 273 | 149 | 170 | 238 |
| WinRAR 5.71 (64-bit), c | 472,3 | 220,2 | 367 | 303 | 296 |
| 7-Zip 19, c | 389,3 | 112,0 | 226 | 211 | 110 |
| Scientific calculations, points | 100 | 271 | 190 | 193 | 242 |
| LAMMPS 64-bit, c | 151,5 | 46,7 | 71 | 72 | 61 |
| NAMD 2.11, p | 167,4 | 49,6 | 87 | 82 | 53 |
| Mathworks Matlab R2018b, c | 71,1 | 31,9 | 38 | 36 | 32 |
| Dassault SolidWorks Premium Edition 2018 SP05 with Flow Simulation 2018 Package, c | 130,0 | 58,7 | 76 | 78 | 65 |
| Integral result without accumulator, points | 100 | 280 | 199 | 214 | 256 |
| WinRAR 5.71 (Store), c | 78,0 | 16,6 | 56 | 66 | 42 |
| Data copy speed, s | 42,6 | 5,7 | 5 | 4 | 8 |
| Integral result of the accumulator, points | 100 | 593 | 345 | 338 | 317 |
| Integral performance result, points | 100 | 351 | 235 | 246 | 273 |
With and without the storage drive, our “hero” of the review showed the best results in the integrated tests, although in some applications and categories it can be inferior or equal to the Maibenben X639 and sometimes to the Acer Nitro 17. However, the new Intel Core Ultra 9 185H processor in the Asus ROG Zephyrus G16 could not surpass the results of the Gravity 16 Max even once.
In comparison, our reference desktop system based on the 6-core Intel Core i5-9600K lags significantly behind.
Now let's consider the impact of profiles in Control Center on performance in real applications, choosing one test from each category. A full run of the test set takes a lot of time even on a high-performance computer, and the time given to us is limited.
| Control Center is not installed | Profile in Control Center | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Office mode | Gaming | High Performance | ||
| HandBrake 1.2.2, c | 64,8 | 108,3 | 81,4 | 65,1 |
| Cinebench R20 | 34,8 | 53,0 | 39,0 | 34,9 |
| Magix Vegas Pro 16.0, c | 158,0 | 250,0 | 176,5 | 157,5 |
| Adobe Photoshop CС 2019, с | 483,1 | 565,2 | 505,6 | 491,5 |
| Abbyy FineReader 14 Enterprise, c | 134,7 | 253,9 | 169,9 | 133,8 |
| WinRAR 5.71 (64-bit), c | 220,2 | 250,9 | 228,1 | 218,9 |
| NAMD 2.11, p | 49,6 | 119,4 | 67,9 | 50,3 |
As expected, installing Control Center and selecting the High Performance profile does not result in a significant performance increase: the difference between the second and right columns of the table is within the range of random fluctuations. Using the other two profiles can only slightly reduce performance (Gaming) or significantly reduce it (Office mode), while reducing noise, heat and power consumption.
Conclusion
It's great to see a gaming laptop lineup that covers all price points, and the Thunderobot brand is fully in line with this approach. The Thunderobot Gravity 16 Max we reviewed is a mid-range gaming laptop: it's neither the cheapest nor the most expensive.
This laptop offers a decent set of features for its class: a 16-inch IPS display with a resolution of 2560×1600 and a refresh rate of 240 Hz, a modern Intel Core i9-14900HX processor, a discrete Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop GPU, 32 GB of DDR5-5600 RAM, 1 TB NVMe SSD PCIe 4.0 x4 with the ability to install a second drive, HDMI video output, four USB ports (including one Type-C with support for Power Delivery and video output, but without Thunderbolt). There are also Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.2 and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces, a keyboard with RGB backlighting and a full-fledged numeric keypad.
The laptop screen has good brightness, a fast matrix and accurate color rendition, although the black color may lose stability when you look away.
The battery, although not small, provides a rather limited battery life, which is typical for gaming laptops. The charge is replenished slowly, but the laptop supports power from any adapter with Power Delivery of at least 100 watts, which allows you not to carry a bulky standard power supply. In extreme cases, you can use a 65-watt adapter.
The 720p webcam does not live up to expectations for such an expensive device, and there is also no fingerprint scanner, but this is not so critical.
The performance in various applications is good, suitable for both educational and amateur tasks, as well as for professional use on a limited budget.
The laptop will also satisfy gamers: most games work comfortably at native resolution and maximum settings, and when the resolution or quality is reduced, the results improve.
The cooling system effectively copes with overheating, although at maximum loads it allows a short-term increase in temperature. The noise from the fan is noticeable, but this is a common occurrence for gaming laptops.